Epigenetics in mood disorders
... dimethyl H3K9. These results implicate epigenetic mechanisms in the activity of MAO inhibitors. Eric Nestler and colleagues have experimental documentation of the associations between histone modifications and changes in behavioral function in response to antidepressant treatment and ECS in the hipp ...
... dimethyl H3K9. These results implicate epigenetic mechanisms in the activity of MAO inhibitors. Eric Nestler and colleagues have experimental documentation of the associations between histone modifications and changes in behavioral function in response to antidepressant treatment and ECS in the hipp ...
Supplementary Notes - Word file
... effects of these mutations on bioluminescence color are not fully understood at the current level of our structural study, but do not exclude the possibility of general and integral role of Ile288 in the firefly luciferases. ...
... effects of these mutations on bioluminescence color are not fully understood at the current level of our structural study, but do not exclude the possibility of general and integral role of Ile288 in the firefly luciferases. ...
1 Biochemistry 462a – Enzyme Mechanisms Reading
... Strain is a classic concept in which it was supposed that binding of the substrate to the enzyme somehow caused the substrate to become distorted toward the transition state. Transition state stabilization is a more modern concept, which states that it is not the substrate that is distorted but rath ...
... Strain is a classic concept in which it was supposed that binding of the substrate to the enzyme somehow caused the substrate to become distorted toward the transition state. Transition state stabilization is a more modern concept, which states that it is not the substrate that is distorted but rath ...
Plant Virology
... • Virus in one part of a plant moves to another slowly by cell-to-cell connections; more rapidly through vascular system, mostly phloem • Plant defense response system exists, but is less specific than vertebrate or invertebrate systems • Plants are developmentally complex; viruses may be excluded f ...
... • Virus in one part of a plant moves to another slowly by cell-to-cell connections; more rapidly through vascular system, mostly phloem • Plant defense response system exists, but is less specific than vertebrate or invertebrate systems • Plants are developmentally complex; viruses may be excluded f ...
Chymotrypsin
... Strain is a classic concept in which it was supposed that binding of the substrate to the enzyme somehow caused the substrate to become distorted toward the transition state. Transition state stabilization is a more modern concept, which states that it is not the substrate that is distorted but rath ...
... Strain is a classic concept in which it was supposed that binding of the substrate to the enzyme somehow caused the substrate to become distorted toward the transition state. Transition state stabilization is a more modern concept, which states that it is not the substrate that is distorted but rath ...
The trimethoprim-resistant dihydrofolate reductase associated with
... weights of 8300. A 11OO bp long DNA segment which confers resistance to trimethoprim was sequenced. The structural gene was identified on the plasmid DNA by comparing the amino acid composition of the deduced proteins with that of the purified enzyme. The gene is 234 bp long and codes for 78 amino a ...
... weights of 8300. A 11OO bp long DNA segment which confers resistance to trimethoprim was sequenced. The structural gene was identified on the plasmid DNA by comparing the amino acid composition of the deduced proteins with that of the purified enzyme. The gene is 234 bp long and codes for 78 amino a ...
Table 1 - Cambridge University Press
... Mitochondria are the major intracellular organelles producing ATP molecules via the electron transport chain. Cancer cells have a deviant energy metabolism, and a high rate of glycolysis is related to a high degree of dedifferentiation and proliferation. The overall net ATP production is diminished ...
... Mitochondria are the major intracellular organelles producing ATP molecules via the electron transport chain. Cancer cells have a deviant energy metabolism, and a high rate of glycolysis is related to a high degree of dedifferentiation and proliferation. The overall net ATP production is diminished ...
4 Regulation Enzyme Activity GOB Structures
... In feedback control, when the end product level is high, • the end product of a series of reactions acts as a negative regulator and binds to the allosteric site. • the substrate cannot bind to the active site, and production of all of the intermediate compounds in the subsequent reaction sequence s ...
... In feedback control, when the end product level is high, • the end product of a series of reactions acts as a negative regulator and binds to the allosteric site. • the substrate cannot bind to the active site, and production of all of the intermediate compounds in the subsequent reaction sequence s ...
Processes for producing lactic acid using yeast transformed with a
... metabolic activities of the producing microorganism. Besides the presence of lactic acid, loWering the pH value also inhibits cell groWth and metabolic activity. As a result, the extent of lactic acid production is greatly reduced. Therefore, the addition of Ca(OH)2, CaCO3, NaOH, or NH4OH to neutral ...
