Cerebellum
... variations in loads encountered during movement and to smooth out small oscillations. This control is thought to be dependent both on information that the spinocerebellum receives from cortical motor areas about the intended motor command and on feedback from the spinal cord and periphery, which pro ...
... variations in loads encountered during movement and to smooth out small oscillations. This control is thought to be dependent both on information that the spinocerebellum receives from cortical motor areas about the intended motor command and on feedback from the spinal cord and periphery, which pro ...
Visual Dysfunction in Brain Injury
... Visual-perceptual processing dysfunction • Visual-Motor Integration - Eye-hand, eye-foot, and eyebody coordination • Visual-Auditory Integration - The ability to relate and associate what is seen and heard • Visual Memory - The ability to remember and recall information that is seen • Visual Closur ...
... Visual-perceptual processing dysfunction • Visual-Motor Integration - Eye-hand, eye-foot, and eyebody coordination • Visual-Auditory Integration - The ability to relate and associate what is seen and heard • Visual Memory - The ability to remember and recall information that is seen • Visual Closur ...
Brain Waves Volunteer Instructor Guide
... should be more accurate when they can use both ears. Our brains use the volume and time it takes for sounds to reach each ear to determine sound locations. ...
... should be more accurate when they can use both ears. Our brains use the volume and time it takes for sounds to reach each ear to determine sound locations. ...
Chapter 5: Brain imaging Multiple Choice Questions (1
... d. brain areas that have been damaged due to stroke or illness 12. You are designing a brain imaging study to investigate language processing in the brain. You decide to have your subjects listen to human speech and then compare their brain response to two other conditions: (1) listening to orchestr ...
... d. brain areas that have been damaged due to stroke or illness 12. You are designing a brain imaging study to investigate language processing in the brain. You decide to have your subjects listen to human speech and then compare their brain response to two other conditions: (1) listening to orchestr ...
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Structural and Functional areas of the
... linked to both fear responses and pleasure. Is responsible for determining what memories are stored and where the memories are stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes. Believed to act as an interface between limibic syste ...
... linked to both fear responses and pleasure. Is responsible for determining what memories are stored and where the memories are stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes. Believed to act as an interface between limibic syste ...
Cerebellum
... Lesions of the cerebellum (damage to input, output or cortex) result in symptoms that occur because the cerebellum’s normal function is interrupted-->ataxia, dysmetria, intention tremor occur. ...
... Lesions of the cerebellum (damage to input, output or cortex) result in symptoms that occur because the cerebellum’s normal function is interrupted-->ataxia, dysmetria, intention tremor occur. ...
Neural structures involved in the control of movement
... e.g., direct and indirect pathways, transmitters - Circuitry involved in movement disorders discussed ...
... e.g., direct and indirect pathways, transmitters - Circuitry involved in movement disorders discussed ...
Chapter 14 - The Brain and Cranial Nerves (pgs. 461
... Each cerebral hemisphere contains one large lateral ventricle (I and II) separated by a thin medial partition, the septum pellucidum. Third ventricle (III) is ventricle of the diencephalon Lateral ventricles communicate with third ventricle via the interventricular foramen (Foramen of Monroe) Fourth ...
... Each cerebral hemisphere contains one large lateral ventricle (I and II) separated by a thin medial partition, the septum pellucidum. Third ventricle (III) is ventricle of the diencephalon Lateral ventricles communicate with third ventricle via the interventricular foramen (Foramen of Monroe) Fourth ...
The Effect of Stimulating and Soothing Smells on Heart Rate and
... The hippocampus is responsible for converting short-term memory into long-term memory, while the amygdala is essential in emotional processing and associating significance to sensory input (Hesselink n.d.), especially fear. Damage to the amygdala results in the flattening of emotion and no response ...
... The hippocampus is responsible for converting short-term memory into long-term memory, while the amygdala is essential in emotional processing and associating significance to sensory input (Hesselink n.d.), especially fear. Damage to the amygdala results in the flattening of emotion and no response ...
Phenomenology without conscious access is a form of
... must be a concern that this might affect sensory processing, and hence that phenomenal experience of the stimulus is affected along with cognitive access. We know, for example, that attention affects visual sensitivity (Solomon 2004). Changes in the response gain of neurons in sensory areas of corte ...
... must be a concern that this might affect sensory processing, and hence that phenomenal experience of the stimulus is affected along with cognitive access. We know, for example, that attention affects visual sensitivity (Solomon 2004). Changes in the response gain of neurons in sensory areas of corte ...
Brain Day Volunteer Instructor Guide
... should be more accurate when they can use both ears. Our brains use the volume and time it takes for sounds to reach each ear to determine sound locations. ...
... should be more accurate when they can use both ears. Our brains use the volume and time it takes for sounds to reach each ear to determine sound locations. ...
BasalGanglia
... e.g., direct and indirect pathways, transmitters - Circuitry involved in movement disorders discussed ...
... e.g., direct and indirect pathways, transmitters - Circuitry involved in movement disorders discussed ...
DECISION MAKING AND THE BRAIN: NEUROLOGISTS` VIEW
... From the non-dualistic perspective decision making is a brain process. Basic knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the central nervous system is crucial for comprehension of the neurological substrate of decision making. The nervous system is divided anatomically into central nervous system and ...
