
Document
... before genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm. RNA Processing Alteration of mRNA ends: Each end of a pre-mRNA molecule is modified in a particular way. The 5’ end, the end made first during transcription is immediately capped of with a _______________ form of a ____________ (G) nucleotide. ...
... before genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm. RNA Processing Alteration of mRNA ends: Each end of a pre-mRNA molecule is modified in a particular way. The 5’ end, the end made first during transcription is immediately capped of with a _______________ form of a ____________ (G) nucleotide. ...
Chapter-13-Mutations-and-Chromosomal-Abnormalities
... change in phenotype, the individual is called a mutant ...
... change in phenotype, the individual is called a mutant ...
Chapter 22. Nucleic Acids
... forth from DNA to RNA in the presence of the correct enzymes, RNA polymerase. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand. As opposed to DNA replication, transcription results in an RNA complement that includes uracil (U) in ...
... forth from DNA to RNA in the presence of the correct enzymes, RNA polymerase. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand. As opposed to DNA replication, transcription results in an RNA complement that includes uracil (U) in ...
Fredric Carlsson, Margaretha Stålhammar-Carlemalm, Klas
... the mature part M6. The structure of the gene encoding this domain swap was verified by DNA sequencing. Finally the construct was transformed into SAM2 and a clone, designated SAM2/pFM, was identified by PCR and by analysis of protein expression. The reciprocal domain swap, designated MF, in which t ...
... the mature part M6. The structure of the gene encoding this domain swap was verified by DNA sequencing. Finally the construct was transformed into SAM2 and a clone, designated SAM2/pFM, was identified by PCR and by analysis of protein expression. The reciprocal domain swap, designated MF, in which t ...
What is DNA?
... the stop codons do not code for amino acids but instead act as signals to stop translation. a protein called release factor binds directly to the stop codon in the A site. The release factor causes a water molecule to be added to the end of the polypeptide chain, and the chain then separates from th ...
... the stop codons do not code for amino acids but instead act as signals to stop translation. a protein called release factor binds directly to the stop codon in the A site. The release factor causes a water molecule to be added to the end of the polypeptide chain, and the chain then separates from th ...
Lecture 3 - Computing for Bioinformatics I
... same libraries and the same sets of books. • Books represent all the information (DNA) that every cell in the body needs so it can grow and carry out its various functions. ...
... same libraries and the same sets of books. • Books represent all the information (DNA) that every cell in the body needs so it can grow and carry out its various functions. ...
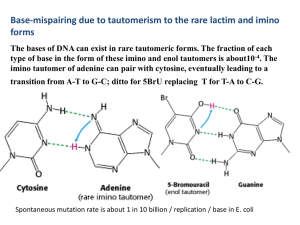
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent for informational base pairing. Note: additional OH at 2' equatorial results in a steric clash between this OH and the neighboring nucleobase. ...
... than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent for informational base pairing. Note: additional OH at 2' equatorial results in a steric clash between this OH and the neighboring nucleobase. ...
Ch. 10, DNA and Proteins
... Initiation: mRNA binds to the ribosome and the tRNA carrying methionine binds to the start codon Elongation: as mRNA codons move through the ribosome, tRNA’s add specific amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain Termination and Disassembly: the process continues until a stop codon is reached and ...
... Initiation: mRNA binds to the ribosome and the tRNA carrying methionine binds to the start codon Elongation: as mRNA codons move through the ribosome, tRNA’s add specific amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain Termination and Disassembly: the process continues until a stop codon is reached and ...
mRNA
... • With a few exceptions, twenty naturally occurring amino acids are encoded by the genetic code – Some amino acids are specified by more than one codon • Example: the amino acid tyrosine is specified by two codons: UAA and UAC ...
... • With a few exceptions, twenty naturally occurring amino acids are encoded by the genetic code – Some amino acids are specified by more than one codon • Example: the amino acid tyrosine is specified by two codons: UAA and UAC ...
Protein Synthesis
... is translated into the sequence of amino acids in a protein. • Newly transcribed proteins must fold into the appropriate three-dimensional structure in order to be functional. Often they are chemically modified, too. • Proteins must travel to the appropriate location in order to do ...
... is translated into the sequence of amino acids in a protein. • Newly transcribed proteins must fold into the appropriate three-dimensional structure in order to be functional. Often they are chemically modified, too. • Proteins must travel to the appropriate location in order to do ...
1. Name of a subject Chemistry (1st year, Faculty of Medicine
... the whole course students have to pass all labs and mid term tests. Students are allowed to pass failures (in the second term) – not more than 4 (one Mid term test within) after the end of the course. In case of 5 and more failures (two Mid term tests within) students do not get credit. 4. A form of ...
