Omega–6/Omega–3 Ratio and Brain-Related Functions - Direct-MS
... Essential Fatty Acids, the Blood-Brain Barrier, and the Brain ...
... Essential Fatty Acids, the Blood-Brain Barrier, and the Brain ...
A Symmetric Approach Elucidates Multisensory Information Integration
... architecture, i.e., the connectome, where hubs/nodes are characterized by preferential railways of information flows [16]. In the last decade, neuroscience has witnessed major advances, emphasizing the potentially vast underestimation of multisensory processing in many brain areas. New mechanisms, s ...
... architecture, i.e., the connectome, where hubs/nodes are characterized by preferential railways of information flows [16]. In the last decade, neuroscience has witnessed major advances, emphasizing the potentially vast underestimation of multisensory processing in many brain areas. New mechanisms, s ...
The role of brain in the regulation of glucose homeostasis
... and were completely silent when plasma glucose level rose to 10–12 mM or to a brain glucose level of 3.2–3.4 mM. Types 2 and 3 neurons were only inhibited by plasma glucose levels of 17 mM and higher. Type 4 neurons increases firing rate when the level of blood glucose exceeds 7 mM.[10,13] According ...
... and were completely silent when plasma glucose level rose to 10–12 mM or to a brain glucose level of 3.2–3.4 mM. Types 2 and 3 neurons were only inhibited by plasma glucose levels of 17 mM and higher. Type 4 neurons increases firing rate when the level of blood glucose exceeds 7 mM.[10,13] According ...
Golgi: a life in science - Oxford Academic
... spinal cord had greatly increased. The nerve cell, or neuron, had been identified as the fundamental unit of the nervous system. The new discoveries had helped to understand the normal functions of the brain and spinal cord and to interpret the causes of neurological disease. The work of two men had ...
... spinal cord had greatly increased. The nerve cell, or neuron, had been identified as the fundamental unit of the nervous system. The new discoveries had helped to understand the normal functions of the brain and spinal cord and to interpret the causes of neurological disease. The work of two men had ...
12 - PHSchool.com
... show maximal metabolic activity in the brain, and functional MRI scans reveal blood flow (Figure 12.7). They have shown that specific motor and sensory functions are localized in discrete cortical areas called domains. However, many higher mental functions, such as memory and language, appear to hav ...
... show maximal metabolic activity in the brain, and functional MRI scans reveal blood flow (Figure 12.7). They have shown that specific motor and sensory functions are localized in discrete cortical areas called domains. However, many higher mental functions, such as memory and language, appear to hav ...
Periosteum - Maryville University
... • Periosteum, consists of collagenous connective tissue and arteries, covers the inner side of the skull. It also continues with the periosteum on the external surface of the cranium at the exit of foramen magnum and smaller foramina for nerves and blood vessels. ...
... • Periosteum, consists of collagenous connective tissue and arteries, covers the inner side of the skull. It also continues with the periosteum on the external surface of the cranium at the exit of foramen magnum and smaller foramina for nerves and blood vessels. ...
Acetaminophen Modulates P-Glycoprotein Functional Expression at
... Downloaded from molpharm.aspetjournals.org at ASPET Journals on June 18, 2017 ...
... Downloaded from molpharm.aspetjournals.org at ASPET Journals on June 18, 2017 ...
Altered brain concentrations of citalopram and escitalopram in P-glycoprotein deficient mice
... The blood-brain barrier (BBB) contains various membrane transporters and one of the most important is P-glycoprotein (P-gp) which regulates the efflux of several central nervous system (CNS) active drugs (Loscher and Potschka, 2005). P-gp can limit the penetration into, and retention within, the bra ...
... The blood-brain barrier (BBB) contains various membrane transporters and one of the most important is P-glycoprotein (P-gp) which regulates the efflux of several central nervous system (CNS) active drugs (Loscher and Potschka, 2005). P-gp can limit the penetration into, and retention within, the bra ...
Melatonin - Nutritional Frontiers
... be responsible for bringing on sleep. Nocturnal melatonin production is highest in children and begins to decline from adolescence on until it is virtually absent in the elderly. Immune Function • Melatonin supports normal immune function by helping maintain the activity of circulating natural kille ...
... be responsible for bringing on sleep. Nocturnal melatonin production is highest in children and begins to decline from adolescence on until it is virtually absent in the elderly. Immune Function • Melatonin supports normal immune function by helping maintain the activity of circulating natural kille ...
03&04 ANS LECTURE Sultan Ayoub Meo Sept 2 2012
... ANS operates by visceral reflexes. Subconscious sensory signals from a visceral organ enter the autonomic ganglia, ...
