Use of a single primer to fluorescently label selective amplified
... produces a population of anonymous DNA fragments with known ends. Selective primers complementary to the adaptors with additional 3′ nucleotides are then used to amplify specific subsets of the modified fragments under stringent PCR conditions. Typically, the resulting AFLP profiles are separated us ...
... produces a population of anonymous DNA fragments with known ends. Selective primers complementary to the adaptors with additional 3′ nucleotides are then used to amplify specific subsets of the modified fragments under stringent PCR conditions. Typically, the resulting AFLP profiles are separated us ...
Macromolecules Packet File
... Sugars - Building Blocks of Carbohydrates Sugars - Building Blocks of Carbohydrates Sugars are the building blocks of carbohydrates. They are literally hydrates of carbon, having the general formula "Cn(H2O)n". Sugars are burned (oxidized) to release energy in cellular respiration and they play an i ...
... Sugars - Building Blocks of Carbohydrates Sugars - Building Blocks of Carbohydrates Sugars are the building blocks of carbohydrates. They are literally hydrates of carbon, having the general formula "Cn(H2O)n". Sugars are burned (oxidized) to release energy in cellular respiration and they play an i ...
Genomics Bioinformatics Medicine. Institute of Medicine, October 15, 2002, Washington DC
... GCTGTATGACTAGAAGATCGAT GCTGTATGACGAGAAGATCGAT • Individual’s genomes differ from each other by 0.1% • There are 3 million polymorphic sites in the human genome • SNPs an be used for identification • SNPs can be used for diagnosis of disease ...
... GCTGTATGACTAGAAGATCGAT GCTGTATGACGAGAAGATCGAT • Individual’s genomes differ from each other by 0.1% • There are 3 million polymorphic sites in the human genome • SNPs an be used for identification • SNPs can be used for diagnosis of disease ...
SouthernHybridization - University of Hawaii
... • Detect PDI protein in wild type plants. • In mutant plants, determine the effect of the T-DNA insert on the expression of the PDI gene through movement or deletion of PDI protein band. ...
... • Detect PDI protein in wild type plants. • In mutant plants, determine the effect of the T-DNA insert on the expression of the PDI gene through movement or deletion of PDI protein band. ...
How cells use DNA, part 1: TRANSCRIPTION
... comes to mind is the process by which we take ideas expressed in one language, & make them intelligible in another language. Often this means a change of script, from one we don’t understand to another we can read. ...
... comes to mind is the process by which we take ideas expressed in one language, & make them intelligible in another language. Often this means a change of script, from one we don’t understand to another we can read. ...
Frequency-Dependent Selection on a Polygenic Trait
... FDS depends on the number of loci and the distribution of their effects. Models based on popular symmetry assumptions, such as equal locus effects or symmetric selection, are often not representative (they maintain more polymorphism). Linkage becomes important only if tight. It produces clustering o ...
... FDS depends on the number of loci and the distribution of their effects. Models based on popular symmetry assumptions, such as equal locus effects or symmetric selection, are often not representative (they maintain more polymorphism). Linkage becomes important only if tight. It produces clustering o ...
Functional Non-Coding DNA
... within mRNA, by several molecular pathways • Micro-RNAs base-pair with complementary sequences within mRNA molecules, often in 3’ or 5’ UTR. • miRNA binding usually results in gene repression either via translational stalling or by triggering mRNA degradation ...
... within mRNA, by several molecular pathways • Micro-RNAs base-pair with complementary sequences within mRNA molecules, often in 3’ or 5’ UTR. • miRNA binding usually results in gene repression either via translational stalling or by triggering mRNA degradation ...
Cloning and characterization in Escherichia coli of the gene
... Transcription is a major event for gene expression. RNA polymerase plays the primary role in this process. Although core RNA polymerase of bacteria is potentially able to elongate RNA chain, speci¢c initiation of transcription requires an additional factor, a sigma factor, which binds to core RNA po ...
