Engineering of factors determining alpha-amylase and
... All A-amylases studied have a small residue at this position (Gly, Leu, Ser, Thr or Val), in contrast to CGTases which have a more bulky aromatic residue (Tyr or Phe) at this position, which is highly conserved. Characterization of the F196G mutant CGTase of T. thermosulfurigenes EM1 revealed that, ...
... All A-amylases studied have a small residue at this position (Gly, Leu, Ser, Thr or Val), in contrast to CGTases which have a more bulky aromatic residue (Tyr or Phe) at this position, which is highly conserved. Characterization of the F196G mutant CGTase of T. thermosulfurigenes EM1 revealed that, ...
PLASMA PROTEINS Plasma is non-cellular portion of blood. The
... 50,000) and two light or L chains or about 220 amino acids (molecular weight 25,000). Over all shape of the molecule represents ‘Y’. Two heavy chains intertwine to form the base of the Y, a disulfide bond links the L chain to H chain to form arm of the Y. The two heavy chains are held together by d ...
... 50,000) and two light or L chains or about 220 amino acids (molecular weight 25,000). Over all shape of the molecule represents ‘Y’. Two heavy chains intertwine to form the base of the Y, a disulfide bond links the L chain to H chain to form arm of the Y. The two heavy chains are held together by d ...
Structural investigation of single biomolecules
... using the AFM, to gain information about both the normal protein structure and its failure modes. In the case of bacteriorhodopsin, the protein forms very highly packed structures in the bacterial cell wall, and so is one of the few membrane proteins that can be crystallized for highresolution struc ...
... using the AFM, to gain information about both the normal protein structure and its failure modes. In the case of bacteriorhodopsin, the protein forms very highly packed structures in the bacterial cell wall, and so is one of the few membrane proteins that can be crystallized for highresolution struc ...
AB1132 Which are the key essential amino acids
... to define the key essential amino acids (AA) needed to support milk production and understand better the link between lactose output and protein supply. Protein and energy metabolism are so closely linked that it is imperative that we integrate both their supply and requirements in our predictive mo ...
... to define the key essential amino acids (AA) needed to support milk production and understand better the link between lactose output and protein supply. Protein and energy metabolism are so closely linked that it is imperative that we integrate both their supply and requirements in our predictive mo ...
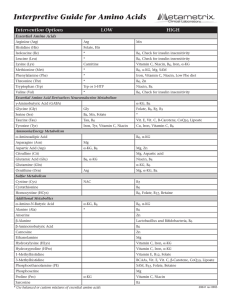
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
The nucleolus and herpesviral usurpation
... motif eight amino acids long, which functions as an NoLS and is necessary and sufficient for nucleolar retention of the N protein and colocalization with nucleolin and fibrillarin, i.e. the NoLS is required for interaction with cell factors (Reed et al., 2006; Sirri et al., 2008). Viral proteins int ...
... motif eight amino acids long, which functions as an NoLS and is necessary and sufficient for nucleolar retention of the N protein and colocalization with nucleolin and fibrillarin, i.e. the NoLS is required for interaction with cell factors (Reed et al., 2006; Sirri et al., 2008). Viral proteins int ...
Lecture #7 Date ______ - Phillips Scientific Methods
... 2) Why did Beadle and Tatum use breadmold spores to determine that one gene forms one polypeptide allowing for the first metabolic pathway to be defined? 3) Transcribe & Translate the following sequence of DNA by determining the nucleotide sequence for mRNA, the anticodon for tRNA, and the overall a ...
... 2) Why did Beadle and Tatum use breadmold spores to determine that one gene forms one polypeptide allowing for the first metabolic pathway to be defined? 3) Transcribe & Translate the following sequence of DNA by determining the nucleotide sequence for mRNA, the anticodon for tRNA, and the overall a ...
The Reactions of Diazonium Compounds with Amino Acids and
... in the normal manner, gave a product with an unchanged As/N quotient of 0-842, but the other, kept at 370 for the same time, gave a product with a diminished As/N quotient of 0-765. A product obtained from bovine-plasma albumin, having an initial As/N quotient of 0 774, was also dissolved in NaHCO2. ...
... in the normal manner, gave a product with an unchanged As/N quotient of 0-842, but the other, kept at 370 for the same time, gave a product with a diminished As/N quotient of 0-765. A product obtained from bovine-plasma albumin, having an initial As/N quotient of 0 774, was also dissolved in NaHCO2. ...
operons operons operons
... • REPRESSABLE OPERONS Usually ON/repressor usually ACTIVE Can be turned off (repressed) Genes for enzymes that make product always needed EX: trp operon makes enzymes used in essential amino acid synthesis ...
... • REPRESSABLE OPERONS Usually ON/repressor usually ACTIVE Can be turned off (repressed) Genes for enzymes that make product always needed EX: trp operon makes enzymes used in essential amino acid synthesis ...
Nucleotide Sequence of the Gene Coding for the
... experiments carried out in our laboratory have shown evolutionary conservation of DNA sequences among thegenes for nitrogenase in 13 different species (7). On the other hand, there are also significant differences in the nitrogenase proteins from different species. For example, the Fe proteins purif ...
... experiments carried out in our laboratory have shown evolutionary conservation of DNA sequences among thegenes for nitrogenase in 13 different species (7). On the other hand, there are also significant differences in the nitrogenase proteins from different species. For example, the Fe proteins purif ...
