Excellence
... The inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) formed close to the sun. These planets are made up of compounds (e.g. iron and nickel), which have high melting points. This is because it is too hot for molecules with low melting points to be present (e.g. water and methane). Also, any gases (H, ...
... The inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) formed close to the sun. These planets are made up of compounds (e.g. iron and nickel), which have high melting points. This is because it is too hot for molecules with low melting points to be present (e.g. water and methane). Also, any gases (H, ...
Powerpoint file
... a Short-Period Planet ("Hot Jupiters") • Transit Probability for the Hot Jupiters: ~ 10% • Therefore 1 Transit/1000 Stars is expected • 30-40 Transits for the full surveyed Stellar Sample are expected if the 47 Tuc Planet occurence is the same as in Field Stars ...
... a Short-Period Planet ("Hot Jupiters") • Transit Probability for the Hot Jupiters: ~ 10% • Therefore 1 Transit/1000 Stars is expected • 30-40 Transits for the full surveyed Stellar Sample are expected if the 47 Tuc Planet occurence is the same as in Field Stars ...
Science Overview
... Transiting Planets • ExoPlanet Task Force Report (draft) – Advice to NASA & NSF on exoplanet research • 5/10/15 year time horizons ...
... Transiting Planets • ExoPlanet Task Force Report (draft) – Advice to NASA & NSF on exoplanet research • 5/10/15 year time horizons ...
What Makes a Planet Habitable?
... a rather regular and predictable way. Comparative studies show that the Sun was, when it started its main-sequence life, brighter by 100-1000 times in X-rays and perhaps a few dozen times in the ultraviolet, compared to the present time (Ribas et al., 2005: 680). This should have had profound effect ...
... a rather regular and predictable way. Comparative studies show that the Sun was, when it started its main-sequence life, brighter by 100-1000 times in X-rays and perhaps a few dozen times in the ultraviolet, compared to the present time (Ribas et al., 2005: 680). This should have had profound effect ...
are solar system
... understood. Most scientist believe that it began about 15,000 million years ago with an unimaginably violent explosion known as the Big bang. This idea is called the Big Bang Theory. ...
... understood. Most scientist believe that it began about 15,000 million years ago with an unimaginably violent explosion known as the Big bang. This idea is called the Big Bang Theory. ...
Phys 214. Planets and Life
... According to our current theory of planet formation, Jupiter-like planet cannot form close to its parent star because it would be too hot for gases to condense. However, they can form farther out and then migrate inward. The inward migration of a Jovian-like planet in an extrasolar planetary system ...
... According to our current theory of planet formation, Jupiter-like planet cannot form close to its parent star because it would be too hot for gases to condense. However, they can form farther out and then migrate inward. The inward migration of a Jovian-like planet in an extrasolar planetary system ...
Jeopardy
... This planet has more water on the surface than any other planet (there are moons with more). ...
... This planet has more water on the surface than any other planet (there are moons with more). ...
Astronomy - AG Web Services
... Merit Requirements: Blue-Bordered Merit ASTRONOMY 1. Define astronomy and name two important astronomers. 2. Explain the major differences between the following: planets, moons, stars, comets, asteroids, meteoroids, solar systems, and galaxies. 3. Find one interesting fact about each planet in our s ...
... Merit Requirements: Blue-Bordered Merit ASTRONOMY 1. Define astronomy and name two important astronomers. 2. Explain the major differences between the following: planets, moons, stars, comets, asteroids, meteoroids, solar systems, and galaxies. 3. Find one interesting fact about each planet in our s ...
Sun, Earth, Moon Foldable Sun Facts
... – Cut off bottom 3 in – Fold in half “hot-dog” style, cut along crease – Give half to a friend, keep the other half – Cover bottom solar system half of foldable, tape it on, draw lines ...
... – Cut off bottom 3 in – Fold in half “hot-dog” style, cut along crease – Give half to a friend, keep the other half – Cover bottom solar system half of foldable, tape it on, draw lines ...
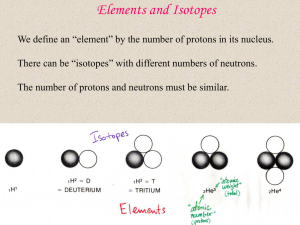
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... If the mass is too low, the object is a “failed star”, and can never stabilize its luminosity with fusion. Brown dwarfs fuse at least deuterium, but then find their pressure support without heat, and fade slowly away. ...
... If the mass is too low, the object is a “failed star”, and can never stabilize its luminosity with fusion. Brown dwarfs fuse at least deuterium, but then find their pressure support without heat, and fade slowly away. ...
