Solar System Teacher Tips
... causes the tides in the Earth’s oceans. Kuiper Belt: a band of icy rocks (including most planetoids) that orbit the Sun, extending from the orbit of Neptune to the Oort Cloud. Meteor: meteoroid burning as it enters a planet’s atmosphere (commonly, but incorrectly identified as “shooting stars”). Met ...
... causes the tides in the Earth’s oceans. Kuiper Belt: a band of icy rocks (including most planetoids) that orbit the Sun, extending from the orbit of Neptune to the Oort Cloud. Meteor: meteoroid burning as it enters a planet’s atmosphere (commonly, but incorrectly identified as “shooting stars”). Met ...
EARTH SCIENCE MIDTERM REVIEW SHEET
... Heliocentric Model - All of the planets revolve around the sun in slightly eccentric ellipses; the sun is at one of the focal points. Earth does rotate. Eccentricity - ESRT formula p. 1; always between 0 and 1 and rounded to the nearest thousandth Major axis – longest distance along an ellipse. This ...
... Heliocentric Model - All of the planets revolve around the sun in slightly eccentric ellipses; the sun is at one of the focal points. Earth does rotate. Eccentricity - ESRT formula p. 1; always between 0 and 1 and rounded to the nearest thousandth Major axis – longest distance along an ellipse. This ...
Astrophysics - Student Reference Packet
... According to this definition, our solar system has eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The IAU determined that Pluto has not cleared its neighborhood because it orbits among the objects of the Kuiper Belt. As such, Pluto is no longer classified as a plan ...
... According to this definition, our solar system has eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The IAU determined that Pluto has not cleared its neighborhood because it orbits among the objects of the Kuiper Belt. As such, Pluto is no longer classified as a plan ...
Glossary
... a satellite closer to a planet. (p. 386) aeronautical—anything related to the science, design, or operation of aircraft. (p. 199) aft—the rear of a spacecraft or any other ship. (p. 309) air lock—an airtight chamber, usually located between two regions of unequal pressure, in which air pressure can ...
... a satellite closer to a planet. (p. 386) aeronautical—anything related to the science, design, or operation of aircraft. (p. 199) aft—the rear of a spacecraft or any other ship. (p. 309) air lock—an airtight chamber, usually located between two regions of unequal pressure, in which air pressure can ...
PowerPoint. - teachearthscience.org
... atmospheres (composed of light gases such as H and He). By comparison, the terrestrial planets have comparatively meager atmospheres (if any) of heavier gases (N2, CO2, and H2O). ...
... atmospheres (composed of light gases such as H and He). By comparison, the terrestrial planets have comparatively meager atmospheres (if any) of heavier gases (N2, CO2, and H2O). ...
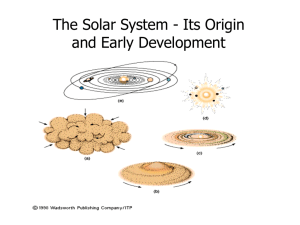
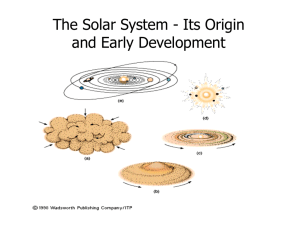
Solar System Formation
... next-generation rover with unprecedented research tools to study the early environmental history of Mars. ...
... next-generation rover with unprecedented research tools to study the early environmental history of Mars. ...
15_LectureOutline
... Planets orbiting within 0.1 AU of their stars are called “hot Jupiters”; they are not included in the previous figure but are numerous. Stars with composition like our Sun are much more likely to have planets, showing that the “dusty disk” theory is plausible. Some of these “planets” may actually be ...
... Planets orbiting within 0.1 AU of their stars are called “hot Jupiters”; they are not included in the previous figure but are numerous. Stars with composition like our Sun are much more likely to have planets, showing that the “dusty disk” theory is plausible. Some of these “planets” may actually be ...
Solar System - eNetLearning
... next-generation rover with unprecedented research tools to study the early environmental history of Mars. ...
... next-generation rover with unprecedented research tools to study the early environmental history of Mars. ...
The Sun - Lauer Science
... ● Solar prominence: arc of gas that erupts from the surface of the Sun which can loop hundreds of thousands of miles into space; can last for several months; sends solar material and radiation into space ● Sunspots: dark spots on the surface of the sun that are caused by intense magnetic activity th ...
... ● Solar prominence: arc of gas that erupts from the surface of the Sun which can loop hundreds of thousands of miles into space; can last for several months; sends solar material and radiation into space ● Sunspots: dark spots on the surface of the sun that are caused by intense magnetic activity th ...
newton`s three laws of motion
... Ptolemaic (geocentric) model, Venus would be seen in only new or crescent phases. ...
... Ptolemaic (geocentric) model, Venus would be seen in only new or crescent phases. ...
L53 SNOWBALL PLANETS AS A POSSIBLE TYPE OF WATER
... to the Earth, although a planet with a mass !0.4 M丣 (M丣 is the Earth’s mass) would not be able to maintain the internal ocean. Liquid water would be absolutely stable for a planet with a mass ⲏ4 M丣 (i.e., super-Earth) either on its surface or beneath the ice, irrespective of planetary orbit and lumi ...
... to the Earth, although a planet with a mass !0.4 M丣 (M丣 is the Earth’s mass) would not be able to maintain the internal ocean. Liquid water would be absolutely stable for a planet with a mass ⲏ4 M丣 (i.e., super-Earth) either on its surface or beneath the ice, irrespective of planetary orbit and lumi ...
Solar System Teacher Notes
... journey to examine the question, ‘When is a planet not a planet?’ This question is posed by Lucy who, along with her scientist mother Lillian, is on board a research craft heading to the outer limits of the Solar System. This trip (taken around the time of Lucy’s birthday) is to gain data to silence ...
