Genetics Syllabus
... Cultural materials are stored in 813 Need to purchase: seeds, soil, fly cultures ...
... Cultural materials are stored in 813 Need to purchase: seeds, soil, fly cultures ...
Microbiology Study Guide – Exam #2
... This is a list of general topics you should be prepared to answer questions on for each chapter. This guide is NOT what you should study but rather is a guide to help organize your studying of the material listed. Your actual studying should involve the textbook, Powerpoint slides, your notes and ot ...
... This is a list of general topics you should be prepared to answer questions on for each chapter. This guide is NOT what you should study but rather is a guide to help organize your studying of the material listed. Your actual studying should involve the textbook, Powerpoint slides, your notes and ot ...
CyberPDX Lesson Plan
... o Students will model the process of transcription and translation. Vocabulary: DNA, RNA, Protein, Nucleus, Transcription, Translation, Amino Acid, Base Pair, Sense Strand, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, mutation, Anti-sense Strand, Codon Prior Knowledge: Students will know the structure and function of DNA, the ...
... o Students will model the process of transcription and translation. Vocabulary: DNA, RNA, Protein, Nucleus, Transcription, Translation, Amino Acid, Base Pair, Sense Strand, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, mutation, Anti-sense Strand, Codon Prior Knowledge: Students will know the structure and function of DNA, the ...
Day 2 (Jan. 23) Scribe Notes
... We have been describing the cellular machinery of eukaryotes, that is, those organisms whose cells have a “true nucleus”. Prokaryotes (such as bacteria) do not have nuclei or ribosomes. Moreover, their DNA includes no introns. This may help them evolve faster by causing more variation among their ge ...
... We have been describing the cellular machinery of eukaryotes, that is, those organisms whose cells have a “true nucleus”. Prokaryotes (such as bacteria) do not have nuclei or ribosomes. Moreover, their DNA includes no introns. This may help them evolve faster by causing more variation among their ge ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... But… How does the information get from the DNA to the cytoplasm? mRNA ...
... But… How does the information get from the DNA to the cytoplasm? mRNA ...
Questions - Humble ISD
... Did you memorize or learn about DNA 1. What is the shape of DNA? Who determined this shape? 2. What biomolecule does DNA belong to? 3. What is the monomer of DNA. 4. What are the 3 parts of the monomer? 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base ...
... Did you memorize or learn about DNA 1. What is the shape of DNA? Who determined this shape? 2. What biomolecule does DNA belong to? 3. What is the monomer of DNA. 4. What are the 3 parts of the monomer? 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base ...
Lecture 10: Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA)
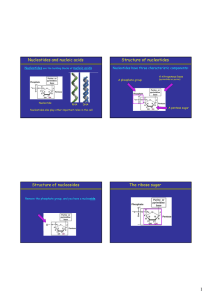
... A nucleotide is formed in the cell when a base attaches to the 1' carbon of the sugar and a phosphate attaches to the 5' carbon of the same sugar . ...
... A nucleotide is formed in the cell when a base attaches to the 1' carbon of the sugar and a phosphate attaches to the 5' carbon of the same sugar . ...
Ch 10
... diverged so much during evolutionary time that the functions of their encoded proteins are now substantially different • A particular exon within a gene could be duplicated on one chromosome and deleted from the homologous chromosome ...
... diverged so much during evolutionary time that the functions of their encoded proteins are now substantially different • A particular exon within a gene could be duplicated on one chromosome and deleted from the homologous chromosome ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... d. The type of RNA that will be transcribed is _____________ e. Where does the mRNA go after it is transcribed? f. ...
... d. The type of RNA that will be transcribed is _____________ e. Where does the mRNA go after it is transcribed? f. ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
... • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
DNA Mutations
... errors in replication, transcription, or cell division. • External factors can also cause mutations. • These mistakes could be good or bad. ...
... errors in replication, transcription, or cell division. • External factors can also cause mutations. • These mistakes could be good or bad. ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)– part of the ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) Messenger RNA (mRNA)– sequence translated into protein sequence. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) – involved in splicing (spliceosome) Micro RNA (mi RNA) – small RNA complementary to mRNA that inhibits translation of the mRNA – Small interferin ...
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)– part of the ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) Messenger RNA (mRNA)– sequence translated into protein sequence. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) – involved in splicing (spliceosome) Micro RNA (mi RNA) – small RNA complementary to mRNA that inhibits translation of the mRNA – Small interferin ...
Nucleotides and nucleic acids Structure of nucleotides Structure of
... DNA strands • The antiparallel strands of DNA are not identical, but are complementary. • This means that they are positioned to align complementary base pairs: C with G, and A with T. • So you can predict the sequence of one strand given the sequence of its complement. • Useful for information sto ...
... DNA strands • The antiparallel strands of DNA are not identical, but are complementary. • This means that they are positioned to align complementary base pairs: C with G, and A with T. • So you can predict the sequence of one strand given the sequence of its complement. • Useful for information sto ...
DNA
... • These beads pack together, forming nucleosomes. • These coil to make chromatin • When the chromatin (stringy DNA) coils it make a chromosome ...
... • These beads pack together, forming nucleosomes. • These coil to make chromatin • When the chromatin (stringy DNA) coils it make a chromosome ...
DNA Technology
... genetic abnormalities seen in 50 major types of cancer. Be able to create drugs that are much more effective and cause fewer side effects than those available today. NIH (National Institute of Health) is striving to cut the cost of sequencing an individual’s genome to $1,000 or less. Having one’s co ...
... genetic abnormalities seen in 50 major types of cancer. Be able to create drugs that are much more effective and cause fewer side effects than those available today. NIH (National Institute of Health) is striving to cut the cost of sequencing an individual’s genome to $1,000 or less. Having one’s co ...
How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell
... How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, ...
... How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, ...
Cell Reproduction
... A man has a discolored area on the back of his hand. The doctor has assured him it is a harmless body cell mutation. Explain why the mutation probably will not appear in his children. This is a body cell mutation. If the mutation had appeared in an egg or sperm, a child that developed from the sex c ...
... A man has a discolored area on the back of his hand. The doctor has assured him it is a harmless body cell mutation. Explain why the mutation probably will not appear in his children. This is a body cell mutation. If the mutation had appeared in an egg or sperm, a child that developed from the sex c ...
Biology EOC Words for Pages 64-80, Teacher Key Codominance
... Gene Expression- proteins are made based on the information encoded in DNA. Also known as protein synthesis. Translation- process that converts or translates a mRNA message into a polypeptide (one or more makes up a protein). Transcription- process of copying a sequence of DNA to produce a complimen ...
... Gene Expression- proteins are made based on the information encoded in DNA. Also known as protein synthesis. Translation- process that converts or translates a mRNA message into a polypeptide (one or more makes up a protein). Transcription- process of copying a sequence of DNA to produce a complimen ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... A gene is a sequence of ____ DNA on a chromosome ___________ that codes for one protein ________. **Remember, not all of the ____ DNA codes for proteins. The parts that do are called ______, genes the parts that don’t are called non-coding regions ___________________. ...
... A gene is a sequence of ____ DNA on a chromosome ___________ that codes for one protein ________. **Remember, not all of the ____ DNA codes for proteins. The parts that do are called ______, genes the parts that don’t are called non-coding regions ___________________. ...
DNA and RNA - Joshua ISD
... Do these terms come to mind?? DNA contains genes or traits Genetic codes to make proteins which keep us alive! ...
... Do these terms come to mind?? DNA contains genes or traits Genetic codes to make proteins which keep us alive! ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.