Biochemistry
... • Molecules are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. (smallest combination that cannot be divided without changing its chemical and ...
... • Molecules are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. (smallest combination that cannot be divided without changing its chemical and ...
The Central Dogma – Protein Synthesis
... – contains the “genetic library” encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA • code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins • determines which specific proteins are to be made in a particular cell type –determines the function of that cell • The synthesis of proteins involves: – ...
... – contains the “genetic library” encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA • code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins • determines which specific proteins are to be made in a particular cell type –determines the function of that cell • The synthesis of proteins involves: – ...
The Central Dogma – Protein Synthesis
... – contains the “genetic library” encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA • code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins • determines which specific proteins are to be made in a particular cell type –determines the function of that cell • The synthesis of proteins involves: – ...
... – contains the “genetic library” encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA • code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins • determines which specific proteins are to be made in a particular cell type –determines the function of that cell • The synthesis of proteins involves: – ...
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... biomolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids and fibrous and globular proteins) and their interrelated functioning in a biological system. Biological membranes and transport will be further discussed. Bioenergetics and oxidative phosphorylations will be covered. Additionally basic concepts of me ...
... biomolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids and fibrous and globular proteins) and their interrelated functioning in a biological system. Biological membranes and transport will be further discussed. Bioenergetics and oxidative phosphorylations will be covered. Additionally basic concepts of me ...
Repair of Broken Chromosomes and Maintenance of Chromosome
... Even when DSBs are “perfectly” repaired by gene conversion, the increase in frequency of repair leads to a dramatic increase in the rate of mutagenesis. The increased rate of mutation may directly contribute to the accumulation of additional mutations in precancerous cells. ...
... Even when DSBs are “perfectly” repaired by gene conversion, the increase in frequency of repair leads to a dramatic increase in the rate of mutagenesis. The increased rate of mutation may directly contribute to the accumulation of additional mutations in precancerous cells. ...
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... biomolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids and fibrous and globular proteins) and their interrelated functioning in a biological system. Biological membranes and transport will be further discussed. Bioenergetics and oxidative phosphorylations will be covered. Additionally basic concepts of me ...
... biomolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids and fibrous and globular proteins) and their interrelated functioning in a biological system. Biological membranes and transport will be further discussed. Bioenergetics and oxidative phosphorylations will be covered. Additionally basic concepts of me ...
syllabus - Hudson Area Schools
... an individual, and a single gene can influence more than one trait. Before a cell divides, this genetic information must be copied and apportioned evenly into the daughter cells. B4.2 DNA The genetic information encoded in DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. Genes a ...
... an individual, and a single gene can influence more than one trait. Before a cell divides, this genetic information must be copied and apportioned evenly into the daughter cells. B4.2 DNA The genetic information encoded in DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. Genes a ...
Genetic Control ms
... ref to complementary/explained with ref to H bonds; R complementary in wrong context (free) nucleotides pair with both, strands/each strand/polynucleotides/sides; both strands act as templates; to produce two DNA molecules that are identical to one another; [max 3] (c) (all nuclei/cells) are genetic ...
... ref to complementary/explained with ref to H bonds; R complementary in wrong context (free) nucleotides pair with both, strands/each strand/polynucleotides/sides; both strands act as templates; to produce two DNA molecules that are identical to one another; [max 3] (c) (all nuclei/cells) are genetic ...
Biological Molecules
... fingernails; and let you see (the lens of your eye is pure crystallised protein). ...
... fingernails; and let you see (the lens of your eye is pure crystallised protein). ...
PowerPoint
... polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, and cellulose), and lipid (?, with different synthesizing method) •Macromolecules are responsible for most of the form and function in living ystems. They are, however, generated by polymerization of small organic molecules, a fundamental principle of cellular chem ...
... polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, and cellulose), and lipid (?, with different synthesizing method) •Macromolecules are responsible for most of the form and function in living ystems. They are, however, generated by polymerization of small organic molecules, a fundamental principle of cellular chem ...
The interaction of DNA gyrase with microcin B17
... agents and the withdrawal of big pharmaceutical companies from anti-bacterial research means that the potential for crisis in infectious diseases has increased. Against this background it is essential that academia steps up its efforts in drug discovery, specifically identifying new lead molecules a ...
... agents and the withdrawal of big pharmaceutical companies from anti-bacterial research means that the potential for crisis in infectious diseases has increased. Against this background it is essential that academia steps up its efforts in drug discovery, specifically identifying new lead molecules a ...
Bio Sem I review
... Energy on earth comes from the sun and is transferred to plants and then to animals. Much is lost as heat. Respiration occurs primarily in the mitochondria of cells of plants and animals. It involves the breaking down of glucose in the presence of oxygen. (aerobic) The products of this reaction are ...