... journey to examine the question, ‘When is a planet not a planet?’ This question is posed by Lucy who, along with her scientist mother Lillian, is on board a research craft heading to the outer limits of the Solar System. This trip (taken around the time of Lucy’s birthday) is to gain data to silence ...
Educator`s Guide
... Why do the Sun and the Moon appear to be the same size in the sky? The diameter of the Sun is 400 times greater than that of the Moon, but the Sun is 400 times farther from Earth than the Moon. That is why you can see a total eclipse of the Sun, during which the Moon blocks the light from the Sun. W ...
... Why do the Sun and the Moon appear to be the same size in the sky? The diameter of the Sun is 400 times greater than that of the Moon, but the Sun is 400 times farther from Earth than the Moon. That is why you can see a total eclipse of the Sun, during which the Moon blocks the light from the Sun. W ...
Targets and their Environments - Pathways Towards Habitable Planets
... Even active M dwarfs show lower UV in their HZ outside flares Different photochemistry: Less molecule formation (OH) or destruction (CH4, N2O) (Segura et al. 2005) ...
... Even active M dwarfs show lower UV in their HZ outside flares Different photochemistry: Less molecule formation (OH) or destruction (CH4, N2O) (Segura et al. 2005) ...
slides - quantware mips center
... The stability diagrams in the plane of initial conditions "pericentric distance — eccentricity" show that Kepler-16b is in dangerous proximity to chaos domain. It is located between the "teeth" of instability in the space of orbital parameters. Kepler-16b survives because its orbit is close to the h ...
... The stability diagrams in the plane of initial conditions "pericentric distance — eccentricity" show that Kepler-16b is in dangerous proximity to chaos domain. It is located between the "teeth" of instability in the space of orbital parameters. Kepler-16b survives because its orbit is close to the h ...
Chapter 1: Origin of the earth
... the rate of retreat, we can calculate that all the pieces must have been together about 14 Ga ago. For some time after the Big Bang, the universe consisted only of gaseous hydrogen and helium – there were no stars or galaxies. All other elements were created during the life and death of stars. Norma ...
... the rate of retreat, we can calculate that all the pieces must have been together about 14 Ga ago. For some time after the Big Bang, the universe consisted only of gaseous hydrogen and helium – there were no stars or galaxies. All other elements were created during the life and death of stars. Norma ...
The Universe and Space Travel
... Set of 10 equations in Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity that describes the fundamental interaction of gravitation as a result of spacetime being curved by matter and energy. First published by Einstein in 1915 as a tensor equation. Reduces to Newton’s law of gravitation when gravity is ...
... Set of 10 equations in Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity that describes the fundamental interaction of gravitation as a result of spacetime being curved by matter and energy. First published by Einstein in 1915 as a tensor equation. Reduces to Newton’s law of gravitation when gravity is ...
In this chapter we briefly review the origin of the Earth, from the Big
... the rate of retreat, we can calculate that all the pieces must have been together about 14 Ga ago. For some time after the Big Bang, the universe consisted only of gaseous hydrogen and helium – there were no stars or galaxies. All other elements were created during the life and death of stars. Norma ...
... the rate of retreat, we can calculate that all the pieces must have been together about 14 Ga ago. For some time after the Big Bang, the universe consisted only of gaseous hydrogen and helium – there were no stars or galaxies. All other elements were created during the life and death of stars. Norma ...
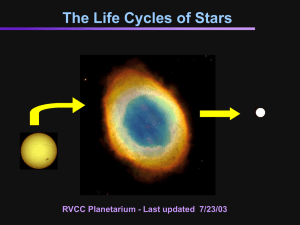
the life cycle of stars
... • A main sequence star with a mass of more than about 10 Suns experiences a spectacular end. • It swells into a red supergiant with cooling, expanding outer layers. • Eventually its core collapses, causing a huge explosion known as a ...
... • A main sequence star with a mass of more than about 10 Suns experiences a spectacular end. • It swells into a red supergiant with cooling, expanding outer layers. • Eventually its core collapses, causing a huge explosion known as a ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
Celestial Objects
... our planet, Earth. This is called the geocentric model of the solar system. (Geo- means “Earth,” so geocentric means “Earth-centered.”) It is easy to see why so many people thought this. As we look at the sky during the day, the Sun appears to move in an arc over our heads. Throughout the year, the ...
... our planet, Earth. This is called the geocentric model of the solar system. (Geo- means “Earth,” so geocentric means “Earth-centered.”) It is easy to see why so many people thought this. As we look at the sky during the day, the Sun appears to move in an arc over our heads. Throughout the year, the ...
or view
... The formation of the Sun had a dramatic effect on the temperatures across the solar nebula, introducing a temperature range that stretched from about 2000K near the Sun to less than 50K at the outer regions. The heat in the inner Solar System only allowed materials with high condensation temperature ...
... The formation of the Sun had a dramatic effect on the temperatures across the solar nebula, introducing a temperature range that stretched from about 2000K near the Sun to less than 50K at the outer regions. The heat in the inner Solar System only allowed materials with high condensation temperature ...
3 - MrFuglestad
... White Dwarf – Earth sized star that is stable with no nuclear reactions and is made of helium or carbon depending on the mass. Less massive than our Sun = Helium. There can be other elements present such as Oxygen, etc. Often the White Dwarf stars are surrounded by nebula. Black Dwarf – This star is ...
... White Dwarf – Earth sized star that is stable with no nuclear reactions and is made of helium or carbon depending on the mass. Less massive than our Sun = Helium. There can be other elements present such as Oxygen, etc. Often the White Dwarf stars are surrounded by nebula. Black Dwarf – This star is ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.