CASE 47
... dopamine-containing nerve cells in the substantia nigra. Patients with Parkinson disease may have a combination of symptoms, including resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, disturbance of gait, and postural problems. The cause of Parkinson disease is unknown. ...
... dopamine-containing nerve cells in the substantia nigra. Patients with Parkinson disease may have a combination of symptoms, including resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, disturbance of gait, and postural problems. The cause of Parkinson disease is unknown. ...
Development of the Nervous System
... neurons, Schwann cells of the PNS, and nonneuronal derivatives such as melanocytes. Above is a cross section through the neural tube. In the neural tube there is symmetrical cell division. Eventually, there is asymmetrical cell division and differentiation of the daughter cells. The first thing that ...
... neurons, Schwann cells of the PNS, and nonneuronal derivatives such as melanocytes. Above is a cross section through the neural tube. In the neural tube there is symmetrical cell division. Eventually, there is asymmetrical cell division and differentiation of the daughter cells. The first thing that ...
Chapter 10
... regions of the motor homunculus are involved in activating motor neurons the arms, hands, and legs primarily on the ________, while the trunk the motor homunculus are primarily involved in activating motor neurons the trunk primarily on the _________. ...
... regions of the motor homunculus are involved in activating motor neurons the arms, hands, and legs primarily on the ________, while the trunk the motor homunculus are primarily involved in activating motor neurons the trunk primarily on the _________. ...
A phase I trial of deep brain stimulation of memory
... and temporal areas, also have a propensity for fibrillar amyloid deposition as visualized at autopsy and in vivo using radioligands such as Pittsburgh compound B,9 both in AD patients and in nondemented older subjects.10,11 Recent evidence suggests amyloid pathology interferes with synaptic transmis ...
... and temporal areas, also have a propensity for fibrillar amyloid deposition as visualized at autopsy and in vivo using radioligands such as Pittsburgh compound B,9 both in AD patients and in nondemented older subjects.10,11 Recent evidence suggests amyloid pathology interferes with synaptic transmis ...
CHAPTER 12: THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE 12.1
... Neocortex is divided into three areas: primary motor cortex, primary sensory cortices, and association areas (continued): o Primary motor cortex – plans and executes movement o Primary sensory cortices – first regions to receive and process sensory input o Association areas integrate different typ ...
... Neocortex is divided into three areas: primary motor cortex, primary sensory cortices, and association areas (continued): o Primary motor cortex – plans and executes movement o Primary sensory cortices – first regions to receive and process sensory input o Association areas integrate different typ ...
Affective neuroscience: the emergence of a discipline
... Fig. 1. Neural circuits of fear conditioning. The neural pathways by which a sensory conditioned stimulus elicits emotional responses involve the relay of sensory inputs to the thalamus. Whereas the lemniscal nuclei (LEM) transmit only to the primary sensory cortex, the extralemniscal areas (EX) tra ...
... Fig. 1. Neural circuits of fear conditioning. The neural pathways by which a sensory conditioned stimulus elicits emotional responses involve the relay of sensory inputs to the thalamus. Whereas the lemniscal nuclei (LEM) transmit only to the primary sensory cortex, the extralemniscal areas (EX) tra ...
No Slide Title
... Grammaticization: From bag of tricks to systematic syntax Karine Megerdoomian: Unlocking the CF of verbs ...
... Grammaticization: From bag of tricks to systematic syntax Karine Megerdoomian: Unlocking the CF of verbs ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... • Site of conscious mind: awareness, sensory perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, memory storage, understanding • Each hemisphere connects to contralateral side of the body • There is lateralization of cortical function in the hemispheres ...
... • Site of conscious mind: awareness, sensory perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, memory storage, understanding • Each hemisphere connects to contralateral side of the body • There is lateralization of cortical function in the hemispheres ...
Nervous System II- The Brain, Cranial Nerves & Autonomic
... • The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is also referred to as the involuntary nervous system – we generally cannot voluntarily control activities which ...
