EARTH & SPACE SCIENCE
... Rotation is the spin of a body on its axis. Each complete rotation takes about one day. The Earth rotates from west to east. At any given moment, the hemisphere of Earth that faces the sun experiences daylight; at the same time, the hemisphere of Earth that faces away from the sun experiences nightt ...
... Rotation is the spin of a body on its axis. Each complete rotation takes about one day. The Earth rotates from west to east. At any given moment, the hemisphere of Earth that faces the sun experiences daylight; at the same time, the hemisphere of Earth that faces away from the sun experiences nightt ...
Stellar Parallax
... We do this with the following arbitarary definition:M = m when the star is viewed from a distance d = 10 pc. Then M = m -5 log10d + 5 We now have a link between M,m and d where d is in parsecs. [Note: we have assumed that the inverse square law is the only reason for the dimming of the light from th ...
... We do this with the following arbitarary definition:M = m when the star is viewed from a distance d = 10 pc. Then M = m -5 log10d + 5 We now have a link between M,m and d where d is in parsecs. [Note: we have assumed that the inverse square law is the only reason for the dimming of the light from th ...
year
... Earth’s orbital revolution around the Sun with reference to the stars. Because of precession (see tropical year), the sidereal year is about 21 minutes longer than the tropical year. Tropical Year The time between successive passages of the Sun through the mean equinox, as from vernal equinox to ver ...
... Earth’s orbital revolution around the Sun with reference to the stars. Because of precession (see tropical year), the sidereal year is about 21 minutes longer than the tropical year. Tropical Year The time between successive passages of the Sun through the mean equinox, as from vernal equinox to ver ...
How We Know the Earth Revolves Activity
... How do scientists know that the Earth actually orbits (revolves about) the sun? Have you ever thought about this? For thousands of years it was thought that the Earth was at the center of the universe and that everything moved around the Earth at different rates. Today, scientists know that the Eart ...
... How do scientists know that the Earth actually orbits (revolves about) the sun? Have you ever thought about this? For thousands of years it was thought that the Earth was at the center of the universe and that everything moved around the Earth at different rates. Today, scientists know that the Eart ...
Lab 1: The Celestial Sphere
... has the brightest stars marked on it and uses the equatorial coordinate system. The frame has been pre-cut to represent the horizon for your latitude on the Earth. By lining up the month and day on the wheel with the time printed on the frame, we are effectively converting between the equatorial and ...
... has the brightest stars marked on it and uses the equatorial coordinate system. The frame has been pre-cut to represent the horizon for your latitude on the Earth. By lining up the month and day on the wheel with the time printed on the frame, we are effectively converting between the equatorial and ...
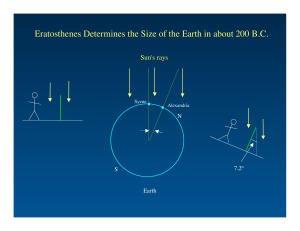
Eratosthenes Determines the Size of the Earth in about 200 B.C.
... To locate an object, two numbers (in degrees), like longitude and latitude are sufficient. Question: why is this “view” totally imaginary? ...
... To locate an object, two numbers (in degrees), like longitude and latitude are sufficient. Question: why is this “view” totally imaginary? ...
here.
... times of the year because A) on any particular night, we can only see stars that are directly opposite (180 degrees away from) the Sun in the sky. B) our evening view of space depends on where Earth is located in its orbit around the Sun. C) some constellations are circumpolar. D) during some times ...
... times of the year because A) on any particular night, we can only see stars that are directly opposite (180 degrees away from) the Sun in the sky. B) our evening view of space depends on where Earth is located in its orbit around the Sun. C) some constellations are circumpolar. D) during some times ...
teaching galileo? get to know riccioli! what a forgotten italian
... around Earth was explained by postulating that they were made of material with special properties not found on Earth, much as today astronomers postulate “dark matter” and “dark energy” to explain observations). ...
... around Earth was explained by postulating that they were made of material with special properties not found on Earth, much as today astronomers postulate “dark matter” and “dark energy” to explain observations). ...
Chapter 2: Perihelion of Mercury`s Orbit
... A third prediction from Einstein’s theory of general relativity is the excess precession of the perihelion of the orbit of Mercury of about 0.01° per century. This effect had been known and unexplained for some time, so in some sense its correct explanation represented an immediate success of the th ...
... A third prediction from Einstein’s theory of general relativity is the excess precession of the perihelion of the orbit of Mercury of about 0.01° per century. This effect had been known and unexplained for some time, so in some sense its correct explanation represented an immediate success of the th ...
