ASTRONOMICAL ERRORS
... 9. From Bad Astronomy web site: One of the TV shopping channels sometimes sells telescopes. They had a segment bragging about the remote controlled focuser on one scope. The sales rep said it's useful for looking at "craters on the Moon... the rings of Saturn, the red spot on Jupiter or the canals o ...
... 9. From Bad Astronomy web site: One of the TV shopping channels sometimes sells telescopes. They had a segment bragging about the remote controlled focuser on one scope. The sales rep said it's useful for looking at "craters on the Moon... the rings of Saturn, the red spot on Jupiter or the canals o ...
Astronomy Mastery Objectives Semester Exam Review Kepler Telescope
... The arch can detach from the Sun’s surface as a Solar Flare (Coronal Mass Ejection/CME) which sends solar wind particles into space. - Sunspot Cycles occur about every 11 years. Cycles are measured by observing the year with the fewest number of Sunspots called the Solar Minimum. Typically, Sunspot ...
... The arch can detach from the Sun’s surface as a Solar Flare (Coronal Mass Ejection/CME) which sends solar wind particles into space. - Sunspot Cycles occur about every 11 years. Cycles are measured by observing the year with the fewest number of Sunspots called the Solar Minimum. Typically, Sunspot ...
Chapter 26 Review - geraldinescience
... 5 Which of the following is evidence of Earth's revolution? A B C D ...
... 5 Which of the following is evidence of Earth's revolution? A B C D ...
Celestial Motions
... The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The 88 official constellations cover the celestial sphere. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The 88 official constellations cover the celestial sphere. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Lecture 2 - Lines in the Sky
... • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. • But first we need to define some terms ...
... • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. • But first we need to define some terms ...
Ch. 2
... • What does the universe look like from Earth? – We can see over 2,000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along t ...
... • What does the universe look like from Earth? – We can see over 2,000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along t ...
geography-vocabulary-word-list
... Q9. Why is the earth called a unique planet? Q10. Fill in the blanks:1. Our solar system is a part of________galaxy. 2. The brightest star in the saptarishi is________. 3. The word planet is derived from greek word________. 4. The planet having rings around it is _______. 5. Planets which rotate fro ...
... Q9. Why is the earth called a unique planet? Q10. Fill in the blanks:1. Our solar system is a part of________galaxy. 2. The brightest star in the saptarishi is________. 3. The word planet is derived from greek word________. 4. The planet having rings around it is _______. 5. Planets which rotate fro ...
Theories
... Heliocentric Theory because he thought the sun was the center of the universe. In Greek, “helios” means sun Galileo made additional observations using a telescope which supported the heliocentric theory. Galileo observed that Venus went through a full cycle of phase’s like the Moon. This could ...
... Heliocentric Theory because he thought the sun was the center of the universe. In Greek, “helios” means sun Galileo made additional observations using a telescope which supported the heliocentric theory. Galileo observed that Venus went through a full cycle of phase’s like the Moon. This could ...
mike-ken_transit
... A 23 year old Parisian, Charles Messier observed the 1753 transitIt was his first recorded observation! ...
... A 23 year old Parisian, Charles Messier observed the 1753 transitIt was his first recorded observation! ...
6, 19, 24, 37, 47 and 65
... The quiz questions will be same or very similar to the following text-book problems. Refer to the course website for the latest version of this document. You are encouraged to seek the help of your instructor during his office hours. ...
... The quiz questions will be same or very similar to the following text-book problems. Refer to the course website for the latest version of this document. You are encouraged to seek the help of your instructor during his office hours. ...
the planets of the milky way solar system
... NEPTUNE Not discovered until 1946 by telescope Scientists believe Neptune’s gravity is what pulls Uranus out of a regular orbit Named for the Roman god of the sea because of its color Also made up of hydrogen and helium and some methane to cause the blue color Neptune rotates (day) fully in 16 hour ...
... NEPTUNE Not discovered until 1946 by telescope Scientists believe Neptune’s gravity is what pulls Uranus out of a regular orbit Named for the Roman god of the sea because of its color Also made up of hydrogen and helium and some methane to cause the blue color Neptune rotates (day) fully in 16 hour ...
Take Home #2 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... 13) “Scientists would expect most stars to have planets because they form with disks of gas and dust around them. This process should be common for most stars.” Which of the following best describes this statement? A. It is a fact. C. It is an inference. B. It is evidence. D. It is a scientific law. ...
... 13) “Scientists would expect most stars to have planets because they form with disks of gas and dust around them. This process should be common for most stars.” Which of the following best describes this statement? A. It is a fact. C. It is an inference. B. It is evidence. D. It is a scientific law. ...