... Energy on earth comes from the sun and is transferred to plants and then to animals. Much is lost as heat. Respiration occurs primarily in the mitochondria of cells of plants and animals. It involves the breaking down of glucose in the presence of oxygen. (aerobic) The products of this reaction are ...
Cell DNA based assays: Example on how to measure the
... subsequently measured using DNA measurements kits (e.g. Quant-‐iT™ PicoGreen® dsDNA Reagent and Kits or CyQUANT™ Cell Proliferation Assay – see note n°5 below, both from Invitrogen) following ...
... subsequently measured using DNA measurements kits (e.g. Quant-‐iT™ PicoGreen® dsDNA Reagent and Kits or CyQUANT™ Cell Proliferation Assay – see note n°5 below, both from Invitrogen) following ...
9783941216242_Leseprobe02
... labelling different proteins with diverse emitting autofluorescent proteins to study their localisation and interaction via Foerster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET). A possible energy transfer from a donor to an acceptor chromophore via FRET can be detected in different ways. One established method ...
... labelling different proteins with diverse emitting autofluorescent proteins to study their localisation and interaction via Foerster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET). A possible energy transfer from a donor to an acceptor chromophore via FRET can be detected in different ways. One established method ...
Document
... development or disease. Be sure to explain why migration is important in this event and document your sources properly. Your answer should be no more than a paragraph, with sources documented below, and submitted through Blackboard or to your TA by 5pm tomorrow. Examples from the homework will be se ...
... development or disease. Be sure to explain why migration is important in this event and document your sources properly. Your answer should be no more than a paragraph, with sources documented below, and submitted through Blackboard or to your TA by 5pm tomorrow. Examples from the homework will be se ...
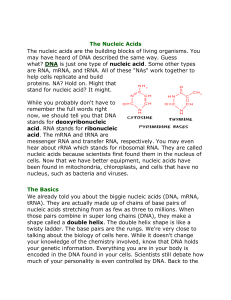
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... messenger RNA and transfer RNA, respectively. You may even hear about rRNA which stands for ribosomal RNA. They are called nucleic acids because scientists first found them in the nucleus of cells. Now that we have better equipment, nucleic acids have been found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and ce ...
... messenger RNA and transfer RNA, respectively. You may even hear about rRNA which stands for ribosomal RNA. They are called nucleic acids because scientists first found them in the nucleus of cells. Now that we have better equipment, nucleic acids have been found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and ce ...
Cells: Chapt. 5 & Chapt. 4: Pgs. 70-75
... • The organelles (chloroplasts and mitochondria) resemble bacteria in size and structure. • These organelles each contain a small amount of DNA but lack a nuclear membrane. • Each has the capability of self-replication. They reproduce by binary fission. • They make their own proteins. • During prote ...
... • The organelles (chloroplasts and mitochondria) resemble bacteria in size and structure. • These organelles each contain a small amount of DNA but lack a nuclear membrane. • Each has the capability of self-replication. They reproduce by binary fission. • They make their own proteins. • During prote ...
Simulating Protein Synthesis
... Post Lab Questions: List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
... Post Lab Questions: List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
Cells Study Guide KEY
... calculated that a bee should not be able to fly. Cell biologists have since found that the muscles which control the wings of the bee have a huge number of mitochondria. Explain why this discovery may help explain why bees are able to fly. -the mitochondria provide energy for cells- the cells of a b ...
... calculated that a bee should not be able to fly. Cell biologists have since found that the muscles which control the wings of the bee have a huge number of mitochondria. Explain why this discovery may help explain why bees are able to fly. -the mitochondria provide energy for cells- the cells of a b ...
What is BIOLOGY?
... Be able to ID the following in a picture: DNA, RNA, ATP, amino acid, nucleotide, phospholipid, glucose Which macromolecules are important in making cell membranes? ...
... Be able to ID the following in a picture: DNA, RNA, ATP, amino acid, nucleotide, phospholipid, glucose Which macromolecules are important in making cell membranes? ...
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
... and other organelles. •The Cytoskeleton Eukaryote cells have a cytoskeleton of microscopic protein fibers that provide the structural framework for the cell and its organelles. There are three different kinds of cytoskeleton fibers: actin fibers, microtubules, and intermediate fibers. ...
... and other organelles. •The Cytoskeleton Eukaryote cells have a cytoskeleton of microscopic protein fibers that provide the structural framework for the cell and its organelles. There are three different kinds of cytoskeleton fibers: actin fibers, microtubules, and intermediate fibers. ...
Mitosis
... • Asexual Reproduction: A single cell or group of cells each duplicates its genetic material and then splits into two new genetically identical cells. – The offspring are genetically identical ...
... • Asexual Reproduction: A single cell or group of cells each duplicates its genetic material and then splits into two new genetically identical cells. – The offspring are genetically identical ...
Slide 1
... • How are proteins organized and how is their shape important to their function? • How are DNA similar and how are they different? ...
... • How are proteins organized and how is their shape important to their function? • How are DNA similar and how are they different? ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.