GMO answerkey
... historical developments in biology that were “controversial” at the time (e.g., vaccination) and current “controversial” developments (e.g., embryonic stem cells). This is another interesting question, but one that is broad in its scope. I do not assign it in most classes. When I do, I have differen ...
... historical developments in biology that were “controversial” at the time (e.g., vaccination) and current “controversial” developments (e.g., embryonic stem cells). This is another interesting question, but one that is broad in its scope. I do not assign it in most classes. When I do, I have differen ...
Chapter 4
... – Adenine and thymine always bind together. – Cytosine and guanine always bind together. ...
... – Adenine and thymine always bind together. – Cytosine and guanine always bind together. ...
41) A Closer Look at Natural Selection
... 1. Selection can act only on existing variations 2. Evolution is limited by historical constraints 3. Adaptations are often compromises (see Fig. 23.19, next slide) 4. Chance, natural selection, and the environment interact ...
... 1. Selection can act only on existing variations 2. Evolution is limited by historical constraints 3. Adaptations are often compromises (see Fig. 23.19, next slide) 4. Chance, natural selection, and the environment interact ...
Corporate Profile
... fitness is defined in the context of the environment in which individuals live, mate, and reproduce ...
... fitness is defined in the context of the environment in which individuals live, mate, and reproduce ...
Processes of Evolution
... entire collection of alleles for a given trait throughout a given population. • The word for all genes for all traits in an individual or population is genome. ...
... entire collection of alleles for a given trait throughout a given population. • The word for all genes for all traits in an individual or population is genome. ...
Skeletal Dwarfism - Info on this condition
... To be more precise, according to our data dogs, which are homozygous (affected) for the SD2 allele, have ~6 cm less shoulder height on average compared to other dogs.” What do I do if I have a dog or bitch DNA tested as a carrier or affected with SDS?. If the other factors of your Labrador are all t ...
... To be more precise, according to our data dogs, which are homozygous (affected) for the SD2 allele, have ~6 cm less shoulder height on average compared to other dogs.” What do I do if I have a dog or bitch DNA tested as a carrier or affected with SDS?. If the other factors of your Labrador are all t ...
Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Finding the genes in
... 1. Introduction (who said annotating prokaryotic genomes is easy?) ...
... 1. Introduction (who said annotating prokaryotic genomes is easy?) ...
Give priority to secured access ThE DIgITAl DNA TEchNology®
... Every digital component can be identified uniquely. This quality is partly used by manufacturers and operating systems editors; however Login People® relies on it in order to create a new approach for IT security. Using this technology, complex equipment can now be identified through their component ...
... Every digital component can be identified uniquely. This quality is partly used by manufacturers and operating systems editors; however Login People® relies on it in order to create a new approach for IT security. Using this technology, complex equipment can now be identified through their component ...
The Process Whereby Your Genes Make Your Proteins
... carboxyl group (COOH or COO-), which is what makes a compound an acid (therefore the name “amino acid”). Note also that they all also have a side chain (also called an organic group, an R group, or a functional group), and that each amino acid’s side chain is different from the other amino acids’ si ...
... carboxyl group (COOH or COO-), which is what makes a compound an acid (therefore the name “amino acid”). Note also that they all also have a side chain (also called an organic group, an R group, or a functional group), and that each amino acid’s side chain is different from the other amino acids’ si ...
How Relevant is the Escherichia coli UvrABC Model for Excision
... system responsible for the preferential repair of UVinduced CPDs from the transcribed strand of active genes (Venema et al. 1990a, for a review on preferential repair, see e.g. Smith and Mellon, 1990). The subpathway dealing with the slower and less-complete removal of lesions from the genome overal ...
... system responsible for the preferential repair of UVinduced CPDs from the transcribed strand of active genes (Venema et al. 1990a, for a review on preferential repair, see e.g. Smith and Mellon, 1990). The subpathway dealing with the slower and less-complete removal of lesions from the genome overal ...
Statistically Significant Patterns in DNA Sequences
... Such motifs can be found in sequences using string search. Sonja Prohaska ...
... Such motifs can be found in sequences using string search. Sonja Prohaska ...