Thoughtfully Navigating the Formula Market
... Natural vitamin E for improved absorption Lutein – increases carotenoids in brain for learning, intentionally added vs. other formulas have trace amounts Lutein and vitamin E protect DHA from being oxidized by free ...
... Natural vitamin E for improved absorption Lutein – increases carotenoids in brain for learning, intentionally added vs. other formulas have trace amounts Lutein and vitamin E protect DHA from being oxidized by free ...
Enzymatic properties of the N- and C
... because the shape of the active site that binds to the substrate is very important, masking or conformational changes that occur during GST fusion can be problematic in enzyme function studies. We therefore decided to use the His tag system to minimize such effects. Furthermore, we added 5X histidin ...
... because the shape of the active site that binds to the substrate is very important, masking or conformational changes that occur during GST fusion can be problematic in enzyme function studies. We therefore decided to use the His tag system to minimize such effects. Furthermore, we added 5X histidin ...
Organic and Bio Chemistry 16
... a. Nucleic acids are strong acids, closely associated with cellular cations & such basic proteins as histones & protamines. b. The 2 main types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. RNA exists in 3 forms. o Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is found in ribosomes, but its functions are not fully understood yet. o Mes ...
... a. Nucleic acids are strong acids, closely associated with cellular cations & such basic proteins as histones & protamines. b. The 2 main types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. RNA exists in 3 forms. o Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is found in ribosomes, but its functions are not fully understood yet. o Mes ...
Document
... First axis: separates Integral Inner Membrane Proteins (IIMP) from the rest; driven by opposition between charged and large hydrophobic residues Second axis: separates proteins according to an opposition driven by the G+C content of the first codon base Third axis: separates proteins by their conten ...
... First axis: separates Integral Inner Membrane Proteins (IIMP) from the rest; driven by opposition between charged and large hydrophobic residues Second axis: separates proteins according to an opposition driven by the G+C content of the first codon base Third axis: separates proteins by their conten ...
Folie 1 - FLI
... As opposed to traditional structural biology, the determination of a protein structure through a structural genomics effort often (but not always) comes before anything is known regarding the protein function. This raises new challenges in structural bioinformatics, i.e. determining protein function ...
... As opposed to traditional structural biology, the determination of a protein structure through a structural genomics effort often (but not always) comes before anything is known regarding the protein function. This raises new challenges in structural bioinformatics, i.e. determining protein function ...
Novel Multiprotein Complexes Identified in the Hyperthermophilic
... scale in a single experiment (23–26). However, they are limited in their dynamic range and typically identify only high abundance proteins (27). The goal of this research is to develop a global method to identify novel protein complexes (PCs)1 independent of a genetic system and applicable to any or ...
... scale in a single experiment (23–26). However, they are limited in their dynamic range and typically identify only high abundance proteins (27). The goal of this research is to develop a global method to identify novel protein complexes (PCs)1 independent of a genetic system and applicable to any or ...
Unit 2 Objectives - Chemistry of Life
... 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH a ...
... 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH a ...
Determination of Nutrient Contents and Amino acid Composition of
... the cell membrane of granulation of copper-treatment on wound into a higher expression of VEGF [29]. Glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine (GHK) is a tripeptide that is paired with the copper ions in the form of GHK-Cu2+ that has been able to be isolated from human plasma [30,31]. This Complex copper tripeptid ...
... the cell membrane of granulation of copper-treatment on wound into a higher expression of VEGF [29]. Glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine (GHK) is a tripeptide that is paired with the copper ions in the form of GHK-Cu2+ that has been able to be isolated from human plasma [30,31]. This Complex copper tripeptid ...
Synthesis and Degradation of Lipids
... - between resting and activated muscle 100x - feed <-> fasting - Breakdown of glycogen and fatty acids concern the whole organism - organs and tissues connected by blood stream, coordination - Blood glucose levels sensed by pancreatic α cells, glucose down -> secrete glucagon -> glycogen degrad ...
... - between resting and activated muscle 100x - feed <-> fasting - Breakdown of glycogen and fatty acids concern the whole organism - organs and tissues connected by blood stream, coordination - Blood glucose levels sensed by pancreatic α cells, glucose down -> secrete glucagon -> glycogen degrad ...
Bio Exam 4 Study Guide- Question Format Fatty acid Synthesis
... a. To control the number of LDL particles that are synthesized by the cell. b. To control the entry of cholesterol into the cell via LDL c. To control the entry of cholesterol precursors into the cell via LDL d. To control the release of cholesterol from the cell via LDL. B 56. Familial hypercholest ...
... a. To control the number of LDL particles that are synthesized by the cell. b. To control the entry of cholesterol into the cell via LDL c. To control the entry of cholesterol precursors into the cell via LDL d. To control the release of cholesterol from the cell via LDL. B 56. Familial hypercholest ...
Chapter 2 powerpoint file
... Types of Biomolecules All four types are composed of either monomers or covalently linked polymers. The first three provide energy to the body. Monomers are connected by dehydration reactions to create polymers Polymers are broken down into monomers by hydrolysis reactions The four groups of ...
... Types of Biomolecules All four types are composed of either monomers or covalently linked polymers. The first three provide energy to the body. Monomers are connected by dehydration reactions to create polymers Polymers are broken down into monomers by hydrolysis reactions The four groups of ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.