CpG methylation analysis from targeted
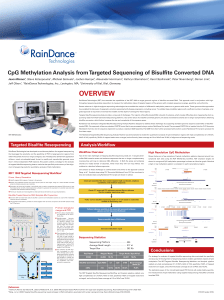
... Targeted bisulfite sequencing data provides a unique set of challenges. The majority of bisulfite-treated DNA is devoid of cytosines, which creates difficulties when mapping the short sequencing reads from Next-Generation Sequencing platforms. Due to the nature of a bisulfite converted genome, the s ...
... Targeted bisulfite sequencing data provides a unique set of challenges. The majority of bisulfite-treated DNA is devoid of cytosines, which creates difficulties when mapping the short sequencing reads from Next-Generation Sequencing platforms. Due to the nature of a bisulfite converted genome, the s ...
Supplementary Information (doc 38K)
... were used against BCL2 (05N51-20), BCL6 (01N23-020) and C-MYC (01N63- ...
... were used against BCL2 (05N51-20), BCL6 (01N23-020) and C-MYC (01N63- ...
Myriad - Tech Transfer Central
... is representative of this class of claims: A method for diagnosing a predisposition for breast cancer in a human subject which comprises comparing the germline sequence of the BRCA2 gene or the sequence of its mRNA in a tissue sample from said subject with the germline sequence of the wild-type BRCA ...
... is representative of this class of claims: A method for diagnosing a predisposition for breast cancer in a human subject which comprises comparing the germline sequence of the BRCA2 gene or the sequence of its mRNA in a tissue sample from said subject with the germline sequence of the wild-type BRCA ...
Chapter 13 Genetics and Biotechnology
... requires heat, the DNA polymerase used in PCR has to be able to withstand high temperatures. This special DNA polymerase was isolated from a thermo–philic, or heat-loving, bacterium such as those found living in ...
... requires heat, the DNA polymerase used in PCR has to be able to withstand high temperatures. This special DNA polymerase was isolated from a thermo–philic, or heat-loving, bacterium such as those found living in ...
Breaking PCR - Integrated DNA Technologies
... We are aware at the same time that, since it was first developed in the early 1980s, many “myths” have grown up around the PCR technique. Given that there are so many ways to do PCR, it occurs to us that much of what we recognize as codified PCR “truths” may be not be true at all or they may have be ...
... We are aware at the same time that, since it was first developed in the early 1980s, many “myths” have grown up around the PCR technique. Given that there are so many ways to do PCR, it occurs to us that much of what we recognize as codified PCR “truths” may be not be true at all or they may have be ...
Recombination, Bacteriophages, and Horizontal Gene Transfer
... • The F factor can exist in three different states: • F+ refers to a factor in an autonomous, extrachromosomal state containing only the genetic information described above. • The "Hfr" (which refers to "high frequency recombination") state describes the situation when the factor has integrated itse ...
... • The F factor can exist in three different states: • F+ refers to a factor in an autonomous, extrachromosomal state containing only the genetic information described above. • The "Hfr" (which refers to "high frequency recombination") state describes the situation when the factor has integrated itse ...
Genetics of Beef Cattle: Moving to the genomics era Matt Spangler
... twice the value of an EPD) accuracy (on the BIF scale) when the MBV explains 10, or 40% of the genetic variation (GV), which is synonymous with R2 values of 0.1, and 0.4. The darker portion of the bars shows the EPD accuracy before the inclusion of genomic information and the lighter colored portion ...
... twice the value of an EPD) accuracy (on the BIF scale) when the MBV explains 10, or 40% of the genetic variation (GV), which is synonymous with R2 values of 0.1, and 0.4. The darker portion of the bars shows the EPD accuracy before the inclusion of genomic information and the lighter colored portion ...
Chromosome Microarray (CMA) Pre-Test Patient
... (DNA) that tells the body how to develop and function. They come in pairs, one from each parent and they are numbered from 1 to 22, except for the sex chromosomes; girls have two Xs (XX) and boys have an X and Y chromosome (XY). Chromosomes are not visible with the naked eye, but if you stain the ...
... (DNA) that tells the body how to develop and function. They come in pairs, one from each parent and they are numbered from 1 to 22, except for the sex chromosomes; girls have two Xs (XX) and boys have an X and Y chromosome (XY). Chromosomes are not visible with the naked eye, but if you stain the ...
Edexcel GCE - The Student Room
... There are 20 pages in this question paper. Any blank pages are indicated. ...
... There are 20 pages in this question paper. Any blank pages are indicated. ...
Perkins, D.D. and V.C. Pollard ... tablished and mapped since the 1982 comoendium
... Perithecia are barren when pen-1 is used as female, even if the fertilizing parent is pen^+. An ostiole is present, but no beak. No ascospores are extruded. A few croziers and asci are present within the beakless perithecia, and a few mature ascospores may be formed. Perithecia are fully fertile and ...