The Sun and the Stars
... • What is the single most distinguishing feature of a star? • Luminosity is a term that astronomers use when describing the total amount of energy it radiated by the star ( the twinkle) • It can be measured more precisely as a star’s total energy output per second, measured in Joules per second (J/s ...
... • What is the single most distinguishing feature of a star? • Luminosity is a term that astronomers use when describing the total amount of energy it radiated by the star ( the twinkle) • It can be measured more precisely as a star’s total energy output per second, measured in Joules per second (J/s ...
Powerpoint
... suggesting that the Earth is not unique – Sunspots; suggests that celestial bodies are not perfect and can change – Observed four moons of Jupiter; showed that not all bodies orbit Earth – Observed phases of Venus (and correlation of apparent size and phase); evidence that Venus orbits the Sun ...
... suggesting that the Earth is not unique – Sunspots; suggests that celestial bodies are not perfect and can change – Observed four moons of Jupiter; showed that not all bodies orbit Earth – Observed phases of Venus (and correlation of apparent size and phase); evidence that Venus orbits the Sun ...
CST Prep- 8th Grade Astronomy
... 62. When these bits enter our atmosphere they burn up as __________________ (also known as “shooting stars”). 63. Bits of outer space material that strike the Earth’s surface and can be found intact are now called __________________. 64. The “hole” left in the ground from an asteroid impact is calle ...
... 62. When these bits enter our atmosphere they burn up as __________________ (also known as “shooting stars”). 63. Bits of outer space material that strike the Earth’s surface and can be found intact are now called __________________. 64. The “hole” left in the ground from an asteroid impact is calle ...
Who am I? - Denton ISD
... stories in cultures around the world, including those of the ancient Egyptians, the Aztecs of Mexico, Native American tribes of North America and Canada, the Chinese, and many others. ...
... stories in cultures around the world, including those of the ancient Egyptians, the Aztecs of Mexico, Native American tribes of North America and Canada, the Chinese, and many others. ...
Looking for Signs of Life Answer Key
... uncertain that the spectrum of the star was taken without any planets in front of it (making it a sample of just the star, not the star plus one or more planets). 14. What combination of substances in a planet's atmosphere would suggest that the planet might be suitable for life? Choose all that app ...
... uncertain that the spectrum of the star was taken without any planets in front of it (making it a sample of just the star, not the star plus one or more planets). 14. What combination of substances in a planet's atmosphere would suggest that the planet might be suitable for life? Choose all that app ...
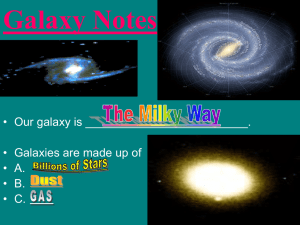
Slide 1
... and 2 or more spiral arms. •Elliptical Galaxy- Spherical or flattened disk. Usually contains the oldest stars. ...
... and 2 or more spiral arms. •Elliptical Galaxy- Spherical or flattened disk. Usually contains the oldest stars. ...
Light Years Away
... 5. The Oort cloud is located A. Between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter B. On the outer rim of our solar system C. Within the atmosphere of Neptune D. Within the Andromeda Galaxy ...
... 5. The Oort cloud is located A. Between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter B. On the outer rim of our solar system C. Within the atmosphere of Neptune D. Within the Andromeda Galaxy ...
Simon P. Balm Astronomy 5, Test #1, Sample Questions
... combined mass is slightly greater than the original nucleus B) a heavy nucleus breaks apart into a number of smaller nuclei whose combined mass are less than the original nucleus C) two or more nuclei fuse or stick together to form a heavier nucleus whose combined mass is slightly less than the orig ...
... combined mass is slightly greater than the original nucleus B) a heavy nucleus breaks apart into a number of smaller nuclei whose combined mass are less than the original nucleus C) two or more nuclei fuse or stick together to form a heavier nucleus whose combined mass is slightly less than the orig ...
The Planets in the Solar System There are an uncountable number
... example, Ida, Jupiter, and Mercury are all big enough to be seen from Earth, but should we classify all three of these objects as planets? This question has made many people wonder: How many planets are there in the solar system? With your group, develop an answer to this simple, but important, ques ...
... example, Ida, Jupiter, and Mercury are all big enough to be seen from Earth, but should we classify all three of these objects as planets? This question has made many people wonder: How many planets are there in the solar system? With your group, develop an answer to this simple, but important, ques ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... Because of Earth’s movement around the sun Apparent Magnitude – What is it? How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
... Because of Earth’s movement around the sun Apparent Magnitude – What is it? How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.