... • The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is also referred to as the involuntary nervous system – we generally cannot voluntarily control activities which ...
Article Page 08.27.20+
... quick reactions by goaltenders in ice hockey are easier to understand when described by such a feedforward system (Regan, 2000). Therefore, it seems that at least part of the advantage of an interlocking perception/action system is the capacity to anticipate and react, which speeds-up reaction time. ...
... quick reactions by goaltenders in ice hockey are easier to understand when described by such a feedforward system (Regan, 2000). Therefore, it seems that at least part of the advantage of an interlocking perception/action system is the capacity to anticipate and react, which speeds-up reaction time. ...
Chapter 9 powerpoint file
... Auditory cortex – Temporal lobe (Auditory association area and Audiotory Cortex Olfactory cortex- Temporal lobe (uncus) Gustatory cortex – Frontal lobe Processed into perception – allows the stimulus to be translated into a different aspect (photons=colors) and “fills-in” missing information ...
... Auditory cortex – Temporal lobe (Auditory association area and Audiotory Cortex Olfactory cortex- Temporal lobe (uncus) Gustatory cortex – Frontal lobe Processed into perception – allows the stimulus to be translated into a different aspect (photons=colors) and “fills-in” missing information ...
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective • To learn the functional
... the base of the cochlea respond selectively to high-frequency stimuli, and fibers from the apex respond to low-frequency stimuli. This differential sensitivity is the basis of the tonotopic organization of the receptive sheet, an organization that is present at virtually every level of the auditory ...
... the base of the cochlea respond selectively to high-frequency stimuli, and fibers from the apex respond to low-frequency stimuli. This differential sensitivity is the basis of the tonotopic organization of the receptive sheet, an organization that is present at virtually every level of the auditory ...
NAlab07_AuditVest
... the base of the cochlea respond selectively to high-frequency stimuli, and fibers from the apex respond to low-frequency stimuli. This differential sensitivity is the basis of the tonotopic organization of the receptive sheet, an organization that is present at virtually every level of the auditory ...
... the base of the cochlea respond selectively to high-frequency stimuli, and fibers from the apex respond to low-frequency stimuli. This differential sensitivity is the basis of the tonotopic organization of the receptive sheet, an organization that is present at virtually every level of the auditory ...
Seeing faces and objects with the “mind`s eye”
... study has shown that the precuneus, which mediates memory-related imagery (Fletcher et al., 1995), is also activated during hypnosis, suggesting that such a state of enhanced self-monitoring is achieved by control of motor responses by internal representations (Cojan et al., 2009). It therefore seem ...
... study has shown that the precuneus, which mediates memory-related imagery (Fletcher et al., 1995), is also activated during hypnosis, suggesting that such a state of enhanced self-monitoring is achieved by control of motor responses by internal representations (Cojan et al., 2009). It therefore seem ...
Ramón y Cajal, 19 th century
... in synapses are rather mushroom-shaped and carry receptor plates (active zones, red, top figure). Spines contact axonal terminals or axonal varicosities in reach and form synapses (left). Knott et al., 2006 ...
... in synapses are rather mushroom-shaped and carry receptor plates (active zones, red, top figure). Spines contact axonal terminals or axonal varicosities in reach and form synapses (left). Knott et al., 2006 ...
nightmares without atonia as an early symptom of diffuse lewy
... nightmares with no atonia (NWNA) about 6 years prior to his first evaluation. One year before the first consult, the patient had an intestinal infection and he started to have visospatial disorder, some memory problems and attention deficits. During all course of the disease he had incapacity to fin ...
... nightmares with no atonia (NWNA) about 6 years prior to his first evaluation. One year before the first consult, the patient had an intestinal infection and he started to have visospatial disorder, some memory problems and attention deficits. During all course of the disease he had incapacity to fin ...
