New Title - Gravette School District
... Function in Living Things. As students read the rest of the section, they should use the table to organize the information they learn about the groups of macromolecules. ...
... Function in Living Things. As students read the rest of the section, they should use the table to organize the information they learn about the groups of macromolecules. ...
Protein Folding and Quality Control
... Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide being synthesized. Proteins will fold during s ...
... Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide being synthesized. Proteins will fold during s ...
Bio 309F
... C. Transfer from RNA to protein. D. Transfer from protein back to RNA. 23. Microbiologist who demonstrated that DNA was the genetic material. A. Oswald Avery B. Herbert Boyer C. Rosalind Franklin D. Barbara McClintock E. James Watson 24. Regions of genes that do not code for a protein are called A P ...
... C. Transfer from RNA to protein. D. Transfer from protein back to RNA. 23. Microbiologist who demonstrated that DNA was the genetic material. A. Oswald Avery B. Herbert Boyer C. Rosalind Franklin D. Barbara McClintock E. James Watson 24. Regions of genes that do not code for a protein are called A P ...
RC 2 Student Notes
... Nucleic acid that uses genetic information from DNA to produce proteins Structure is single stranded Sugar is ribose Proteins Proteins are chains of amino acids Amino acids are determined by codons A codon is a sequence of 3 nucleotides (like AAA or CGG) from the mRNA (which was set from the DNA) ...
... Nucleic acid that uses genetic information from DNA to produce proteins Structure is single stranded Sugar is ribose Proteins Proteins are chains of amino acids Amino acids are determined by codons A codon is a sequence of 3 nucleotides (like AAA or CGG) from the mRNA (which was set from the DNA) ...
Ch. 2 Macromolecules
... ate the last granola bar I had after being stuck for only two hours. I am still walking around trying to find a way out of the woods, where am I getting the energy to walk around from? Lipids/lipid stores because lipids are used to store energy and accessed when there are no carbohydrates available. ...
... ate the last granola bar I had after being stuck for only two hours. I am still walking around trying to find a way out of the woods, where am I getting the energy to walk around from? Lipids/lipid stores because lipids are used to store energy and accessed when there are no carbohydrates available. ...
Molecular Genetics
... 4. There is at least one tRNA molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer tRNAs than codons because some tRNAs pair with more than one codon; if an anticodon contains a U in the third position, it will pair with either an A or G–this is called the wobble hypothesis. ...
... 4. There is at least one tRNA molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer tRNAs than codons because some tRNAs pair with more than one codon; if an anticodon contains a U in the third position, it will pair with either an A or G–this is called the wobble hypothesis. ...
Pre-exam 2
... Use the paper chromosomes left over from lab to demonstrate and talk through the events of mitosis and of meiosis. (If you are doing this at home, you can make your own chromosomes.) You can als ...
... Use the paper chromosomes left over from lab to demonstrate and talk through the events of mitosis and of meiosis. (If you are doing this at home, you can make your own chromosomes.) You can als ...
RNA - Gulf Coast State College
... The Language of Proteins • There are 64 (43) possible codes, but only 20 amino acids. • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
... The Language of Proteins • There are 64 (43) possible codes, but only 20 amino acids. • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
RNA - Gulf Coast State College
... The Language of Proteins • There are 64 (43) possible codes, but only 20 amino acids. • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
... The Language of Proteins • There are 64 (43) possible codes, but only 20 amino acids. • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
Replication, Transcription, Translation
... Transcription is the synthesis of rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA, using the nucleotide sequence information from DNA. The RNA is synthesized as a complementary copy of one of the two DNA single strands (template strand), in a process similar to DNA synthesis. The template strand in a transcription bubble is r ...
... Transcription is the synthesis of rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA, using the nucleotide sequence information from DNA. The RNA is synthesized as a complementary copy of one of the two DNA single strands (template strand), in a process similar to DNA synthesis. The template strand in a transcription bubble is r ...
Lecture 8 (9/18/14) Protein Folding
... Alpha helix is a right-handed coil, with left-handed amino acids. (There is steric hinderance for a lefthanded helix from left-handed amino acids.) Similar for -sheets. ...
... Alpha helix is a right-handed coil, with left-handed amino acids. (There is steric hinderance for a lefthanded helix from left-handed amino acids.) Similar for -sheets. ...
CP Biology Chapter 8 Structure of DNA notes
... Errors in meiosis can result in changes in large parts of a chromosome. Recall that crossing over a normal process in which chromosomes exchange pieces. Errors in crossing over or in other parts of meiosis can result in chromosomes with two copies of the same gene. Pieces of non-homologous chromosom ...
... Errors in meiosis can result in changes in large parts of a chromosome. Recall that crossing over a normal process in which chromosomes exchange pieces. Errors in crossing over or in other parts of meiosis can result in chromosomes with two copies of the same gene. Pieces of non-homologous chromosom ...
7.5 Proteins - HS Biology IB
... determined by base sequence in the gene; (largely) determines higher level structures/secondary structure/tertiary structure; secondary structure is regular repeating patterns; such as alpha/α helix and beta/β (pleated) sheet; determined by H bonds (within chain); contributes to the strength of fibr ...