An introduction to population genetics
... genetics were all amassing evidence that Darwin’s gradualist theory of evolution by natural selection was both theoretically and empirically feasible, and that evidence for its influence was everywhere in nature. What was the contribution of population genetics to this slow revolution? This is an ar ...
... genetics were all amassing evidence that Darwin’s gradualist theory of evolution by natural selection was both theoretically and empirically feasible, and that evidence for its influence was everywhere in nature. What was the contribution of population genetics to this slow revolution? This is an ar ...
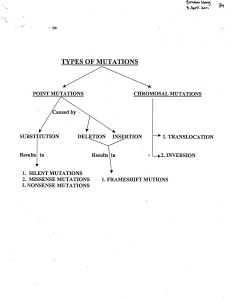
CHROMOSAL MUTATIONS SUBSTITUTION
... stop codon is produced, and the fragment may be digested by the proteases. ' Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell. ...
... stop codon is produced, and the fragment may be digested by the proteases. ' Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell. ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Nijmegen breakage syndrome Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Cytogenetics Inborn conditions - Lymphocyte cultures often show low mitotic index. - Structural chromosome aberrations are observed in 10-30% of metaphases; most of the rearrangements occur in or between chromosomes 7 and 14, at bands 7p13, 7q35, 14q11, and 14q32, as in AT; these bands contain immun ...
... Cytogenetics Inborn conditions - Lymphocyte cultures often show low mitotic index. - Structural chromosome aberrations are observed in 10-30% of metaphases; most of the rearrangements occur in or between chromosomes 7 and 14, at bands 7p13, 7q35, 14q11, and 14q32, as in AT; these bands contain immun ...
igcse_enzyme_ppt
... Cheese is made by adding an enzyme called rennet after bacteria have produced lactic acid ...
... Cheese is made by adding an enzyme called rennet after bacteria have produced lactic acid ...
RNA Molecules: More than Mere Information Intermediaries
... only poorly, if at all, leading to increased virulence gene expression. However, among other pathogens, RNA molecules rather than repressor proteins directly sense temperature changes. For example, thermal control over lcrF, the main transcriptional virulence regulator in Yersinia pestis, appears to ...
... only poorly, if at all, leading to increased virulence gene expression. However, among other pathogens, RNA molecules rather than repressor proteins directly sense temperature changes. For example, thermal control over lcrF, the main transcriptional virulence regulator in Yersinia pestis, appears to ...
History of Biological Taxonomy
... Classification solely on shared derived characters (=synapomorphies) ...
... Classification solely on shared derived characters (=synapomorphies) ...
KAPA Blood Direct PCR from Whole Blood
... Of great interest was the amplification of Huntington disease samples. These samples contain a variable number of CAG repeats, which could be amplified directly with the KAPA Blood PCR Kit B. The highest repeat we tested was 18/53 but it will be interesting to see how long of a CAG repeat can be amp ...
... Of great interest was the amplification of Huntington disease samples. These samples contain a variable number of CAG repeats, which could be amplified directly with the KAPA Blood PCR Kit B. The highest repeat we tested was 18/53 but it will be interesting to see how long of a CAG repeat can be amp ...
Metabolic Pathways
... • Controlling number of enzyme molecules in cell • Keeping reactions (and enzymes) in compartments eg. Mitochondria or lysosome. • Changing enzyme shape (most effective) ...
... • Controlling number of enzyme molecules in cell • Keeping reactions (and enzymes) in compartments eg. Mitochondria or lysosome. • Changing enzyme shape (most effective) ...
recombinant DNA - interactive eBook
... DNA fragments can be rejoined, by DNA ligase in bacterial plasmids, to form a new molecule of recombinant DNA (rDNA). ...
... DNA fragments can be rejoined, by DNA ligase in bacterial plasmids, to form a new molecule of recombinant DNA (rDNA). ...
Lecture 2 - CSB@Pitt
... • DNA is randomly fragmented followed by size selection • Adapters are ligated at each end so that the fragment can bind to the flow cell surface • Each single fragment is amplified in place with “bridge amplification” • There are 4 reversible terminators which are added at the same time • Locations ...
... • DNA is randomly fragmented followed by size selection • Adapters are ligated at each end so that the fragment can bind to the flow cell surface • Each single fragment is amplified in place with “bridge amplification” • There are 4 reversible terminators which are added at the same time • Locations ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.