... ANS operates by visceral reflexes. Subconscious sensory signals from a visceral organ enter the autonomic ganglia, ...
file for Erin Woller - The University of Texas at Dallas
... traumatic brain injury (TBI), becomes more severe over a period of days, spreads outside the primary injury area, and involves increasing amounts of brain tissue (7). Edema can have many consequences, including intracranial swelling, production of free radicals, and, ultimately, neuronal death (1). ...
... traumatic brain injury (TBI), becomes more severe over a period of days, spreads outside the primary injury area, and involves increasing amounts of brain tissue (7). Edema can have many consequences, including intracranial swelling, production of free radicals, and, ultimately, neuronal death (1). ...
Messages from the Brain Connectivity Regarding Neural Correlates
... effects [3, 46, 47], and thus may serve as a key component of the anesthetic-induced consciousness switch [48]. However, thalamic activity alone may not be a sufficient basis for consciousness. Instead, the explanation about the cause of anesthetic-induced unconsciousness by functional disconnection ...
... effects [3, 46, 47], and thus may serve as a key component of the anesthetic-induced consciousness switch [48]. However, thalamic activity alone may not be a sufficient basis for consciousness. Instead, the explanation about the cause of anesthetic-induced unconsciousness by functional disconnection ...
Neurologic Manifestations of Hypoglycemia
... Unlike most other body tissues, the brain requires a continuous supply of glucose. It has very limited endogenous glycogen stores, and does not produce glucose intrinsically.1 Although it accounts for 2% of body weight, the brain utilizes 25% of the body’s glucose due to its high metabolic rate.2, 3 ...
... Unlike most other body tissues, the brain requires a continuous supply of glucose. It has very limited endogenous glycogen stores, and does not produce glucose intrinsically.1 Although it accounts for 2% of body weight, the brain utilizes 25% of the body’s glucose due to its high metabolic rate.2, 3 ...
Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions during Learning May Occur by Lactate
... and debate in the field. During the last two decades a large number of studies by many different investigators have been carried out to prove or disprove this hypothesis. Whatever the study and the specific outcome, the intercellular trafficking of lactate was always interpreted as movement of fuel, ...
... and debate in the field. During the last two decades a large number of studies by many different investigators have been carried out to prove or disprove this hypothesis. Whatever the study and the specific outcome, the intercellular trafficking of lactate was always interpreted as movement of fuel, ...
3.Lecturenotes(Placenta and fetal membrane)
... Note: At the end of the 3rd month, the amnion has expanded to such an extent that it comes in contact with the chorion, thereby obliterating the chorion cavity. The yolk sac then usually shrinks and is gradually obliterated. D. Yolk Sac - Early in gestation the yolk sac may provide some limited nutr ...
... Note: At the end of the 3rd month, the amnion has expanded to such an extent that it comes in contact with the chorion, thereby obliterating the chorion cavity. The yolk sac then usually shrinks and is gradually obliterated. D. Yolk Sac - Early in gestation the yolk sac may provide some limited nutr ...
Towards Detection of Brain Tumor in Electroencephalogram
... metabolic demand on already compromised brain tissue adjacent to a tumor. Physicians who treat brain tumor associated with seizures also need to be aware of other peculiar issues. Many patients obtain chemotherapy agents which may result in drowsiness, reduce white and red blood cell counts besides ...
... metabolic demand on already compromised brain tissue adjacent to a tumor. Physicians who treat brain tumor associated with seizures also need to be aware of other peculiar issues. Many patients obtain chemotherapy agents which may result in drowsiness, reduce white and red blood cell counts besides ...
Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of - e
... an attempt was made to study the brain bioavailability of commonly used anti-Alzheimer drug donepezil (DNP) liposomal formulation by intranasal route in rats. We adopted the thin layer hydration technique for the preparation of liposomes by using cholesterol, polyethylene glycol, and 1,2-distearyl-s ...
... an attempt was made to study the brain bioavailability of commonly used anti-Alzheimer drug donepezil (DNP) liposomal formulation by intranasal route in rats. We adopted the thin layer hydration technique for the preparation of liposomes by using cholesterol, polyethylene glycol, and 1,2-distearyl-s ...
Full-Text PDF
... Investigation of White Matter Using Structural MRI Structural MRI data were used for the initial investigations into WM differences between musicians and non-musicians. Schlaug and colleagues [11] first reported that when divided into seven segments, the anterior half (segments 1–4) of the corpus ca ...
... Investigation of White Matter Using Structural MRI Structural MRI data were used for the initial investigations into WM differences between musicians and non-musicians. Schlaug and colleagues [11] first reported that when divided into seven segments, the anterior half (segments 1–4) of the corpus ca ...