... determined by base sequence in the gene; (largely) determines higher level structures/secondary structure/tertiary structure; secondary structure is regular repeating patterns; such as alpha/α helix and beta/β (pleated) sheet; determined by H bonds (within chain); contributes to the strength of fibr ...
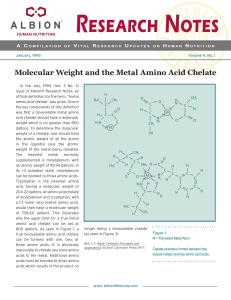
Molecular Weight and the Metal Amino Acid Chelate
... “chelate” suppliers stating that their products are formed from metal salts and hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein. The ability to interchange words like hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein has lead to a wide disparity as to what those suppliers call “met ...
... “chelate” suppliers stating that their products are formed from metal salts and hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein. The ability to interchange words like hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein has lead to a wide disparity as to what those suppliers call “met ...
26 DNA Transcription - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... between a given amino acid and the correct (cognate) tRNA is catalyzed by a specific aminoacyltRNA synthetase (one for each amino acid). The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases establish and enforce the genetic code. 4)MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are around 22 nucleotides in length and are found only in eukaryotic ce ...
... between a given amino acid and the correct (cognate) tRNA is catalyzed by a specific aminoacyltRNA synthetase (one for each amino acid). The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases establish and enforce the genetic code. 4)MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are around 22 nucleotides in length and are found only in eukaryotic ce ...
ANTHR1 - Physical Anthropology
... 21. Your textbook uses giraffes to illustrate the differences between Lamarck’s theory and Darwin’s. According to Darwin’s theory, there were changes in neck length because: a. some giraffes changed their neck length in response to ...
... 21. Your textbook uses giraffes to illustrate the differences between Lamarck’s theory and Darwin’s. According to Darwin’s theory, there were changes in neck length because: a. some giraffes changed their neck length in response to ...
Chemistry 100 Exam 3 Part 2
... You may write on this part of the test, but mark your final answers on a separate bubble sheet! 16. The enzyme amylase breaks down what types of things in our food? a. carbohydrates ...
... You may write on this part of the test, but mark your final answers on a separate bubble sheet! 16. The enzyme amylase breaks down what types of things in our food? a. carbohydrates ...
Biotechnology
... Certain disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, are linked to speci c genes. Some scientists would like to use gene therapy to cure such disorders. Gene therapy involves replacing the nonworking cells with cells that have been genetically altered. Which of these is a logical argument against gene the ...
... Certain disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, are linked to speci c genes. Some scientists would like to use gene therapy to cure such disorders. Gene therapy involves replacing the nonworking cells with cells that have been genetically altered. Which of these is a logical argument against gene the ...
Lecture 15, Feb 26
... A polypeptide chain that is folded into its normal, functional conformation is said to be in its native conformation. A polypeptide that is folded improperly so that it cannot function is said to be to be denatured or in a denatured conformation. ...
... A polypeptide chain that is folded into its normal, functional conformation is said to be in its native conformation. A polypeptide that is folded improperly so that it cannot function is said to be to be denatured or in a denatured conformation. ...
Genetics 16 - Protein Synthesis Transcription Translation
... b) Where does transcription occur at in a cell? ________________________________________ c) What enzyme is responsible for allowing transcription in the cell? ...
... b) Where does transcription occur at in a cell? ________________________________________ c) What enzyme is responsible for allowing transcription in the cell? ...
Chapter 9 Genetics Chromosome Genes • DNA RNA Protein Flow of
... In one type of conjugation, the population of cells capable of conjugating contain two types of cells F+ and F- - the former are the donor cells and the latter are the recipient cells. The donor cells have an F plasmid – sex pili and DNA Transfer. Conjugation in this case is a transfer of the F plas ...
... In one type of conjugation, the population of cells capable of conjugating contain two types of cells F+ and F- - the former are the donor cells and the latter are the recipient cells. The donor cells have an F plasmid – sex pili and DNA Transfer. Conjugation in this case is a transfer of the F plas ...
Week 3 Pre-Lecture Slides
... – Find a start codon and assess the location of ribosome binding – Indicate the codons and anticodons used, as well as the peptide bonds created – Change the sequence of the RNA such that you program the ribosome to create a 10-amino-acid polymer • What would happen to translation if: – The rib ...
... – Find a start codon and assess the location of ribosome binding – Indicate the codons and anticodons used, as well as the peptide bonds created – Change the sequence of the RNA such that you program the ribosome to create a 10-amino-acid polymer • What would happen to translation if: – The rib ...
slides
... (TFs) can bind to promoter regions: chemical modifications • Addition of a methyl group (CH3) make DNA inaccessible; TFs can’t bind • Addition of an acetyl group (COCH3) to the histone proteins opens the structure of the chromosome, allowing TFs to bind ...
... (TFs) can bind to promoter regions: chemical modifications • Addition of a methyl group (CH3) make DNA inaccessible; TFs can’t bind • Addition of an acetyl group (COCH3) to the histone proteins opens the structure of the chromosome, allowing TFs to bind ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.