solar_system
... A year on Mars takes as long as two Earth years. A day on Mars lasts only thirty minutes longer than a day on Earth ...
... A year on Mars takes as long as two Earth years. A day on Mars lasts only thirty minutes longer than a day on Earth ...
A Relative-Scaled Model of the Solar System
... d. How about the other planets? Might you possibly see them at midnight? How about right before sunrise or right after sunset? ...
... d. How about the other planets? Might you possibly see them at midnight? How about right before sunrise or right after sunset? ...
Allison McGraw - WordPress.com
... Scintillation: The twinkling of star light is a beautiful effect of the Earth's atmosphere. As light passes through our atmosphere, its path is deviated (refracted) multiple times before reaching the ground. Stars that are near to the horizon will scintillate much more than stars high overhead since ...
... Scintillation: The twinkling of star light is a beautiful effect of the Earth's atmosphere. As light passes through our atmosphere, its path is deviated (refracted) multiple times before reaching the ground. Stars that are near to the horizon will scintillate much more than stars high overhead since ...
Space - PAMS-Doyle
... • The distance between planets and sizes of the planets vary greatly. The outer, “gas” planets are very large, and the four inner planets are comparatively small and rocky. On one end write the sun and the other Pluto. Fold your paper in half, at the crease write Uranus. Fold Pluto up to Uranus, at ...
... • The distance between planets and sizes of the planets vary greatly. The outer, “gas” planets are very large, and the four inner planets are comparatively small and rocky. On one end write the sun and the other Pluto. Fold your paper in half, at the crease write Uranus. Fold Pluto up to Uranus, at ...
The Solar System 2003
... Saturn became famous by beauty of its bright rings. Regardless they have radius over 100,000 km, they are at most a few hundred metres thick. They look as a series of thousands of differently bright and differently transparent ringlets, but in reality they are composed of individual icy–stony fragme ...
... Saturn became famous by beauty of its bright rings. Regardless they have radius over 100,000 km, they are at most a few hundred metres thick. They look as a series of thousands of differently bright and differently transparent ringlets, but in reality they are composed of individual icy–stony fragme ...
EARTH SCIENCE HOMEWORK 11-7 Sun`s surface
... 4. The intense __________ fields associated with sunspots might cause ___________, which are huge arching columns of ______. (pg. 730, P4) 5. Gases near a _________ sometimes brighten suddenly, shooting outward at high speed. These violent eruptions are called _______ ___________. (2 words) (pg. 730 ...
... 4. The intense __________ fields associated with sunspots might cause ___________, which are huge arching columns of ______. (pg. 730, P4) 5. Gases near a _________ sometimes brighten suddenly, shooting outward at high speed. These violent eruptions are called _______ ___________. (2 words) (pg. 730 ...
WHAT IS A STAR? - cloudfront.net
... 3. Explore how stars have constantly changed outer space over time. ...
... 3. Explore how stars have constantly changed outer space over time. ...
What is a planet? Why? How?
... Based upon a combination of how they move and what they look like ...
... Based upon a combination of how they move and what they look like ...
Telephone Quizzes for ASTR 200 1999 Revision
... is the same as that of the Sun as mass does not affect the lifetime of a star. is shorter than that of the Sun since there is less fuel to burn. is longer than that of the Sun because the star generates energy (uses fuel) at a very slow rate. cannot be discussed as such a star is too small to genera ...
... is the same as that of the Sun as mass does not affect the lifetime of a star. is shorter than that of the Sun since there is less fuel to burn. is longer than that of the Sun because the star generates energy (uses fuel) at a very slow rate. cannot be discussed as such a star is too small to genera ...
Questions - HCC Learning Web
... another person 2.0 m away. In your solution, state the quantities you measure / estimate and their values. ...
... another person 2.0 m away. In your solution, state the quantities you measure / estimate and their values. ...
Chapter 16: The Origin of the Solar System RQ 16
... different ability of materials (elements, molecules) to condense at a certain temperature (condensation sequence). In the case of the terrestrial planets, the gas was so hot (since it was near to the center of the system), that only matters with high “boiling points” were able to condense. Therefore ...
... different ability of materials (elements, molecules) to condense at a certain temperature (condensation sequence). In the case of the terrestrial planets, the gas was so hot (since it was near to the center of the system), that only matters with high “boiling points” were able to condense. Therefore ...
File - Mrs. MacGowan 6-2
... They are 140 moons that orbit the eight planets in the solar system. The moons rather then the planets don’t orbit the sun they about the planet they are nearest too. The planet that used to be considered a planet is Pluto which is now considered a dwarf planet because of its size and the fact that ...
... They are 140 moons that orbit the eight planets in the solar system. The moons rather then the planets don’t orbit the sun they about the planet they are nearest too. The planet that used to be considered a planet is Pluto which is now considered a dwarf planet because of its size and the fact that ...
