The One Sigma Method
... To be market neutral and have your Delta as close to zero as possible, your short strikes to be an equal distance from 110 Adjust your short strikes farther and farther out from 110 until you get about a .68 to .79 credit price Remember, Keep your long strikes 2 points away from your short strikes . ...
... To be market neutral and have your Delta as close to zero as possible, your short strikes to be an equal distance from 110 Adjust your short strikes farther and farther out from 110 until you get about a .68 to .79 credit price Remember, Keep your long strikes 2 points away from your short strikes . ...
some process - LPD
... field of the removed node • But that doesn’t mean this is still the next field of the removed node • CAS doesn’t ensure the next field of the removed node is unchanged • It ensures the next field of the previous node is unchanged (this is also necessary) ...
... field of the removed node • But that doesn’t mean this is still the next field of the removed node • CAS doesn’t ensure the next field of the removed node is unchanged • It ensures the next field of the previous node is unchanged (this is also necessary) ...
Soln Ch 21 Futures intro
... The strategy that would take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity is a “reverse cash and carry.” A reverse cash and carry opportunity results when the following relationship does not hold true: F0 ≥ S0 (1+ C) If the futures price is less than the spot price plus the cost of carrying the goods to t ...
... The strategy that would take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity is a “reverse cash and carry.” A reverse cash and carry opportunity results when the following relationship does not hold true: F0 ≥ S0 (1+ C) If the futures price is less than the spot price plus the cost of carrying the goods to t ...
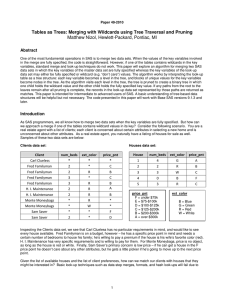
Tables As Trees: Merging with Wildcards Using Tree Traversal and Pruning
... Storing the Tree Because a tree structure is typically dynamic and can grow and shrink over time, programmers traditionally use dynamic memory allocation to store trees. The structure of a single node is determined by the programmer, and then nodes are created and destroyed on an as-needed basis dur ...
... Storing the Tree Because a tree structure is typically dynamic and can grow and shrink over time, programmers traditionally use dynamic memory allocation to store trees. The structure of a single node is determined by the programmer, and then nodes are created and destroyed on an as-needed basis dur ...
lecture1428550942
... First, the cost of accessing an item is orders of magnitude greater than any bookkeeping or calculating costs. ƒ Second, over and above with this higher cost, there are severe restrictions on access, depending on the external storage medium used: for example, items on a magnetic tape can be accessed ...
... First, the cost of accessing an item is orders of magnitude greater than any bookkeeping or calculating costs. ƒ Second, over and above with this higher cost, there are severe restrictions on access, depending on the external storage medium used: for example, items on a magnetic tape can be accessed ...
Jet Fuel Hedging questions
... the fluctuations in fuel prices. A jet fuel swap refers to an agreement between two parties which ensures that a floating (market) price is exchanged for a fixed price over a specific time period. Moreover, options, costless collars and call option spreads are other hedging strategies utilized by ca ...
... the fluctuations in fuel prices. A jet fuel swap refers to an agreement between two parties which ensures that a floating (market) price is exchanged for a fixed price over a specific time period. Moreover, options, costless collars and call option spreads are other hedging strategies utilized by ca ...
What is a B
... m non-null references to data blocks B0, B1, B2, . . . , Bm-1. The number of keys is one less than the number of non-null references. 4. The keys in a non-leaf node and the referenced blocks are ordered as: B0, p1, B1, p2, B2, . . . , pm-1, Bm-1 such that: • All data in block B0 correspond to keys t ...
... m non-null references to data blocks B0, B1, B2, . . . , Bm-1. The number of keys is one less than the number of non-null references. 4. The keys in a non-leaf node and the referenced blocks are ordered as: B0, p1, B1, p2, B2, . . . , pm-1, Bm-1 such that: • All data in block B0 correspond to keys t ...
Setting aside the debate on when the exact date of an interest rate
... companies. Companies have been able to issue bonds to investors at all‐time low interest rates. While this is a good deal for companies, it’s not a great outcome for investors, who are forced to take increasingly lower compensation for the risk of lending this money. The yield on the Barclays ...
... companies. Companies have been able to issue bonds to investors at all‐time low interest rates. While this is a good deal for companies, it’s not a great outcome for investors, who are forced to take increasingly lower compensation for the risk of lending this money. The yield on the Barclays ...
Risk
... • There are S possible states indexed by s=0, 1, …, S-1. • A pure security (or say an Arrow-Debreu asset) stays in each state, paying $1 if a given state occurs and nothing if any other state occurs at the end of the period • Let Пs denote the price of the Arrow-Debreu security associated with s, i. ...
... • There are S possible states indexed by s=0, 1, …, S-1. • A pure security (or say an Arrow-Debreu asset) stays in each state, paying $1 if a given state occurs and nothing if any other state occurs at the end of the period • Let Пs denote the price of the Arrow-Debreu security associated with s, i. ...
binary search tree
... due to their recursive nature, trees are naturally handled recursively to count the number of nodes in a binary tree: BASE CASE: if the tree is empty, number of nodes is 0 RECURSIVE: otherwise, number of nodes is (# nodes in left subtree) + (# nodes in right subtree) + 1 for the root ...
... due to their recursive nature, trees are naturally handled recursively to count the number of nodes in a binary tree: BASE CASE: if the tree is empty, number of nodes is 0 RECURSIVE: otherwise, number of nodes is (# nodes in left subtree) + (# nodes in right subtree) + 1 for the root ...
Fixed Income in a Rising Rate Enviornment
... levels have more room to tighten. This may help reduce the overall yield increase if spreads tighten. The result is less of a decline in the prices of non-government bonds. However, if credit spreads are tight at the start of the rising rate period, there is little potential offset to falling bond p ...
... levels have more room to tighten. This may help reduce the overall yield increase if spreads tighten. The result is less of a decline in the prices of non-government bonds. However, if credit spreads are tight at the start of the rising rate period, there is little potential offset to falling bond p ...
Download attachment
... realizations of the asset. Realized gains and losses provide historical information on the variance in asset valuation. The mixed-measurement model, in which assets are measured using a variety of measurement bases such as cost, lower of cost and current market value, fair value2, will also produce ...
... realizations of the asset. Realized gains and losses provide historical information on the variance in asset valuation. The mixed-measurement model, in which assets are measured using a variety of measurement bases such as cost, lower of cost and current market value, fair value2, will also produce ...
20Tall
... A leaf is a node with no children. In the tree above, the nodes with 4, 5, and 6 are leafs. All nodes that are not leaves are called the internal nodes of a tree, which are 1, 2, and 3 above. A leaf node could later grow a nonempty tree as a child. That leaf node would then become an internal node. ...
... A leaf is a node with no children. In the tree above, the nodes with 4, 5, and 6 are leafs. All nodes that are not leaves are called the internal nodes of a tree, which are 1, 2, and 3 above. A leaf node could later grow a nonempty tree as a child. That leaf node would then become an internal node. ...
Lattice model (finance)

For other meanings, see lattice model (disambiguation)In finance, a lattice model [1] is a technique applied to the valuation of derivatives, where, because of path dependence in the payoff, 1) a discretized model is required and 2) Monte Carlo methods fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise. For equity options, a typical example would be pricing an American option, where a decision as to option exercise is required at ""all"" times (any time) before and including maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as Black Scholes, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is on the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par.