... From the non-dualistic perspective decision making is a brain process. Basic knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the central nervous system is crucial for comprehension of the neurological substrate of decision making. The nervous system is divided anatomically into central nervous system and ...
Document
... IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS: This material logically splits into six basic topic areas, the organization of the brain, the functional relationships among the parts of the brain, the organization of the spinal cord, the functional relationships among the parts of the spinal cord, the functional relation ...
... IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS: This material logically splits into six basic topic areas, the organization of the brain, the functional relationships among the parts of the brain, the organization of the spinal cord, the functional relationships among the parts of the spinal cord, the functional relation ...
08_chapter 2
... The longitudinal fissure separating the two hemispheres is largely occupied by a field of dura matter , the falx cerebri. The convolutions are called as gyri, the fissures between them as sulci, and many of the both are named in the Figure 2.3. The frontal lobe lies anterior to the central or Roland ...
... The longitudinal fissure separating the two hemispheres is largely occupied by a field of dura matter , the falx cerebri. The convolutions are called as gyri, the fissures between them as sulci, and many of the both are named in the Figure 2.3. The frontal lobe lies anterior to the central or Roland ...
Convergent evolution of complex brains and high intelligence
... sociality in the sense of the well-known ‘social brain hypothesis’ developed in the context of primate –human brain evolution [15]. However, a recent comparative study by Farris & Schulmeister [16] demonstrated that complex MBs are likewise found among non-social insects, including solitary and para ...
... sociality in the sense of the well-known ‘social brain hypothesis’ developed in the context of primate –human brain evolution [15]. However, a recent comparative study by Farris & Schulmeister [16] demonstrated that complex MBs are likewise found among non-social insects, including solitary and para ...
Parietal Cortex and Hippocampal Contributions to RuleBased
... Different cells have different place firing fields, such that the animal’s entire environment is represented by these different “place fields.” These place fields can also remap, changing which cells fire as well as rate of firing in new environments. In rats, these place fields were found to be a ...
... Different cells have different place firing fields, such that the animal’s entire environment is represented by these different “place fields.” These place fields can also remap, changing which cells fire as well as rate of firing in new environments. In rats, these place fields were found to be a ...
to BIO 210 chapter 16 study notes
... Higher order functions Higher order functions share the following characteristics: o The cerebral cortex is required for their performance o They involve both conscious and unconscious information processing o The are not part of the programmed “wiring” of the brain Memory Memories Fact memori ...
... Higher order functions Higher order functions share the following characteristics: o The cerebral cortex is required for their performance o They involve both conscious and unconscious information processing o The are not part of the programmed “wiring” of the brain Memory Memories Fact memori ...
DIENCEPHALON
... • Distributing most of afferent inputs to cerebral cortex • Control of electrocortical activity of cerebral cortex – plays important roles in arousal, consciousness and sleep mechanisms • Integration of motor functions by providing the relays – impulses from the basal ganglia and cerebellum can reac ...
... • Distributing most of afferent inputs to cerebral cortex • Control of electrocortical activity of cerebral cortex – plays important roles in arousal, consciousness and sleep mechanisms • Integration of motor functions by providing the relays – impulses from the basal ganglia and cerebellum can reac ...
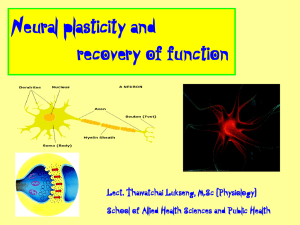
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... • Neural (adj.) = involving a nerve or the system of nerves that includes the brain • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve ce ...
... • Neural (adj.) = involving a nerve or the system of nerves that includes the brain • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve ce ...
Brain rhythms in mental time travel
... associative circuitry of the brain, which is assumed to consist of both long-standing associations as well as associations based on recent experience. Stimulus-related neural activity projected along these associative pathways forms the major source of input to the contextual representation. As such ...
... associative circuitry of the brain, which is assumed to consist of both long-standing associations as well as associations based on recent experience. Stimulus-related neural activity projected along these associative pathways forms the major source of input to the contextual representation. As such ...
Central Emotional Integration
... Calcification of human amygdala (Urbach-Wiethe disease) → disrupts implicit processing of facial cues of fear but does not impair explicit recognition of faces/objects. ...
... Calcification of human amygdala (Urbach-Wiethe disease) → disrupts implicit processing of facial cues of fear but does not impair explicit recognition of faces/objects. ...
Central Emotional System
... Calcification of human amygdala (Urbach-Wiethe disease) → disrupts implicit processing of facial cues of fear but does not impair explicit recognition of faces/objects. ...
... Calcification of human amygdala (Urbach-Wiethe disease) → disrupts implicit processing of facial cues of fear but does not impair explicit recognition of faces/objects. ...
download file
... agreement and disagreement. It should be noted at the outset that the level of agreement was high. Each member had made independently subtle shifts from the traditional views of their respective areas, leading to the resolution of previously disparate opinions between different disciplines. The con ...
... agreement and disagreement. It should be noted at the outset that the level of agreement was high. Each member had made independently subtle shifts from the traditional views of their respective areas, leading to the resolution of previously disparate opinions between different disciplines. The con ...
Neuroanatomy of memory

The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.