Useful Things to Study (#2)
... What is a dwarf planet? The destructive power of a collision with an asteroid or comet nucleus comes from the kinetic energy of the object hitting the Earth. Since kinetic energy is 1/2 m v2 , it goes up rapidly with the velocity of the impact. What are the three most abundant elements in the Earth’ ...
... What is a dwarf planet? The destructive power of a collision with an asteroid or comet nucleus comes from the kinetic energy of the object hitting the Earth. Since kinetic energy is 1/2 m v2 , it goes up rapidly with the velocity of the impact. What are the three most abundant elements in the Earth’ ...
Space Study Guide
... As technology increased, scientists made more and more observations that supported the Big Bang Model. 1. In 1929, Edwin Hubble observed that the spectral lines from other galaxies tended to always shift toward the red end of the spectrum. According to the Doppler Effect, causes this change of obser ...
... As technology increased, scientists made more and more observations that supported the Big Bang Model. 1. In 1929, Edwin Hubble observed that the spectral lines from other galaxies tended to always shift toward the red end of the spectrum. According to the Doppler Effect, causes this change of obser ...
X-RAY OBSERVATIONS OF SEYFERT GALAXIES The dawn of a …
... AND we should not underestimate the struggles/difficulties early thinkers had attempting to explain the universe within their various cultural, religious & technological environments…. ...
... AND we should not underestimate the struggles/difficulties early thinkers had attempting to explain the universe within their various cultural, religious & technological environments…. ...
Solutions
... Many of you identified the fact that we are orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is at the center of the solar system, as a contributing factor. This is irrelevant to phases. Suppose the sun were a very low-mass but very bright point of light orbiting the Earth. As it went around the Earth, it would still ...
... Many of you identified the fact that we are orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is at the center of the solar system, as a contributing factor. This is irrelevant to phases. Suppose the sun were a very low-mass but very bright point of light orbiting the Earth. As it went around the Earth, it would still ...
Lecture 4 - Orbits of the planets
... move together with the epicycle of Venus centered on a line between the Earth and the Sun • Then, Venus can never be the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth, so it can never have gibbous phases – no “full Venus”. ...
... move together with the epicycle of Venus centered on a line between the Earth and the Sun • Then, Venus can never be the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth, so it can never have gibbous phases – no “full Venus”. ...
Science at a Glance
... 3.E. 1.2 – Recognize that changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow indicate the apparent changing position of the Sun during the day although the patterns of the stars in the sky, to include the Sun, stay the same. ...
... 3.E. 1.2 – Recognize that changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow indicate the apparent changing position of the Sun during the day although the patterns of the stars in the sky, to include the Sun, stay the same. ...
Number of planets - Associazione Astrofili "Crab Nebula"
... A bit of history How did the Solar System form? The Working Group on Extrasolar Planets (WGESP) of the IAU defines as an extrasolar planet (shortened exoplanet) “…a body whose mass lies below the threshold value for the onset of deuterium thermo-nuclear fusion (which is about 13 Jupiter masses [MJ] ...
... A bit of history How did the Solar System form? The Working Group on Extrasolar Planets (WGESP) of the IAU defines as an extrasolar planet (shortened exoplanet) “…a body whose mass lies below the threshold value for the onset of deuterium thermo-nuclear fusion (which is about 13 Jupiter masses [MJ] ...
Document
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant (c) of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant (c) of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • ...
What are stars?
... - We know now that the stars in a constellation are not necessarily very close together, but appear to be due to our line of sight - Examples – Orion, Ursa Major (Big Dipper) ...
... - We know now that the stars in a constellation are not necessarily very close together, but appear to be due to our line of sight - Examples – Orion, Ursa Major (Big Dipper) ...
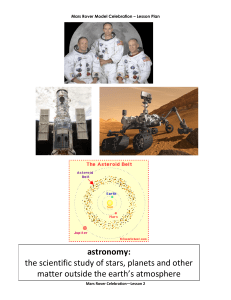
astronomy - Mars Rover Celebration
... Hubble Telescope. Astronomy involves learning about objects very far away. The Hubble telescope allows scientists to look at objects that are so far away it would take millions of years to reach them using our fastest spaceships. Astronomy also involves studying the planets. The next picture shows a ...
... Hubble Telescope. Astronomy involves learning about objects very far away. The Hubble telescope allows scientists to look at objects that are so far away it would take millions of years to reach them using our fastest spaceships. Astronomy also involves studying the planets. The next picture shows a ...
Slide 1
... gravitational collapse of a cloud (nebula) of dust and gas • As the nebula collapses, it forms a spinning disk (due to conservation of angular momentum) • The collapse releases gravitational energy, which heats the centre; this central hot portion forms a star • The outer, cooler particles suffer re ...
... gravitational collapse of a cloud (nebula) of dust and gas • As the nebula collapses, it forms a spinning disk (due to conservation of angular momentum) • The collapse releases gravitational energy, which heats the centre; this central hot portion forms a star • The outer, cooler particles suffer re ...
Sun: The Nearest Star
... It contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. It is a G2 type star. Its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and has a temperature of 6,000°C (11,000°F). The core has a temperature (15,000,000° C; 27,000,000° F) and pres ...
... It contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. It is a G2 type star. Its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and has a temperature of 6,000°C (11,000°F). The core has a temperature (15,000,000° C; 27,000,000° F) and pres ...
