File
... 31. Rotating retrograde (opposite the direction of rotation of other planets). 32. Primary atmospheric gas is carbon dioxide. 33. Has a very thin atmosphere when compared with Earth. 34. Features a huge canyon over 3,000 miles long known as Vallis Marineris. ...
... 31. Rotating retrograde (opposite the direction of rotation of other planets). 32. Primary atmospheric gas is carbon dioxide. 33. Has a very thin atmosphere when compared with Earth. 34. Features a huge canyon over 3,000 miles long known as Vallis Marineris. ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... _____ 14. An important property of air circulation is a. warm air is denser than cold air. b. cold air and warm air have the same density c. cold air is denser than warm air. d. air has no mass _____ 15. Which of the following gases is most responsible for the greenhouse effect? a. nitrous oxide b. ...
... _____ 14. An important property of air circulation is a. warm air is denser than cold air. b. cold air and warm air have the same density c. cold air is denser than warm air. d. air has no mass _____ 15. Which of the following gases is most responsible for the greenhouse effect? a. nitrous oxide b. ...
Mid-term Exam 3 - Practice Version
... _____ 21. Which world does Titan's atmosphere most resemble, if we consider only the dominant gas in its atmosphere and its surface pressure? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... _____ 21. Which world does Titan's atmosphere most resemble, if we consider only the dominant gas in its atmosphere and its surface pressure? a. b. c. d. e. ...
chapter10AtmosphersT..
... • Why did Mars change? – Its atmosphere must have once been much thicker for its greenhouse effect to allow liquid water on the surface – Somehow Mars lost most of its atmosphere, perhaps because of declining magnetic field ...
... • Why did Mars change? – Its atmosphere must have once been much thicker for its greenhouse effect to allow liquid water on the surface – Somehow Mars lost most of its atmosphere, perhaps because of declining magnetic field ...
Larsen - Mars Climate Database
... Basic scaling laws: The scaling laws have been validated, analysing the Martian surface layer data for the relations between power spectra of wind, pressure and temperature turbulence and the corresponding mean values of wind speed and temperature. Usual spectral formulations have been used based on ...
... Basic scaling laws: The scaling laws have been validated, analysing the Martian surface layer data for the relations between power spectra of wind, pressure and temperature turbulence and the corresponding mean values of wind speed and temperature. Usual spectral formulations have been used based on ...
Biogeochemical cycles are part of the larger cycles that
... 3. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are thought to be controlled by weathering rates and rates of volcanic eruptions. 4. Weathering rates are thought to be controlled by rate of tectonic uplift. The more uplift = more weathering = less atmospheric carbon dioxide. 5. May explain the sl ...
... 3. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are thought to be controlled by weathering rates and rates of volcanic eruptions. 4. Weathering rates are thought to be controlled by rate of tectonic uplift. The more uplift = more weathering = less atmospheric carbon dioxide. 5. May explain the sl ...
Interiors of Jupiter and Saturn - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... Reasons for the interest and importance of Titan: it has a dense atmosphere and a hydrological cycle based on another compound. Despite its alien nature, in some ways it is the most Earth-‐like ...
... Reasons for the interest and importance of Titan: it has a dense atmosphere and a hydrological cycle based on another compound. Despite its alien nature, in some ways it is the most Earth-‐like ...
SOLAR SYSTEM
... Asteroids are small, irregularly-shaped bodies made of rock or metal Contains a dwarf planet named Ceres Jupiter - Gas Giant 5th planet from the sun Largest of all planets (all other planets could easily fit inside of it) Enormous ball of gas – mostly hydrogen and helium like the Sun Gre ...
... Asteroids are small, irregularly-shaped bodies made of rock or metal Contains a dwarf planet named Ceres Jupiter - Gas Giant 5th planet from the sun Largest of all planets (all other planets could easily fit inside of it) Enormous ball of gas – mostly hydrogen and helium like the Sun Gre ...
Solar System - Legacy High School
... • As the Sun grew hot enough to ignite the nuclear reactions which sustain it today, it vaporized the cold ices and frozen gasses in the inner solar system, leaving behind the rocky dust and metals which form the inner planets. • The outer Solar System remained cold, and the ices and gas there colle ...
... • As the Sun grew hot enough to ignite the nuclear reactions which sustain it today, it vaporized the cold ices and frozen gasses in the inner solar system, leaving behind the rocky dust and metals which form the inner planets. • The outer Solar System remained cold, and the ices and gas there colle ...
Solar System
... • As the Sun grew hot enough to ignite the nuclear reactions which sustain it today, it vaporized the cold ices and frozen gasses in the inner solar system, leaving behind the rocky dust and metals which form the inner planets. • The outer Solar System remained cold, and the ices and gas there colle ...
... • As the Sun grew hot enough to ignite the nuclear reactions which sustain it today, it vaporized the cold ices and frozen gasses in the inner solar system, leaving behind the rocky dust and metals which form the inner planets. • The outer Solar System remained cold, and the ices and gas there colle ...
3 slides per page with notes
... • On Earth, because of its distance from the sun, liquid water formed at the surface and CO2 produced by volcanic outgassing was dissolved in the water to form carbonate rock. • This “locked” the CO2 into rock and controlled the amount present in the atmosphere limiting its ability to heat (through ...
... • On Earth, because of its distance from the sun, liquid water formed at the surface and CO2 produced by volcanic outgassing was dissolved in the water to form carbonate rock. • This “locked” the CO2 into rock and controlled the amount present in the atmosphere limiting its ability to heat (through ...
Earth`s Atmospheric Layers
... • Average Temperature: -50º to 70º F • All weather happens here. • Warm air rises to form clouds, rain falls. • As altitude increases, temperature decreases. (The higher you go the colder it gets) • Warmed by the ground below ...