Morshed, Trisha
... resulting in the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, which are associated with brain atrophy, cognitive impairment, and neurotransmitter derangements. The process first involves the hippocampus, and then spreads gradually to involve the frontal lobes in later stages. In PD, Lewy‐type synucleino ...
... resulting in the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, which are associated with brain atrophy, cognitive impairment, and neurotransmitter derangements. The process first involves the hippocampus, and then spreads gradually to involve the frontal lobes in later stages. In PD, Lewy‐type synucleino ...
Human Physiology
... to specialization of each hemisphere for certain functions Each cerebral hemisphere controls movement on opposite side of body And receives sensory info from opposite side of body Hemispheres communicate thru the corpus callosum (Fig 8.1) which contains about 200 million fibers ...
... to specialization of each hemisphere for certain functions Each cerebral hemisphere controls movement on opposite side of body And receives sensory info from opposite side of body Hemispheres communicate thru the corpus callosum (Fig 8.1) which contains about 200 million fibers ...
striatum
... Important for stimulus – response behavior THE VENTRAL STRIATUM (nc. Accumbens) The learning and execution of reward-related movements and activities. The ventral striatum is activated in reward situations. Reward= smoking, alcohol, drugs, sex, economic reward ...
... Important for stimulus – response behavior THE VENTRAL STRIATUM (nc. Accumbens) The learning and execution of reward-related movements and activities. The ventral striatum is activated in reward situations. Reward= smoking, alcohol, drugs, sex, economic reward ...
2320Lecture20
... – changes accompanied by full-field transients are hard to detect • e.g. change blindness • orienting mechanism is blinded by the transient ...
... – changes accompanied by full-field transients are hard to detect • e.g. change blindness • orienting mechanism is blinded by the transient ...
Principles of Neural Science
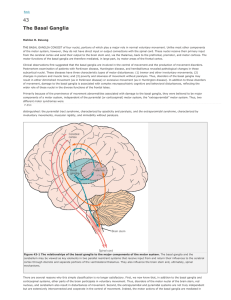
... THE BASAL GANGLIA CONSIST of four nuclei, portions of which play a major role in normal voluntary movement. Unlike most other components of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral ...
... THE BASAL GANGLIA CONSIST of four nuclei, portions of which play a major role in normal voluntary movement. Unlike most other components of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral ...
REVIEW Time Course of Auditory Processing, Visual Processing
... (Auditory Cortex), Wernicke’s Area within temporal lobe, save these sounds and its mean; and record this information to language related processing centers.The frontal and temporal areas in speech comprehension in that temporal regions subserve bottom-up processing of speech, whereas frontal areas a ...
... (Auditory Cortex), Wernicke’s Area within temporal lobe, save these sounds and its mean; and record this information to language related processing centers.The frontal and temporal areas in speech comprehension in that temporal regions subserve bottom-up processing of speech, whereas frontal areas a ...
The Central Nervous System
... Lobes of the Cerebrum Frontal – “somatomotor” functions (voluntary movement), intellectual functions, aggression, sexual behavior, olfaction, motor area, Broca’s area of speech (on left side only; coordinates speech muscles) Parietal – abstract reasoning (mathematics), use of symbols for communicat ...
... Lobes of the Cerebrum Frontal – “somatomotor” functions (voluntary movement), intellectual functions, aggression, sexual behavior, olfaction, motor area, Broca’s area of speech (on left side only; coordinates speech muscles) Parietal – abstract reasoning (mathematics), use of symbols for communicat ...
Eagleman Ch 7. The Motor System
... Most motor areas receive extensive input from somatosensory areas. The frontopolar cortex receives no sensory input and connects with other prefrontal areas. This helps set and maintain long-term goals. ...
... Most motor areas receive extensive input from somatosensory areas. The frontopolar cortex receives no sensory input and connects with other prefrontal areas. This helps set and maintain long-term goals. ...
Neuroanatomy of memory

The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.