Stellar aberration
... assumed to reverse its direction of motion every six-month period. Average relative linear speed of earth, with respect to sun, is estimated at 29780 m/sec. Even without considering linear speed of solar system (as a whole), it is absurd to think that a composite macro body of earth’s size and movin ...
... assumed to reverse its direction of motion every six-month period. Average relative linear speed of earth, with respect to sun, is estimated at 29780 m/sec. Even without considering linear speed of solar system (as a whole), it is absurd to think that a composite macro body of earth’s size and movin ...
Earth & Space
... – As the cloud of dust and gas collapsed when the universe was forming, the solar system did not form uniformly, the spinning of the gases and other planets is what made each different, hence the tilting of the planets – Essentially, the numerical value of this axis tilt is an artifact of the way th ...
... – As the cloud of dust and gas collapsed when the universe was forming, the solar system did not form uniformly, the spinning of the gases and other planets is what made each different, hence the tilting of the planets – Essentially, the numerical value of this axis tilt is an artifact of the way th ...
PowerPoint
... • From January to July, the position of star A, when viewed from an observer on Earth, appeared to move a certain amount with respect to the distant stars. In class we used the diagram below to determine how the observer's view would change throughout the year. Suppose Earth's orbital distance shrun ...
... • From January to July, the position of star A, when viewed from an observer on Earth, appeared to move a certain amount with respect to the distant stars. In class we used the diagram below to determine how the observer's view would change throughout the year. Suppose Earth's orbital distance shrun ...
The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to
... A planet (P) is moving around the Sun (S) in an elliptical orbit. As the planet moves from aphelion to perihelion, the Sun’s gravitational force A. does positive work on the planet. B. does negative work on the planet. C. does positive work on the planet during part of the motion and negative work d ...
... A planet (P) is moving around the Sun (S) in an elliptical orbit. As the planet moves from aphelion to perihelion, the Sun’s gravitational force A. does positive work on the planet. B. does negative work on the planet. C. does positive work on the planet during part of the motion and negative work d ...
The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to
... Compared to the Earth, Planet X has twice the mass and twice the radius. This means that compared to the amount of energy required to move an object from the Earth’s surface to infinity, the amount of energy required to move that same object from Planet X’s surface to infinity is A. 4 times as much. ...
... Compared to the Earth, Planet X has twice the mass and twice the radius. This means that compared to the amount of energy required to move an object from the Earth’s surface to infinity, the amount of energy required to move that same object from Planet X’s surface to infinity is A. 4 times as much. ...
Tessmann Show Descriptions
... What Color is Your Planet? –Bob Menn (60 minutes) Discover how astronomical observations of planets and stars have given us clues to their composition and environments. As we visit the planets of our solar system, the shows covers science curriculum, presenting topics such as the nature of gravity; ...
... What Color is Your Planet? –Bob Menn (60 minutes) Discover how astronomical observations of planets and stars have given us clues to their composition and environments. As we visit the planets of our solar system, the shows covers science curriculum, presenting topics such as the nature of gravity; ...
ONLINE practice exam
... d.) Reduce the mass of the ship by throwing almost everything overboard. e.) Fall into the black hole and get frozen at its horizon. 3. What is actually located at the event horizon of a black hole? a.) Nothing b.) an infinitely dense concentration of mass c.) The outer boundary of a wormhole d.) a ...
... d.) Reduce the mass of the ship by throwing almost everything overboard. e.) Fall into the black hole and get frozen at its horizon. 3. What is actually located at the event horizon of a black hole? a.) Nothing b.) an infinitely dense concentration of mass c.) The outer boundary of a wormhole d.) a ...
speed
... Compared to the Earth, Planet X has twice the mass and twice the radius. This means that compared to the amount of energy required to move an object from the Earth’s surface to infinity, the amount of energy required to move that same object from Planet X’s surface to infinity is A. 4 times as much. ...
... Compared to the Earth, Planet X has twice the mass and twice the radius. This means that compared to the amount of energy required to move an object from the Earth’s surface to infinity, the amount of energy required to move that same object from Planet X’s surface to infinity is A. 4 times as much. ...
power_point_slides
... star neither too close nor too far from the galactic center. • A planet like Earth, in the “habitable zone” of the star for the right temperature range, big enough to have an atmosphere and plate tectonics, not so big as to be a “gas giant.” • Or possibly a moon like Europa, a rocky/icy moon with a ...
... star neither too close nor too far from the galactic center. • A planet like Earth, in the “habitable zone” of the star for the right temperature range, big enough to have an atmosphere and plate tectonics, not so big as to be a “gas giant.” • Or possibly a moon like Europa, a rocky/icy moon with a ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.