... Transcription is a major event for gene expression. RNA polymerase plays the primary role in this process. Although core RNA polymerase of bacteria is potentially able to elongate RNA chain, speci¢c initiation of transcription requires an additional factor, a sigma factor, which binds to core RNA po ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... between the hydrogen atom on the amine group and the oxygen atom on the carboxyl group. A) quintary B) primary C) tertiary D) secondary E) quaternary ...
... between the hydrogen atom on the amine group and the oxygen atom on the carboxyl group. A) quintary B) primary C) tertiary D) secondary E) quaternary ...
ENZYME: an essential catalyst
... Isoenzymes have a different amino acid sequence and might be distinguished by their optimal pH, kinetic properties or immunologically. • Isoenzyme and isozyme are homologous proteins. • Furthermore, the normal physiological reaction an enzyme catalyzes may not be the same as under artificial conditi ...
... Isoenzymes have a different amino acid sequence and might be distinguished by their optimal pH, kinetic properties or immunologically. • Isoenzyme and isozyme are homologous proteins. • Furthermore, the normal physiological reaction an enzyme catalyzes may not be the same as under artificial conditi ...
Nuclear Matrix Proteins and Nuclear Targeting
... 4. Matrin Cyp (cyclophilin) a ~88 kDa protein that contains the complete cyclophilin protein sequence at the N-T and SR repeats - characteristic of splicing factors – within the carboxyl half. The protein has peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase activity and co-localizes with splicing factor-rich nucl ...
... 4. Matrin Cyp (cyclophilin) a ~88 kDa protein that contains the complete cyclophilin protein sequence at the N-T and SR repeats - characteristic of splicing factors – within the carboxyl half. The protein has peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase activity and co-localizes with splicing factor-rich nucl ...
Curriculum Vitae - Genomic Sciences Training Program
... available, none are well-suited for use in genetically-uncharacterized organisms. Because of this limitation, I have an equally matched interest in developing and implementing suitable technologies able to acquire genotypes from individuals in natural populations. In my doctoral thesis, I developed ...
... available, none are well-suited for use in genetically-uncharacterized organisms. Because of this limitation, I have an equally matched interest in developing and implementing suitable technologies able to acquire genotypes from individuals in natural populations. In my doctoral thesis, I developed ...
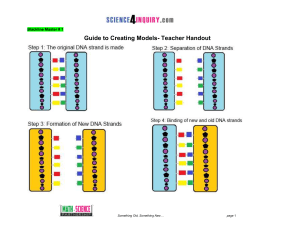
Activity Name - Science4Inquiry.com
... Inversion Mutation: reverse one section of bases (a whole gene) Original Strand: ...
... Inversion Mutation: reverse one section of bases (a whole gene) Original Strand: ...
DNA Testing - Who Murdered Robert Wone
... known for many years that a single germ (bacterial cell or virus) contaminating a wound can produce a massive infection. Similarly, a DNA molecule can contaminate (infect) a PCR and become a significant problem. The ability of small amounts of DNA to produce false and misleading results is well-know ...
... known for many years that a single germ (bacterial cell or virus) contaminating a wound can produce a massive infection. Similarly, a DNA molecule can contaminate (infect) a PCR and become a significant problem. The ability of small amounts of DNA to produce false and misleading results is well-know ...
Translation Study Guide
... nucleotides - the building blocks of DNA and RNA molecules that contain the cell’s genetic code. Adenosine, cytidine, guanosine, thymidine, and uridine are all nucleotides. polypeptide chain – the long chain of amino acids that is created during translation. A polypeptide chain becomes a protein whe ...
... nucleotides - the building blocks of DNA and RNA molecules that contain the cell’s genetic code. Adenosine, cytidine, guanosine, thymidine, and uridine are all nucleotides. polypeptide chain – the long chain of amino acids that is created during translation. A polypeptide chain becomes a protein whe ...
Patents at the Supreme Court: It Could Have Been
... that sprouted from the original. Absent unexpected (and unlikely) genetic mutations, these new seeds have the same features as the original seed-they too are Roundup-proof. Theoretically, then, a farmer wishing to grow Roundup Ready soybeans only needs to buy seeds from Monsanto once with every subs ...