... Perithecia are barren when pen-1 is used as female, even if the fertilizing parent is pen^+. An ostiole is present, but no beak. No ascospores are extruded. A few croziers and asci are present within the beakless perithecia, and a few mature ascospores may be formed. Perithecia are fully fertile and ...
mutations that affect an entire chromosomes Chromosomal
... Silent: some mutations have no apparent effect • A point mutation may not change the amino acid that is coded for • Even if a change occurs, the change may be in an intron that is removed & this has no effect • A change may not significantly affect the function of a protein if the new amino acid is ...
... Silent: some mutations have no apparent effect • A point mutation may not change the amino acid that is coded for • Even if a change occurs, the change may be in an intron that is removed & this has no effect • A change may not significantly affect the function of a protein if the new amino acid is ...
Rearrangement
... The exons that code for the variable regions of the immunoglobulin molecules and TCRs are called the variable (V) segments, diversity (D) segments, and junctional (J) segments, and those that code for the constant regions are called the C segments. ...
... The exons that code for the variable regions of the immunoglobulin molecules and TCRs are called the variable (V) segments, diversity (D) segments, and junctional (J) segments, and those that code for the constant regions are called the C segments. ...
High-throughput cloning of eukaryotic open reading frames (ORFs
... again via the Gateway™ recombination. We have developed and tested several different Gateway™ compatible E. coli expression vectors that contain different solubility and purification tags. To expand the prospects of finding high value targets we have begun to clone ORFs from other model eukaryotic o ...
... again via the Gateway™ recombination. We have developed and tested several different Gateway™ compatible E. coli expression vectors that contain different solubility and purification tags. To expand the prospects of finding high value targets we have begun to clone ORFs from other model eukaryotic o ...
primary structure
... strands wrap around each other – The two strands are associated because particular bases always hydrogen bond to one another – A pairs with T, and C pairs with G, producing base pairs ...
... strands wrap around each other – The two strands are associated because particular bases always hydrogen bond to one another – A pairs with T, and C pairs with G, producing base pairs ...
Chapter 21~The Evolution of Populations
... If there is no gene flow or genetic drift, random mating, occurrence of mutation, or any type of selection, microevolution should not occur. Small populations are especially vulnerable to genetic drift- chance events that in a small population may remove some alleles completely and may cause oth ...
... If there is no gene flow or genetic drift, random mating, occurrence of mutation, or any type of selection, microevolution should not occur. Small populations are especially vulnerable to genetic drift- chance events that in a small population may remove some alleles completely and may cause oth ...
Isolating, Cloning, and Sequencing DNA
... to separate these by size, the much more porous gels formed by dilute solutions of agarose (a polysaccharide isolated from seaweed) are used (Figure 8-23B). These DNA separation methods are widely used for both analytical and preparative purposes. Figure 8-23. Gel electrophoresis techniques for sepa ...
... to separate these by size, the much more porous gels formed by dilute solutions of agarose (a polysaccharide isolated from seaweed) are used (Figure 8-23B). These DNA separation methods are widely used for both analytical and preparative purposes. Figure 8-23. Gel electrophoresis techniques for sepa ...
deschamp_2009_sequencing
... • Small genomes that are not too complex (repeats, duplications...) • The longer the reads, the better – Targeted Resequencing • Complex genomes (crops) – Reduced representation libraries (methyl-sensitive enzymes) ...
... • Small genomes that are not too complex (repeats, duplications...) • The longer the reads, the better – Targeted Resequencing • Complex genomes (crops) – Reduced representation libraries (methyl-sensitive enzymes) ...
DNA Structure Changes Coupled to Protein Binding
... DNA molecule in which bends arise only from thermal agitation remain straight on the average, while intrinsically bent DNA sequences produce nonlinear structures with a preferred direction of bending. Induced DNA bending is usually associated with protein binding, but can also be caused by binding o ...
... DNA molecule in which bends arise only from thermal agitation remain straight on the average, while intrinsically bent DNA sequences produce nonlinear structures with a preferred direction of bending. Induced DNA bending is usually associated with protein binding, but can also be caused by binding o ...
Chapter 8 Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics
... 8.1 Enzymes are powerful and highly specific catalysts -Enzymes accelerate reactions by factors of as much as million or more. -Most reactions in biological systems do not take place in the absence of enzymes. -One of the fastest enzymes known is carbonic anhydrase (hydrate 106 molecules of CO2 per ...
... 8.1 Enzymes are powerful and highly specific catalysts -Enzymes accelerate reactions by factors of as much as million or more. -Most reactions in biological systems do not take place in the absence of enzymes. -One of the fastest enzymes known is carbonic anhydrase (hydrate 106 molecules of CO2 per ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
... syndromes: Werner and Bloom Syndromes. MRE11 complex is mutated in genetic instability syndromes: Nijmegen breakage syndrome and ataxia telangiectasia-like disorder. All three may be involved in the resolution of a stalled replication fork and in checkpoint signaling during S phase. DNA replication ...
... syndromes: Werner and Bloom Syndromes. MRE11 complex is mutated in genetic instability syndromes: Nijmegen breakage syndrome and ataxia telangiectasia-like disorder. All three may be involved in the resolution of a stalled replication fork and in checkpoint signaling during S phase. DNA replication ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.