... the whole course students have to pass all labs and mid term tests. Students are allowed to pass failures (in the second term) – not more than 4 (one Mid term test within) after the end of the course. In case of 5 and more failures (two Mid term tests within) students do not get credit. 4. A form of ...
Monomer polymer2011
... Monomer A small repeating unit that can make larger more complex molecules. ...
... Monomer A small repeating unit that can make larger more complex molecules. ...
breakfast proteins
... Making the cereal chain is a model of how proteins are made in the cell. The initial template represents a single copy of DNA that sits in the nucleus of a cell and gives instructions for how proteins are made. In order to get this information to an area where proteins can be made, it must be copied ...
... Making the cereal chain is a model of how proteins are made in the cell. The initial template represents a single copy of DNA that sits in the nucleus of a cell and gives instructions for how proteins are made. In order to get this information to an area where proteins can be made, it must be copied ...
Unit 4 Review
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 45. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. _________________________ ____ 46. An organism with a dominant allele for a particular ...
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 45. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. _________________________ ____ 46. An organism with a dominant allele for a particular ...
Codon bias domains over bacterial chromosomes
... Each group is defined by the probability distribution of codon usage generated by the genes it contains A good classification is one which maximize the gain of information on these probability distributions, relative to a uniform prior distribution ...
... Each group is defined by the probability distribution of codon usage generated by the genes it contains A good classification is one which maximize the gain of information on these probability distributions, relative to a uniform prior distribution ...
L-‐Lysine Monohydrochloride [Feed Grade (78.8%)]
... amino acid requirements of swine and poultry, high-‐protein ingredients such as soybean meal and animal by-‐product meals are blended with corn. In the past, excess protein was fed ...
... amino acid requirements of swine and poultry, high-‐protein ingredients such as soybean meal and animal by-‐product meals are blended with corn. In the past, excess protein was fed ...
Protein Synthesis
... The Genetic Code • Codons: 3 base code for the production of a specific amino acid, sequence of three of the four different nucleotides • Since there are 4 bases and 3 positions in each codon, there are 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 possible codons • 64 codons but only 20 amino acids, therefore most have more tha ...
... The Genetic Code • Codons: 3 base code for the production of a specific amino acid, sequence of three of the four different nucleotides • Since there are 4 bases and 3 positions in each codon, there are 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 possible codons • 64 codons but only 20 amino acids, therefore most have more tha ...
The organization of alphabets of nucleic acids and
... 2. Methods of research: analogy search and analysis of similarity level The fundamental principal of general systems theory is the similarity principle (Gigch 1978: 55, 336). A good example of this is mathematics itself. It is based on a postulate about the similarity of characteristics and relation ...
... 2. Methods of research: analogy search and analysis of similarity level The fundamental principal of general systems theory is the similarity principle (Gigch 1978: 55, 336). A good example of this is mathematics itself. It is based on a postulate about the similarity of characteristics and relation ...
Honors Biology Module 7 Cellular Reproduction
... When a cell needs to make a protein, its DNA has the plan for making that protein in a long series of threenucleotide base sequences. Messenger RNA reads this sequence and makes a “negative image” of the relevant portion of DNA. It then takes this series of nucleotide base sequences out to the ribo ...
... When a cell needs to make a protein, its DNA has the plan for making that protein in a long series of threenucleotide base sequences. Messenger RNA reads this sequence and makes a “negative image” of the relevant portion of DNA. It then takes this series of nucleotide base sequences out to the ribo ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... • Vector –an organism (bacteria or virus) that carries and leaves its genetic material in a host cell. The host then replicates the vector’s genetic ...
... • Vector –an organism (bacteria or virus) that carries and leaves its genetic material in a host cell. The host then replicates the vector’s genetic ...
DNA replication notes
... *These are 3 letter sequences called START and STOP codons. Codons – 3 letter base segments on the mRNA 5) DNA strand “zips” back together and mRNA is now free to leave the nucleus and head towards the ribosomes in the cytoplasm to make proteins. ...
... *These are 3 letter sequences called START and STOP codons. Codons – 3 letter base segments on the mRNA 5) DNA strand “zips” back together and mRNA is now free to leave the nucleus and head towards the ribosomes in the cytoplasm to make proteins. ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... • Vector –an organism (bacteria or virus) that carries and leaves its genetic material in a host cell. The host then replicates the vector’s genetic ...
... • Vector –an organism (bacteria or virus) that carries and leaves its genetic material in a host cell. The host then replicates the vector’s genetic ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.















![L-‐Lysine Monohydrochloride [Feed Grade (78.8%)]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007857369_1-57c2188e57086807bb71bba81a3737e6-300x300.png)