... that sprouted from the original. Absent unexpected (and unlikely) genetic mutations, these new seeds have the same features as the original seed-they too are Roundup-proof. Theoretically, then, a farmer wishing to grow Roundup Ready soybeans only needs to buy seeds from Monsanto once with every subs ...
Ppt
... W. Szybalski (a very famous microbiologist) decided to set up a system whereby mammalian cells could be induced to take up DNA, much like bacteria - first successful report in 1962. – To maximize success he also developed the HAT selection method. – By analogy to bacterial transformation, it was dis ...
... W. Szybalski (a very famous microbiologist) decided to set up a system whereby mammalian cells could be induced to take up DNA, much like bacteria - first successful report in 1962. – To maximize success he also developed the HAT selection method. – By analogy to bacterial transformation, it was dis ...
Your EasyGuide to DNA Polymerases
... • Reduces smearing and background • Developed to enhance the performance and specificity of any thermostable DNA polymerase in enzyme reactions Description: PolyMate is a special 2x additive for use in reactions involving any thermostable DNA polymerase. PolyMate provides an optimised composition of ...
... • Reduces smearing and background • Developed to enhance the performance and specificity of any thermostable DNA polymerase in enzyme reactions Description: PolyMate is a special 2x additive for use in reactions involving any thermostable DNA polymerase. PolyMate provides an optimised composition of ...
BioTeke Corporation
... Transfer the Spin-column AC to a clean tube, add 100μl Buffer EB (having been incubated at 65-70℃ water-bath), stand for 3-5 min in RT. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min. Take flow-through back the Spin-column AC, stand for 3-5 min in RT, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min. More elution volume, mor ...
... Transfer the Spin-column AC to a clean tube, add 100μl Buffer EB (having been incubated at 65-70℃ water-bath), stand for 3-5 min in RT. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min. Take flow-through back the Spin-column AC, stand for 3-5 min in RT, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min. More elution volume, mor ...
A GRAPHICAL MODEL FORMULATION OF THE DNA BASE
... small artifacts and noise for every channel. In practice we may use P (yi |si , sl ) ≈ P (yi |si ) without any loss in performance. 3. Class conditional probabilities (third term) characterize the event weight (size of the allele) given the class indicator variable (which tells us if the event repre ...
... small artifacts and noise for every channel. In practice we may use P (yi |si , sl ) ≈ P (yi |si ) without any loss in performance. 3. Class conditional probabilities (third term) characterize the event weight (size of the allele) given the class indicator variable (which tells us if the event repre ...
ISOLATE II PCR and Gel Kit
... The Binding Buffer CB is sufficiently buffered to maintain an optimal pH of 5.0–6.0. It will even bind small DNA fragments to the silica membrane of the ISOLATE II PCR and Gel Columns, for all standard PCR reaction buffers or agarose gel buffer systems. In addition, the colored binding buffer helps ...
... The Binding Buffer CB is sufficiently buffered to maintain an optimal pH of 5.0–6.0. It will even bind small DNA fragments to the silica membrane of the ISOLATE II PCR and Gel Columns, for all standard PCR reaction buffers or agarose gel buffer systems. In addition, the colored binding buffer helps ...
DNA, Inheritance, and Genetic Variation
... replication and protein synthesis. First, they model how one DNA molecule copies itself during DNA replication to produce two identical daughter molecules. Next, they explore how a gene works and model the process of protein synthesis. ...
... replication and protein synthesis. First, they model how one DNA molecule copies itself during DNA replication to produce two identical daughter molecules. Next, they explore how a gene works and model the process of protein synthesis. ...
Carcinomas with DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency
... mutations are heterozygous, and involve only one allele. Small frameshift mutations are the most common and result in premature protein truncation, followed by nonsense mutations and larger genomic deletions. Some patients with HNPCC harbor point mutations that result in amino acid substitutions at ...
... mutations are heterozygous, and involve only one allele. Small frameshift mutations are the most common and result in premature protein truncation, followed by nonsense mutations and larger genomic deletions. Some patients with HNPCC harbor point mutations that result in amino acid substitutions at ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.