1 N SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION
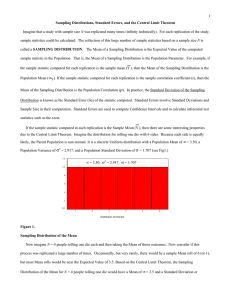
... has particular importance because it implies that even if data are sampled from a non-normal distribution, the sampling distribution of the mean (or sum) is normal as N becomes large (Hays, 1994). Thus, “normal theory” test statistics regarding means (or sums) can be applied if sample sizes are “suf ...
... has particular importance because it implies that even if data are sampled from a non-normal distribution, the sampling distribution of the mean (or sum) is normal as N becomes large (Hays, 1994). Thus, “normal theory” test statistics regarding means (or sums) can be applied if sample sizes are “suf ...
Edwards
... Presentations: There will be four presentations, each worth 15 points. The descriptions of the presentations are in the Day By Day Notes. I will assign you to your groups for these presentations as I want to avoid you having the same members each time. I expect each person in a group to contribute t ...
... Presentations: There will be four presentations, each worth 15 points. The descriptions of the presentations are in the Day By Day Notes. I will assign you to your groups for these presentations as I want to avoid you having the same members each time. I expect each person in a group to contribute t ...
Two-Side Confidence Intervals for the Poisson Means
... [3]-[5], [6]. We have known that common method used maximum likelihood estimator. So, we require to developed the CIs by Bayes estimator with Wald CI, Score CI and Score continuity correction CI which the prior distribution of is assumed to be gamma distribution with and parameters. [7] showed ...
... [3]-[5], [6]. We have known that common method used maximum likelihood estimator. So, we require to developed the CIs by Bayes estimator with Wald CI, Score CI and Score continuity correction CI which the prior distribution of is assumed to be gamma distribution with and parameters. [7] showed ...
Box and Whisker Plot
... If the chi square value ≤ the critical value the Null Hypothesis is accepted as statistically reasonable. If the chi square value is > the critical value, then it is seen as a “statistically significant” difference – meaning that the validity of the hypothesis would be under question, suggesting tha ...
... If the chi square value ≤ the critical value the Null Hypothesis is accepted as statistically reasonable. If the chi square value is > the critical value, then it is seen as a “statistically significant” difference – meaning that the validity of the hypothesis would be under question, suggesting tha ...
Review for Final
... the compliment: the probability that 0 or 1 of the burritos weigh less than 20 ounces. These are each binomial probabilities (verify conditions) and have total probability 0.91. Thus, the probability there will be at least two is 1 − 0.91 = 0.09. (g) Without doing any computations, which of the fol ...
... the compliment: the probability that 0 or 1 of the burritos weigh less than 20 ounces. These are each binomial probabilities (verify conditions) and have total probability 0.91. Thus, the probability there will be at least two is 1 − 0.91 = 0.09. (g) Without doing any computations, which of the fol ...
biol.582.f2011.lec.4
... This stat converts the difference in means to a “t stat”, which can be evaluated with a t distribution. Recall that the t distribution is like a standard normal distribution, corrected for small sample sizes. There are different t distributions for different sample sizes (degrees of freedom). The de ...
... This stat converts the difference in means to a “t stat”, which can be evaluated with a t distribution. Recall that the t distribution is like a standard normal distribution, corrected for small sample sizes. There are different t distributions for different sample sizes (degrees of freedom). The de ...
Study Guide for Exam 3
... • The Binomial Distribution (§7.3) – This is where you do a two-outcome experiment repeatedly and count the number of successes. n = number of times you repeat the experiment p = probability of success during each trial q = 1 − p = probability of failure X = number of successes – Important facts abo ...
... • The Binomial Distribution (§7.3) – This is where you do a two-outcome experiment repeatedly and count the number of successes. n = number of times you repeat the experiment p = probability of success during each trial q = 1 − p = probability of failure X = number of successes – Important facts abo ...
Lecture 5
... Consequently, the interim analyses and the final analyses must be done at significance levels that are lower than the desired overall 0.05 significance level. Typically, each interim analyses are done at a much smaller significance level than the final analysis. ...
... Consequently, the interim analyses and the final analyses must be done at significance levels that are lower than the desired overall 0.05 significance level. Typically, each interim analyses are done at a much smaller significance level than the final analysis. ...