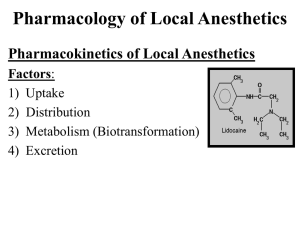
Pharmacology of Local Anesthetics
... o duration of seizures is related to blood level of anesthetic and inversely related to arterial pCO2 levels o at a normal pCO2, a Lidocaine blood level between 7.5 and 10 micrograms/ml usually result in a convulsive episode o when CO2 levels are increased, the blood level of local anesthetic necess ...
... o duration of seizures is related to blood level of anesthetic and inversely related to arterial pCO2 levels o at a normal pCO2, a Lidocaine blood level between 7.5 and 10 micrograms/ml usually result in a convulsive episode o when CO2 levels are increased, the blood level of local anesthetic necess ...
The epistemic value of brain-machine systems for the study of the
... addition, leading researchers have claimed that bionics technologies can provide unique and new experimental tools to discover brain mechanisms. For example, Wander and Rao (2014) claim that brain-machine interfaces “can … be tremendously powerful tools for scientific inquiry into the workings of th ...
... addition, leading researchers have claimed that bionics technologies can provide unique and new experimental tools to discover brain mechanisms. For example, Wander and Rao (2014) claim that brain-machine interfaces “can … be tremendously powerful tools for scientific inquiry into the workings of th ...
BRAIN Response inhibition and serotonin in autism: depletion
... prefrontal cortex) that mediate executive and inhibitory functioning (Murphy et al., 2006; Nakamura et al., 2010). There are also reports of significant associations between ASD and genetic polymorphisms for serotonin synthesis, transporters and receptors (Devlin et al., 2005; Anderson et al., 2009) ...
... prefrontal cortex) that mediate executive and inhibitory functioning (Murphy et al., 2006; Nakamura et al., 2010). There are also reports of significant associations between ASD and genetic polymorphisms for serotonin synthesis, transporters and receptors (Devlin et al., 2005; Anderson et al., 2009) ...
Chapter 3 - University of South Alabama
... unusual body odor. 6-OH-DA may be converted into a hallucinogen (2-hydroxy 4,5 dimethoxyphenethanolamine). Revision 2006 PSB ...
... unusual body odor. 6-OH-DA may be converted into a hallucinogen (2-hydroxy 4,5 dimethoxyphenethanolamine). Revision 2006 PSB ...
Module 1 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... – miniature container that stores chemicals called neurotransmitters (used to communicate with neighboring cells) ...
... – miniature container that stores chemicals called neurotransmitters (used to communicate with neighboring cells) ...
Time Is Brain—Quantified
... infarct size because of less contrast between tissue compartments, less spatial resolution, and the “fogging” effect causing isodense appearance of some infarcted tissue during the first 2 weeks to 3 months poststroke. Unless fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) is used to suppress CSF backgr ...
... infarct size because of less contrast between tissue compartments, less spatial resolution, and the “fogging” effect causing isodense appearance of some infarcted tissue during the first 2 weeks to 3 months poststroke. Unless fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) is used to suppress CSF backgr ...
8129402
... E. R. Jaensch of the University of Marburg, Germany, who devoted a lifetime to the study of visual phenomena, believed that eidetic imagery and synesthesia were nat ural human abilities educated out of most individuals. He and his associates found eidetic imagery in 80-90 percent of the children at ...
... E. R. Jaensch of the University of Marburg, Germany, who devoted a lifetime to the study of visual phenomena, believed that eidetic imagery and synesthesia were nat ural human abilities educated out of most individuals. He and his associates found eidetic imagery in 80-90 percent of the children at ...
Blood–brain barrier

The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective permeability barrier that separates the circulating blood from the brain extracellular fluid (BECF) in the central nervous system (CNS). The blood–brain barrier is formed by brain endothelial cells, which are connected by tight junctions with an extremely high electrical resistivity of at least 0.1 Ω⋅m. The blood–brain barrier allows the passage of water, some gases, and lipid-soluble molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. On the other hand, the blood–brain barrier may prevent the entry of lipophilic, potential neurotoxins by way of an active transport mechanism mediated by P-glycoprotein. Astrocytes are necessary to create the blood–brain barrier. A small number of regions in the brain, including the circumventricular organs (CVOs), do not have a blood–brain barrier.The blood–brain barrier occurs along all capillaries and consists of tight junctions around the capillaries that do not exist in normal circulation. Endothelial cells restrict the diffusion of microscopic objects (e.g., bacteria) and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), while allowing the diffusion of small hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones). Cells of the barrier actively transport metabolic products such as glucose across the barrier with specific proteins. This barrier also includes a thick basement membrane and astrocytic endfeet.