Lecture1
... Part I: Basic physical concepts; layout of the solar system; dynamics of orbiting bodies; properties of light Part II: Origin of the Solar System. Meteors, asteroids and comets as clues to our beginnings. Formation of stars and planets Part III: Properties of the planets. Interiors, surfaces and atm ...
... Part I: Basic physical concepts; layout of the solar system; dynamics of orbiting bodies; properties of light Part II: Origin of the Solar System. Meteors, asteroids and comets as clues to our beginnings. Formation of stars and planets Part III: Properties of the planets. Interiors, surfaces and atm ...
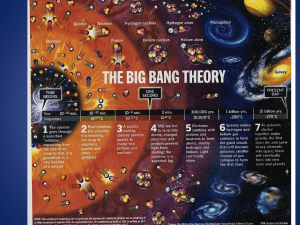
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
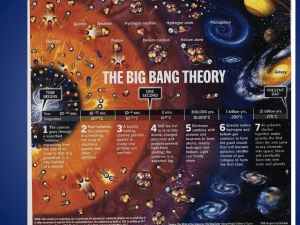
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
Five Planets
... named Cassini is traveling to Saturn now. It will arrive in July. There are no people onboard Cassini; the spaceship is a robot. Cassini is going to explore Saturn's rings, study Saturn's weather, and drop a probe into the thick orange atmosphere of Titan. What's hiding beneath Titan's clouds? No on ...
... named Cassini is traveling to Saturn now. It will arrive in July. There are no people onboard Cassini; the spaceship is a robot. Cassini is going to explore Saturn's rings, study Saturn's weather, and drop a probe into the thick orange atmosphere of Titan. What's hiding beneath Titan's clouds? No on ...
HERE
... 6. … but not all 7. planetary rotations are prograde 8. … but not all 9. cometary orbits have high a, e, i 10. many moons are tidally locked and/or in resonance PAPER TOPIC: Where is the Oort Cloud anyway? ...
... 6. … but not all 7. planetary rotations are prograde 8. … but not all 9. cometary orbits have high a, e, i 10. many moons are tidally locked and/or in resonance PAPER TOPIC: Where is the Oort Cloud anyway? ...
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how
... What force holds the different astronomical systems described in this section together? Gravity keeps the crust of the Earth, where we live, attached to the planet. Gravity keeps the planets, comets, and asteroids of the solar system bound in orbit around the Sun. Gravity keeps the Sun in orbit arou ...
... What force holds the different astronomical systems described in this section together? Gravity keeps the crust of the Earth, where we live, attached to the planet. Gravity keeps the planets, comets, and asteroids of the solar system bound in orbit around the Sun. Gravity keeps the Sun in orbit arou ...
Search for Life in the Universe
... – Habitable until now: optimistic 0.731.5 AU, pessimistic 0.851.15 AU – Habitable also until the death of the Sun: optimistic 1.31.5 AU, pessimistic at most another 2.5 byr ...
... – Habitable until now: optimistic 0.731.5 AU, pessimistic 0.851.15 AU – Habitable also until the death of the Sun: optimistic 1.31.5 AU, pessimistic at most another 2.5 byr ...
Fall 2014 -- Astronomy 1010: Planetary Astronomy Exam 1
... a. the universe is expanding in all directions at the same rate b. a unique center of the universe exists c. the universe looks the same everywhere and in all directions as long as you look on large enough spatial scales d. physical laws change from place to place in the universe e. the universe is ...
... a. the universe is expanding in all directions at the same rate b. a unique center of the universe exists c. the universe looks the same everywhere and in all directions as long as you look on large enough spatial scales d. physical laws change from place to place in the universe e. the universe is ...
Name: Period : _____ Bulldog Review #9 1. The Milky Wa
... B. Gravity is a force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. Gravity is caused by tectonic plate movement. C. Gravity is the force that is formed in the crust of the planet and it holds objects to the surface of the Earth. D. Gravity is the natural force that causes objects to m ...
... B. Gravity is a force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. Gravity is caused by tectonic plate movement. C. Gravity is the force that is formed in the crust of the planet and it holds objects to the surface of the Earth. D. Gravity is the natural force that causes objects to m ...
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2
... that died as supernovae, long before our Sun was formed. A star like our Sun, can only form elements up to carbon. Elements beyond carbon require stars that are greater than about 3.8 solar masses. Therefore, the statement given makes sense, since we need heavier stars to make the chemical elements ...
... that died as supernovae, long before our Sun was formed. A star like our Sun, can only form elements up to carbon. Elements beyond carbon require stars that are greater than about 3.8 solar masses. Therefore, the statement given makes sense, since we need heavier stars to make the chemical elements ...
Lecture 3 notes - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... that died as supernovae, long before our Sun was formed. A star like our Sun, can only form elements up to carbon. Elements beyond carbon require stars that are greater than about 3.8 solar masses. Therefore, the statement given makes sense, since we need heavier stars to make the chemical elements ...
... that died as supernovae, long before our Sun was formed. A star like our Sun, can only form elements up to carbon. Elements beyond carbon require stars that are greater than about 3.8 solar masses. Therefore, the statement given makes sense, since we need heavier stars to make the chemical elements ...