... metabolic activities of the producing microorganism. Besides the presence of lactic acid, loWering the pH value also inhibits cell groWth and metabolic activity. As a result, the extent of lactic acid production is greatly reduced. Therefore, the addition of Ca(OH)2, CaCO3, NaOH, or NH4OH to neutral ...
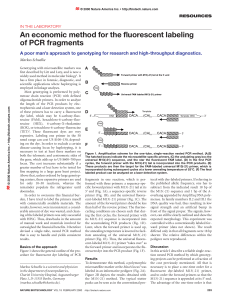
An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments
... the various PCR products indicated on the right side. In family members II.2 and III.1, the DNA was degraded because of long-time storage. Therefore, can be size-fractionated the signals are lower and an artifact appears. The signal sufficiently. Even old, strength, however, is still sufficient to m ...
... the various PCR products indicated on the right side. In family members II.2 and III.1, the DNA was degraded because of long-time storage. Therefore, can be size-fractionated the signals are lower and an artifact appears. The signal sufficiently. Even old, strength, however, is still sufficient to m ...
Genetics - davis.k12.ut.us
... Have you ever seen a black ladybug? It is less common than the orange variety you might know, but both are the same species of beetle. So why do they look different? Believe it or not, a study of pea plants helped scientists explain these differences. ...
... Have you ever seen a black ladybug? It is less common than the orange variety you might know, but both are the same species of beetle. So why do they look different? Believe it or not, a study of pea plants helped scientists explain these differences. ...
Quiz - Columbus Labs
... LDH regenerates NAD+ from NADH converting pyruvate to lactate so glycolysis can continue. The lactate produced is released into the blood. The muscle LDH isozyme (A4) works best in the NAD+-regenerating direction. Heart tissue is aerobic and uses lactate as a fuel, converting it to pyruvate via LDH ...
... LDH regenerates NAD+ from NADH converting pyruvate to lactate so glycolysis can continue. The lactate produced is released into the blood. The muscle LDH isozyme (A4) works best in the NAD+-regenerating direction. Heart tissue is aerobic and uses lactate as a fuel, converting it to pyruvate via LDH ...
Enzymes
... Examples of hydrolysis in the body: • Large molecules of food are converted to smaller molecules by digestive enzymes. • In cell respiration, glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide and water and release energy. • Hydrogen peroxide can be produced in chemical reactions in cells. It is toxic to tiss ...
... Examples of hydrolysis in the body: • Large molecules of food are converted to smaller molecules by digestive enzymes. • In cell respiration, glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide and water and release energy. • Hydrogen peroxide can be produced in chemical reactions in cells. It is toxic to tiss ...
2 - cellbiochem.ca
... • Antibiotic resistance gene: allow for selection for bacterial cells that have taken up the vector ...
... • Antibiotic resistance gene: allow for selection for bacterial cells that have taken up the vector ...
BMI 731 Chapter1: SNP Analysis
... • Each strand of the DNA molecule is held together at its base by weak hydrogen bonds. • The four bases pair in a set manner: Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), while cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). These pairs of bases are known as Base Pairs (bp). • The DNA is organized into separate long se ...
... • Each strand of the DNA molecule is held together at its base by weak hydrogen bonds. • The four bases pair in a set manner: Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), while cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). These pairs of bases are known as Base Pairs (bp). • The DNA is organized into separate long se ...
Full-Text PDF
... planet [1,2]. The traditional method for obtaining microorganisms that are useful for human life is to search for such microorganisms in the natural environment. Once the strain has been identified, it is cultured in the laboratory, and the original strain is often bred for higher performance throug ...
... planet [1,2]. The traditional method for obtaining microorganisms that are useful for human life is to search for such microorganisms in the natural environment. Once the strain has been identified, it is cultured in the laboratory, and the original strain is often bred for higher performance throug ...
First mutation in the red blood cell-specific
... Utrecht), in a patient previously diagnosed with HK deficiency. To our knowledge, these three patients are the only ones in which the molecular basis has been studied. In all three cases mutations were located in that part of the gene that encodes both HK-R and HK-1. The erythroid-specific promoter ...