Astrobiology notes for October 18th - 22nd
... Venus rotates too slowly, with 243 days per rotation. It may never have generated a magnetic field, but there is no surface rock old enough on Venus for us to tell. What sort of volatiles (atmospheric or liquid materials) should a potentially habitable terrestrial planet have when it forms? H2O and ...
... Venus rotates too slowly, with 243 days per rotation. It may never have generated a magnetic field, but there is no surface rock old enough on Venus for us to tell. What sort of volatiles (atmospheric or liquid materials) should a potentially habitable terrestrial planet have when it forms? H2O and ...
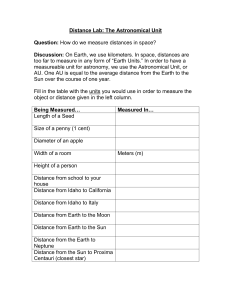
Distance Lab: The Astronomical Unit
... 1. Define Astronomical Unit, Parallax, and light year in your notebook. Use page 104 in the textbook to help you out. 2. Parallax: Look up at the balloon globe hanging above the teachers’ desk. Behind the globe are some pictures of mountains and glaciers that are numbered 1-10. Which number do you s ...
... 1. Define Astronomical Unit, Parallax, and light year in your notebook. Use page 104 in the textbook to help you out. 2. Parallax: Look up at the balloon globe hanging above the teachers’ desk. Behind the globe are some pictures of mountains and glaciers that are numbered 1-10. Which number do you s ...
File
... Why Does the Moon Follow You Around? Driving down a road with mountains in the distance, you'll notice that the mountains don't seem to move much at all, while the farm houses closer to the road move much faster, but still a lot slower than the mailboxes blurring past you right beside the road. ...
... Why Does the Moon Follow You Around? Driving down a road with mountains in the distance, you'll notice that the mountains don't seem to move much at all, while the farm houses closer to the road move much faster, but still a lot slower than the mailboxes blurring past you right beside the road. ...
The Origins of Modern Astronomy Astronomy goes back to well
... sun each had three spheres dedicated to their motion, while each of the five visible planets had four spheres. Although an amazing model, able to explain many motions in the sky, it could not explain the change in brightness of the planets. In his model, the planets were all at the same distance fro ...
... sun each had three spheres dedicated to their motion, while each of the five visible planets had four spheres. Although an amazing model, able to explain many motions in the sky, it could not explain the change in brightness of the planets. In his model, the planets were all at the same distance fro ...
Chapter 17 Earth`s Cycles
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
Chapter 17 Earth`s Cycles
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
Chapter 17 Earth`s Cycles
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
Chapter 17 PowerPoint
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
Assignment 2 - utoledo.edu
... a. the planets were not moving along the ecliptic but all over the celestial sphere b. the planets moved in very elongated ellipses, and their speed in orbit changed radically over the course of a year c. the Sun moved among the planets, and pulled them out of their circular orbits d. the planets m ...
... a. the planets were not moving along the ecliptic but all over the celestial sphere b. the planets moved in very elongated ellipses, and their speed in orbit changed radically over the course of a year c. the Sun moved among the planets, and pulled them out of their circular orbits d. the planets m ...
January 23
... A globular cluster is a roughly spherical collection of up to millions of stars bound together by the force of gravity. Astronomers can measure the velocities of the stars (rotation curves) in the cluster to get an idea of the mass distribution (as shown Monday). Assuming the stars have roughly the ...
... A globular cluster is a roughly spherical collection of up to millions of stars bound together by the force of gravity. Astronomers can measure the velocities of the stars (rotation curves) in the cluster to get an idea of the mass distribution (as shown Monday). Assuming the stars have roughly the ...
SKYTRACK Glossary of Terms
... Solstice – (a) The two points at which the Sun is at its greatest distance from the celestial equator. It happens twice each year, when the tilt of the Earth's axis is most inclined toward or away from the Sun, causing the Sun's apparent position in the sky to reach its northernmost or southernmost ...
... Solstice – (a) The two points at which the Sun is at its greatest distance from the celestial equator. It happens twice each year, when the tilt of the Earth's axis is most inclined toward or away from the Sun, causing the Sun's apparent position in the sky to reach its northernmost or southernmost ...
Untitled
... The Moon rotates on its …………………………., which takes 29.5 days. Its …………………………. around the Earth also takes 29.5 days. Because of this, we always see the same …………………………. of the Moon. The Moon does not produce its own light; it …………………………. sunlight. Obviously, we can only see the illuminated part that i ...
... The Moon rotates on its …………………………., which takes 29.5 days. Its …………………………. around the Earth also takes 29.5 days. Because of this, we always see the same …………………………. of the Moon. The Moon does not produce its own light; it …………………………. sunlight. Obviously, we can only see the illuminated part that i ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.