... • Average Temperature: -50º to 70º F • All weather happens here. • Warm air rises to form clouds, rain falls. • As altitude increases, temperature decreases. (The higher you go the colder it gets) • Warmed by the ground below ...
Boyle`s Law Lab
... 2 books atmosphere + 3 books atmosphere + 4 books atmosphere + 5 books CHEMISTRY: A Study of Matter © 2004, GPB ...
... 2 books atmosphere + 3 books atmosphere + 4 books atmosphere + 5 books CHEMISTRY: A Study of Matter © 2004, GPB ...
Goal to get to know the moons of Saturn a bit better
... has two small “trojan” moons which share its orbit (60 degrees in front and in back) – Calypso and Telesto ...
... has two small “trojan” moons which share its orbit (60 degrees in front and in back) – Calypso and Telesto ...
Saturn is the only planet in our Solar System less den
... The temperature on Earth ranges from between -127°F to 136°F (-88°C to 58°C; 185 K to 311 K). ...
... The temperature on Earth ranges from between -127°F to 136°F (-88°C to 58°C; 185 K to 311 K). ...
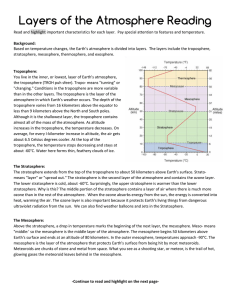
Layers of the Atmosphere Reading
... Near the top of the atmosphere, the air is very thin. At 80 kilometers above Earth's surface, the air is only about 0.001 percent as dense as the air at sea level. It's as though you took a cubic meter of air at sea level and expanded it into 100,000 cubic meters at the top of the mesosphere. The ...
... Near the top of the atmosphere, the air is very thin. At 80 kilometers above Earth's surface, the air is only about 0.001 percent as dense as the air at sea level. It's as though you took a cubic meter of air at sea level and expanded it into 100,000 cubic meters at the top of the mesosphere. The ...
signatures of life on other worlds
... timing of pulsar flashes for neutron stars, or through brightness changes caused by gravitational microlensing and planetary transits. From space, the Kepler mission, which launched in 2009, is now taking a census of stars to determine the fraction that have ...
... timing of pulsar flashes for neutron stars, or through brightness changes caused by gravitational microlensing and planetary transits. From space, the Kepler mission, which launched in 2009, is now taking a census of stars to determine the fraction that have ...
wkbk p 49 (6)0001
... 7. Most of Earth's ozone is in the stratosphere. 8. Ozone in the stratosphere shields us from ultraviolet sunrays. 9. The mesosphere, the third layer of our atmosphere, ends about 53 miles above Earth. 10. It is cold in the mesosphere; gas trails left by meteors can be seen there. 11. The outermost ...
... 7. Most of Earth's ozone is in the stratosphere. 8. Ozone in the stratosphere shields us from ultraviolet sunrays. 9. The mesosphere, the third layer of our atmosphere, ends about 53 miles above Earth. 10. It is cold in the mesosphere; gas trails left by meteors can be seen there. 11. The outermost ...
Chapter 11
... Consists of different wavelengths Gamma (very short waves) X-rays Ultraviolet (UV) Visible Infrared Microwaves and radio waves ...
... Consists of different wavelengths Gamma (very short waves) X-rays Ultraviolet (UV) Visible Infrared Microwaves and radio waves ...
Layers of the Atmosphere
... • Average Temperature: -50º to 70º F • All weather happens here. • Warm air rises to form clouds, rain falls. • As altitude increases, temperature decreases. (The higher you go the colder it gets) • Warmed by the ground below ...
... • Average Temperature: -50º to 70º F • All weather happens here. • Warm air rises to form clouds, rain falls. • As altitude increases, temperature decreases. (The higher you go the colder it gets) • Warmed by the ground below ...
The Troposphere The Stratosphere The Mesosphere The
... Near the top of the atmosphere, the air is very thin. At 80 kilometers above Earth’s surface, the air is only about 0.001 percent as dense as the air at sea level. It’s as though you took a cubic meter of air at sea level and expanded it into 100,000 cubic meters at the top of the mesosphere. The ou ...
... Near the top of the atmosphere, the air is very thin. At 80 kilometers above Earth’s surface, the air is only about 0.001 percent as dense as the air at sea level. It’s as though you took a cubic meter of air at sea level and expanded it into 100,000 cubic meters at the top of the mesosphere. The ou ...
The Earth`s Atmosphere-I
... 3. The earth’s first atmosphere (4.6 billion years ago) consisted mostly of He, H2. Outgassing (volcanic eruption) releases CO2, N2, H2O, forming the earth’s second atmosphere. After plants evolved, the atmospheric O2 increased more rapidly as a result of photosynthesis. ...
... 3. The earth’s first atmosphere (4.6 billion years ago) consisted mostly of He, H2. Outgassing (volcanic eruption) releases CO2, N2, H2O, forming the earth’s second atmosphere. After plants evolved, the atmospheric O2 increased more rapidly as a result of photosynthesis. ...
Moly-D Element Atmospheres
... This atmosphere typically comprises 20% CO, 40% H2 and the balance N2. The Maximum use temperature will be determined by dewpoint and gas velocity. Carburizing atmosphere MOLY-D elements are not attacked by the atmosphere in a Carburizing furnace. If carbon builds up in this type of furnace it shoul ...
... This atmosphere typically comprises 20% CO, 40% H2 and the balance N2. The Maximum use temperature will be determined by dewpoint and gas velocity. Carburizing atmosphere MOLY-D elements are not attacked by the atmosphere in a Carburizing furnace. If carbon builds up in this type of furnace it shoul ...