Topic 1 – Introduction to Earth`s Changing Environment
... radiation. The red shift also supports that the universe is still _________________. - The ___________ __________________ is about 4.6 billion years old - We live in the ________________ ________________, which is a spiral galaxy. Our location is 2/3 of the way out on the Orion arm. - Stars spend th ...
... radiation. The red shift also supports that the universe is still _________________. - The ___________ __________________ is about 4.6 billion years old - We live in the ________________ ________________, which is a spiral galaxy. Our location is 2/3 of the way out on the Orion arm. - Stars spend th ...
Basketball Earth
... Circumference of the Earth compared to the Earth Moon distance. The circumference of a circle is pi times the diameter. So 3.14 x 12700 is approximately 40,000km. The distance to the Moon is 384,000km – how do they compare? – about 10x Demonstrate the distance to the Moon by wrapping the string arou ...
... Circumference of the Earth compared to the Earth Moon distance. The circumference of a circle is pi times the diameter. So 3.14 x 12700 is approximately 40,000km. The distance to the Moon is 384,000km – how do they compare? – about 10x Demonstrate the distance to the Moon by wrapping the string arou ...
apparent retrograde motion - Indiana University Astronomy
... predictions made very accurate observations of positions (this was prior to the development of the telescope) ...
... predictions made very accurate observations of positions (this was prior to the development of the telescope) ...
ONLINE practice exam
... nearby universe to be 0.2 H atom per cubic meter. In this case what is the matter density parameter? (e) Using the information from this galaxy, and assuming that there is NO dark energy. What is the fate of the universe? (f) On average, how much closer were galaxies to each other at z=0.2 than toda ...
... nearby universe to be 0.2 H atom per cubic meter. In this case what is the matter density parameter? (e) Using the information from this galaxy, and assuming that there is NO dark energy. What is the fate of the universe? (f) On average, how much closer were galaxies to each other at z=0.2 than toda ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... Ancient astronomers could not detect stellar parallax • If Earth orbited the Sun, ancient astronomers believed that they would see differences in angular separation of stars as the Earth rotated around the Sun • Since they saw no changes in angular separation of the stars, they assumed the Earth wa ...
... Ancient astronomers could not detect stellar parallax • If Earth orbited the Sun, ancient astronomers believed that they would see differences in angular separation of stars as the Earth rotated around the Sun • Since they saw no changes in angular separation of the stars, they assumed the Earth wa ...
The Planets
... Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, moons, dwarf planets, an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, the asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas all orbit the sun. The nine planets that orbit the sun are (in ...
... Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, moons, dwarf planets, an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, the asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas all orbit the sun. The nine planets that orbit the sun are (in ...
The Earth & Beyond - Primary Resources
... My Very Easy Method Just Shows Us the Names of Planets. ...
... My Very Easy Method Just Shows Us the Names of Planets. ...
Heliocentric Model by Copernicus
... Why did Copernicus (1473-1543) think that the Earth and the other planets go around the Sun? How did Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) attempt to test the ideas of Copernicus? What paths do the planets follow as they move around the Sun? Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) What did Galileo (1564-1642) see in his tele ...
... Why did Copernicus (1473-1543) think that the Earth and the other planets go around the Sun? How did Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) attempt to test the ideas of Copernicus? What paths do the planets follow as they move around the Sun? Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) What did Galileo (1564-1642) see in his tele ...
Inquiry Plan, Year 5/6 - Owairoa Primary School
... centre of our solar system and that it has eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune (Pluto as a ‘dwarf planet’). They should understand that a moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet (Earth has one moon; Jupiter has four large moons and numerous smaller o ...
... centre of our solar system and that it has eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune (Pluto as a ‘dwarf planet’). They should understand that a moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet (Earth has one moon; Jupiter has four large moons and numerous smaller o ...
Lecture 1 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... When you look at an object 1 million light years away, you are looking at it 1 million years ago. The universe is thought to be 13.66 billion years old, so when you look back 12.7 billion years - are you looking back to a time when the universe was “young”. Cosmic evolution can be studied by looki ...
... When you look at an object 1 million light years away, you are looking at it 1 million years ago. The universe is thought to be 13.66 billion years old, so when you look back 12.7 billion years - are you looking back to a time when the universe was “young”. Cosmic evolution can be studied by looki ...
Extraterrestrial life

Extraterrestrial life is life that does not originate from Earth. It is also called alien life, or, if it is a sentient and/or relatively complex individual, an ""extraterrestrial"" or ""alien"" (or, to avoid confusion with the legal sense of ""alien"", a ""space alien""). These as-yet-hypothetical life forms range from simple bacteria-like organisms to beings with civilizations far more advanced than humanity. Although many scientists expect extraterrestrial life to exist, so far no unambiguous evidence for its existence exists.The science of extraterrestrial life is known as exobiology. The science of astrobiology also considers life on Earth as well, and in the broader astronomical context. Meteorites that have fallen to Earth have sometimes been examined for signs of microscopic extraterrestrial life. Since the mid-20th century, there has been an ongoing search for signs of extraterrestrial intelligence, from radios used to detect possible extraterrestrial signals, to telescopes used to search for potentially habitable extrasolar planets. It has also played a major role in works of science fiction. Over the years, science fiction works, especially Hollywood's involvement, has increased the public's interest in the possibility of extraterrestrial life. Some encourage aggressive methods to try to get in contact with life in outer space, whereas others argue that it might be dangerous to actively call attention to Earth.