The astronauts in the upper left of this photo are working on the
... coefficient of static friction for a car not to skid when traveling at 95 km h? ...
... coefficient of static friction for a car not to skid when traveling at 95 km h? ...
PowerPoint. - teachearthscience.org
... by NASA to discover Earth-like planets orbiting other stars. Kepler was designed to observe a portion of our region of the Milky Way. Kepler's primary instrument was a photometer that continually monitored the brightness of over 145,000 main sequence stars as exoplanets pass in front of them. If we ...
... by NASA to discover Earth-like planets orbiting other stars. Kepler was designed to observe a portion of our region of the Milky Way. Kepler's primary instrument was a photometer that continually monitored the brightness of over 145,000 main sequence stars as exoplanets pass in front of them. If we ...
Class 26: EXAM 2
... A) It is a hundred times more massive than the earth. B) It is a thousand times more massive than the earth. C) It is a hundred times more massive than all the planets combined. D) It is about as massive as all the planets combined. E) It is a thousand times more massive than all the planets combine ...
... A) It is a hundred times more massive than the earth. B) It is a thousand times more massive than the earth. C) It is a hundred times more massive than all the planets combined. D) It is about as massive as all the planets combined. E) It is a thousand times more massive than all the planets combine ...
Henry6SCI (H6SCIASTRO)
... A. Earth and the Sun. B. Earth and the Moon. C. Neptune and Pluto. D. Mars and Jupiter. 15. Daylight in the Northern Hemisphere lasts longer in summer than in winter, and the change in the length of day happens in a predictable pattern. Which statement correctly explains this condition of Earth's en ...
... A. Earth and the Sun. B. Earth and the Moon. C. Neptune and Pluto. D. Mars and Jupiter. 15. Daylight in the Northern Hemisphere lasts longer in summer than in winter, and the change in the length of day happens in a predictable pattern. Which statement correctly explains this condition of Earth's en ...
Study Guide - Experience Astronomy
... Axis -‐ the line around with the Earth (or any planetary body) rotates Day -‐ the amount of time it takes for the Earth to spin on its own axis one time The Galilean Moons -‐ four largest moons of Jupiter: Europa, Io, Callisto, and Ganymede Geocent ...
... Axis -‐ the line around with the Earth (or any planetary body) rotates Day -‐ the amount of time it takes for the Earth to spin on its own axis one time The Galilean Moons -‐ four largest moons of Jupiter: Europa, Io, Callisto, and Ganymede Geocent ...
Objection (Parallax)
... The biggest problem of studying Greek astronomy is the lack of the original works ...
... The biggest problem of studying Greek astronomy is the lack of the original works ...
Universe and Solar System
... development of thinking regarding the motion of planets and other objects as well as the Big Bang theory, 2) the size, composition and relative location of each planet from the Sun., 3.) the question of how scientists might determine the likely presence of life in the distant solar system, 4.) and w ...
... development of thinking regarding the motion of planets and other objects as well as the Big Bang theory, 2) the size, composition and relative location of each planet from the Sun., 3.) the question of how scientists might determine the likely presence of life in the distant solar system, 4.) and w ...
WARM-UP # 32 Which planets are the terrestrial planets and which
... In the frozen void it's a meteoroid. In the atmosphere it's a meteor. At the impact site it's a meteorite ...
... In the frozen void it's a meteoroid. In the atmosphere it's a meteor. At the impact site it's a meteorite ...
ESSR_HOS_Panspermia_V01
... humans owe our genesis and evolution to a continual rain of foreign microbes. It means, simply, that we might all be aliens. It's an idea that has been around [a long time], but which still struggles to gain strong support among most scientists. But two recent discoveries are breathing new life into ...
... humans owe our genesis and evolution to a continual rain of foreign microbes. It means, simply, that we might all be aliens. It's an idea that has been around [a long time], but which still struggles to gain strong support among most scientists. But two recent discoveries are breathing new life into ...
Our Solar System
... recorded temperature was on the continent of Antarctica (Vostok in July, 1983). The hottest recorded temperature was on the continent of Africa (Libya in September, 1922). Life: teeming with life. Planet is “just right” for life as we know it. No Rings Satellites: 1 Name: Moon ...
... recorded temperature was on the continent of Antarctica (Vostok in July, 1983). The hottest recorded temperature was on the continent of Africa (Libya in September, 1922). Life: teeming with life. Planet is “just right” for life as we know it. No Rings Satellites: 1 Name: Moon ...
10.1 PPT
... • Early astronomers were able to observe outer space by using the best instruments of the time, early telescopes. • With the development of more powerful telescopes in the 1920’s, suddenly more celestial bodies were discovered. • Celestial bodies is a general term for all the objects in the sky, in ...
... • Early astronomers were able to observe outer space by using the best instruments of the time, early telescopes. • With the development of more powerful telescopes in the 1920’s, suddenly more celestial bodies were discovered. • Celestial bodies is a general term for all the objects in the sky, in ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.