Solar system
... 1) Creation of elements: At the core of the star, heavier “stuff” is created, including carbon and iron. 2) Gases are pulled together by gravity into clouds called Nebulas. 3) The singularity: All matter is crammed into a tiny point the size of a proton. 4) Protostars are formed: a dense cloud of ga ...
... 1) Creation of elements: At the core of the star, heavier “stuff” is created, including carbon and iron. 2) Gases are pulled together by gravity into clouds called Nebulas. 3) The singularity: All matter is crammed into a tiny point the size of a proton. 4) Protostars are formed: a dense cloud of ga ...
Unit 3 - Section 8.9 2011 Celestrial Objects from Earth
... The word retrograde applies to the apparent backward motion of a planet. An old encyclopedia of astrology describes this retrograde motion as "…the effect of a slow-moving train as viewed from another train traveling parallel to it but at a more rapid rate, wherein the slower train appears to be mov ...
... The word retrograde applies to the apparent backward motion of a planet. An old encyclopedia of astrology describes this retrograde motion as "…the effect of a slow-moving train as viewed from another train traveling parallel to it but at a more rapid rate, wherein the slower train appears to be mov ...
Solar System
... Could be remnants from the formation of SS, which have failed to join the gravitational interference of Jupiter The size of asteroids rangs from several hundreds of kilometers to microscopic dust. There are millions, but their total mass is only 4% that of our moon. ...
... Could be remnants from the formation of SS, which have failed to join the gravitational interference of Jupiter The size of asteroids rangs from several hundreds of kilometers to microscopic dust. There are millions, but their total mass is only 4% that of our moon. ...
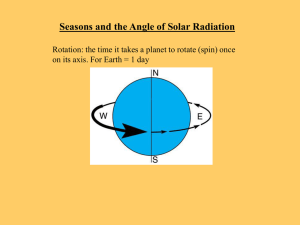
Seasons
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
100 Greatest Discoveries in Science
... 1. The Planets Move (2000 B.C. – 500 B.C.) A thousand years of observations reveal that there are stars that move in the sky and follow patterns, showing that the Earth is part of a solar system of planets separate from the fixed stars. Why is the Venus tablet of Amozogania important? It’s the earli ...
... 1. The Planets Move (2000 B.C. – 500 B.C.) A thousand years of observations reveal that there are stars that move in the sky and follow patterns, showing that the Earth is part of a solar system of planets separate from the fixed stars. Why is the Venus tablet of Amozogania important? It’s the earli ...
Stream: sciences. E THIRD TERM ENGLISH EXAMINATION PART
... Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. It includes also the satellites of the planets; numerous comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. The moon is the satellite rotating around the earth and the closest body to it. The Sun is the richest source of electromagnetic energy ( mostly in the ...
... Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. It includes also the satellites of the planets; numerous comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. The moon is the satellite rotating around the earth and the closest body to it. The Sun is the richest source of electromagnetic energy ( mostly in the ...
Space
... in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. One hundred and nine Earths would be required to fit across the Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and ha ...
... in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. One hundred and nine Earths would be required to fit across the Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and ha ...
Our Solar System The Sun
... surface, 3 moons, and it orbits in a tilted plane. Charon is the largest moon of Pluto. • Makemake is smaller than Pluto, but farther • Eris is larger than Pluto, but farther away • More dwarf planets and plutoids are expected to ...
... surface, 3 moons, and it orbits in a tilted plane. Charon is the largest moon of Pluto. • Makemake is smaller than Pluto, but farther • Eris is larger than Pluto, but farther away • More dwarf planets and plutoids are expected to ...
Our Solar System - Hardeman School
... Our Moon is many times smaller than Earth Many scientists think the Moon used to be a part of Earth The Moon causes Earths ocean tides too It reflects light from the sun ...
... Our Moon is many times smaller than Earth Many scientists think the Moon used to be a part of Earth The Moon causes Earths ocean tides too It reflects light from the sun ...
Unit 1: Earth History 1. Distinguish among eons
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
Planet formation
... Jupiter migrated in to ~2AU. Its migration was stopped and reversed by the inward migration of Saturn to a 3:2 resonance. The inward migration of Jupiter brought volatile-rich material from ~5AU which was incorporated in the formation of the terrestrial planets. It also cleared much of the material ...
... Jupiter migrated in to ~2AU. Its migration was stopped and reversed by the inward migration of Saturn to a 3:2 resonance. The inward migration of Jupiter brought volatile-rich material from ~5AU which was incorporated in the formation of the terrestrial planets. It also cleared much of the material ...
THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... Asteroids What is an Asteroid? •Small rocky bodies that have been compared to “flying mountains” •Ceres is the largest (@ 1000 km in diameter) and first to be discovered Asteroids show up as streaks on photos. ...
... Asteroids What is an Asteroid? •Small rocky bodies that have been compared to “flying mountains” •Ceres is the largest (@ 1000 km in diameter) and first to be discovered Asteroids show up as streaks on photos. ...
Astronomy Test Review
... What does the tail of a comet tell us about the direction the comet is moving? ...
... What does the tail of a comet tell us about the direction the comet is moving? ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.