... Utrecht), in a patient previously diagnosed with HK deficiency. To our knowledge, these three patients are the only ones in which the molecular basis has been studied. In all three cases mutations were located in that part of the gene that encodes both HK-R and HK-1. The erythroid-specific promoter ...
Chapter 5- Enzymes
... 2. An enzyme is specific, this means A. It has a certain amino acid sequence B. It is found only in a certain place C. It speeds up a particular reaction D. It occurs in only one type of cell ...
... 2. An enzyme is specific, this means A. It has a certain amino acid sequence B. It is found only in a certain place C. It speeds up a particular reaction D. It occurs in only one type of cell ...
Mitochondrial DNA Mutations and Disease
... with mitochondrial myopathy and exercise intolerance may have mtDNA mutations in muscle only. Therefore, the absence of mtDNA mutations in blood sample does not always rule out the diagnosis of mitochondrial DNA disorders. There are some common mtDNA point mutations and deletions with classical, rec ...
... with mitochondrial myopathy and exercise intolerance may have mtDNA mutations in muscle only. Therefore, the absence of mtDNA mutations in blood sample does not always rule out the diagnosis of mitochondrial DNA disorders. There are some common mtDNA point mutations and deletions with classical, rec ...
Biosynthesis of Pyrimidines
... • Substances take part in de-novo synthesis: • i.Carbamoyl phosphate: • Carbamoyl phosphate use in the synthesis of Pyrimidines synthesized in cytosol by the catalysis of Carbamoyl phosphate synthase-2. • ii.Aspartic acid: • React with Carbamoyl phosphate forming Ncarbamoyl aspartate. • iii.ATP: ...
... • Substances take part in de-novo synthesis: • i.Carbamoyl phosphate: • Carbamoyl phosphate use in the synthesis of Pyrimidines synthesized in cytosol by the catalysis of Carbamoyl phosphate synthase-2. • ii.Aspartic acid: • React with Carbamoyl phosphate forming Ncarbamoyl aspartate. • iii.ATP: ...
paper - Lirmm
... resulting from scoring them equally, based on a classic scoring matrix. The main drawback of this approach is that it was not designed to cope with frameshift mutations. Regarding frameshift mutation discovery, many studies [1-4] preferred the plain BLAST [5,6] alignment approach: BLASTN on DNA and ...
... resulting from scoring them equally, based on a classic scoring matrix. The main drawback of this approach is that it was not designed to cope with frameshift mutations. Regarding frameshift mutation discovery, many studies [1-4] preferred the plain BLAST [5,6] alignment approach: BLASTN on DNA and ...
A Major Species of Mouse μ-opioid Receptor mRNA and Its
... 3ⴕ-RACE and DNA Sequencing. Total RNA was extracted from mouse brain as described under Northern Blot Analysis. The 3⬘RACE experiments were performed as described in the protocol of 3⬘-RACE System for rapid amplification of cDNA ends Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). In brief, the first-strand cDNA wa ...
... 3ⴕ-RACE and DNA Sequencing. Total RNA was extracted from mouse brain as described under Northern Blot Analysis. The 3⬘RACE experiments were performed as described in the protocol of 3⬘-RACE System for rapid amplification of cDNA ends Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). In brief, the first-strand cDNA wa ...
DNAse I Qualification and Sample Treatment | Molecular Devices
... Operator's Manual. This procedure will determine if the sample contains DNA levels that exceed the dynamic range of the Total DNA Assay standard curve (3200 pg/test) which can cause reduced spike recovery. DNase I digestion must be done prior to a protease digestion. SDS inhibits DNase I and Protein ...
... Operator's Manual. This procedure will determine if the sample contains DNA levels that exceed the dynamic range of the Total DNA Assay standard curve (3200 pg/test) which can cause reduced spike recovery. DNase I digestion must be done prior to a protease digestion. SDS inhibits DNase I and Protein ...
Molecular events during translocation and proofreading extracted
... Structural meta-analysis based on singular value decomposition (SVD) of interatomic distance matrices has enabled a large-scale joint analysis of related protein structures (12–14). This computational method of structural analysis takes advantage of a mathematical, yet practical, definition of confo ...
... Structural meta-analysis based on singular value decomposition (SVD) of interatomic distance matrices has enabled a large-scale joint analysis of related protein structures (12–14). This computational method of structural analysis takes advantage of a mathematical, yet practical, definition of confo ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.