out of this world crossword
... 7. Halley’s _ _ _ _ _ is the most famous of these bright heavenly bodies with tails. ...
... 7. Halley’s _ _ _ _ _ is the most famous of these bright heavenly bodies with tails. ...
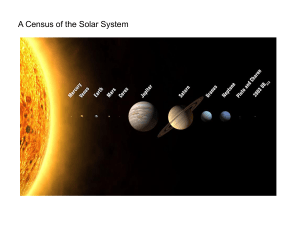
A Census of the Solar System
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
We live in a solar system that consists of a star we call the Sun and
... Eclipse When the Moon blocks the sunlight to the Earth (Solar Eclipse) or when the Earth blocks the sunlight to the Moon (Lunar Eclipse). Atmosphere A mixture of gases that surround any celestial body that has a gravitational field. Solar System Made up of planets and moons that orbit a sun. Light Y ...
... Eclipse When the Moon blocks the sunlight to the Earth (Solar Eclipse) or when the Earth blocks the sunlight to the Moon (Lunar Eclipse). Atmosphere A mixture of gases that surround any celestial body that has a gravitational field. Solar System Made up of planets and moons that orbit a sun. Light Y ...
Solar System and Inner Planets
... covered by craters caused by meteorites Venus-second planet from the sun covered with heavy clouds atmosphere is carbon dioxide winds blowing at high speeds it IS the hottest planet can be seen early in the morning or late in the evening called the “morning star” or “evening star” do ...
... covered by craters caused by meteorites Venus-second planet from the sun covered with heavy clouds atmosphere is carbon dioxide winds blowing at high speeds it IS the hottest planet can be seen early in the morning or late in the evening called the “morning star” or “evening star” do ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 77 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 3 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 77 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 3 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
Document
... orbit • Has no moon • Almost no atmosphere—high daytime temperatures, low nighttime temperature ...
... orbit • Has no moon • Almost no atmosphere—high daytime temperatures, low nighttime temperature ...
Public Lecture - Our Solar System
... Venus • Thick CO2, H20 and H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) atmosphere traps sunlight and broils the planet’s surface – Maximum surface temperature reaches up to 900oF ...
... Venus • Thick CO2, H20 and H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) atmosphere traps sunlight and broils the planet’s surface – Maximum surface temperature reaches up to 900oF ...
Day-7
... Stellar Radii and Planetary Orbital Semi-Major Axis (A.U.) The Habitable Zone (HZ) in green is defined here (and often) as the distance from a star where liquid water is expected to exist on the planets surface (Kasting, Whitmire, and Reynolds 1993). ...
... Stellar Radii and Planetary Orbital Semi-Major Axis (A.U.) The Habitable Zone (HZ) in green is defined here (and often) as the distance from a star where liquid water is expected to exist on the planets surface (Kasting, Whitmire, and Reynolds 1993). ...
1 DS 3.10 Grade 9 Review
... 12. What are the two most common elements on the Sun? 13. Explain a lunar and solar eclipse. 14. What is nuclear fusion? 15. What does the colour of a star indicate? 16. What is a galaxy? 17. Name our galaxies and the group it is part of. 18. Describe 3 galaxy shapes. 19. Describe the 3 main stages ...
... 12. What are the two most common elements on the Sun? 13. Explain a lunar and solar eclipse. 14. What is nuclear fusion? 15. What does the colour of a star indicate? 16. What is a galaxy? 17. Name our galaxies and the group it is part of. 18. Describe 3 galaxy shapes. 19. Describe the 3 main stages ...
Document
... Earth is the planet we live on. Earth is the largest inner planet. Earth’s distance from the sun helps the temperature maintain so it can support life. ...
... Earth is the planet we live on. Earth is the largest inner planet. Earth’s distance from the sun helps the temperature maintain so it can support life. ...
Tutorial - TIL BIRNSTIEL
... • In a real mission, the astrometric precision depends on the magnitude of the star. The future mission GAIA will have an astrometric precision of 7 µas, but only for stars brighter than 10 mag. What would be the maximum distance at which you could detect Jupiter with that precision? What would be t ...
... • In a real mission, the astrometric precision depends on the magnitude of the star. The future mission GAIA will have an astrometric precision of 7 µas, but only for stars brighter than 10 mag. What would be the maximum distance at which you could detect Jupiter with that precision? What would be t ...
Jim_lecture_Chapter
... have liquid water on their surfaces • This means that we should look within the conventional habitable zone around nearby stars ...
... have liquid water on their surfaces • This means that we should look within the conventional habitable zone around nearby stars ...
File Space Test (March 11th) - Bonus Points
... A chunk of rock that burns up in the atmosphere. ...
... A chunk of rock that burns up in the atmosphere. ...
File
... Moons revolve around planets, which revolve around stars, which revolve around the center of a galaxy, which is a typical unit of the universe. 2. Explain what is meant by this statement. "When you look at a star, it might not actually be there." Many stars are thousands of light years away. The lig ...
... Moons revolve around planets, which revolve around stars, which revolve around the center of a galaxy, which is a typical unit of the universe. 2. Explain what is meant by this statement. "When you look at a star, it might not actually be there." Many stars are thousands of light years away. The lig ...
Solar System and Astronomy puzzle 001
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
It`s a bird, it`s a plane…
... our solar system • Planets must be round, orbit the sun, and not be close to objects of similar mass • Pluto’s moon, Charon, is almost the same size, which disqualifies Pluto from Planethood ...
... our solar system • Planets must be round, orbit the sun, and not be close to objects of similar mass • Pluto’s moon, Charon, is almost the same size, which disqualifies Pluto from Planethood ...
14.2 The Solar System Solar System: made of 9 planets and
... o Largest planet, Great Red Spot is a huge red whirlwind rotating slowly around middle of planet, 28 moons, Io moon has more active volcanoes than anywhere else in solar system Asteroid Belt o Between Jupiter and Mars o Asteroids are pieces of rock made of minerals similar to planet materials o The ...
... o Largest planet, Great Red Spot is a huge red whirlwind rotating slowly around middle of planet, 28 moons, Io moon has more active volcanoes than anywhere else in solar system Asteroid Belt o Between Jupiter and Mars o Asteroids are pieces of rock made of minerals similar to planet materials o The ...
Study Guide for Earth/ Space Science Test 1. Rotation – The Earth
... 5. Seasons – opposite in hemispheres and caused by the tilt toward or away from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar ...
... 5. Seasons – opposite in hemispheres and caused by the tilt toward or away from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar ...
Inner planets
... Outer planets: they are further from the sun, large and made up mainly of light gases and ices Astronomers: scientists who study the universe Moon: a natural object that revolves around a planet (are called satellites) Asteroids: large pieces of space rock with irregular shapes most found in asteroi ...
... Outer planets: they are further from the sun, large and made up mainly of light gases and ices Astronomers: scientists who study the universe Moon: a natural object that revolves around a planet (are called satellites) Asteroids: large pieces of space rock with irregular shapes most found in asteroi ...
Saint Mary`s College ASTRONOMY EXAM -
... 35. What characterized the early phases of planetary formation into protoplanets? (hint: what do planetary surfaces have in common?) 36. Where does most of our knowledge of the structure of the earth's interior come from? 37. Why is the surface of Venus is hotter than we might have expected? 38. Wha ...
... 35. What characterized the early phases of planetary formation into protoplanets? (hint: what do planetary surfaces have in common?) 36. Where does most of our knowledge of the structure of the earth's interior come from? 37. Why is the surface of Venus is hotter than we might have expected? 38. Wha ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.