Presentation
... • Population growth models – Limits to exponential growth • Population Density (the number of individuals per unit of land area or water volume) increases as well • Competition follows as nutrients and resources are used up • The limit to population size that a particular environment can support is ...
... • Population growth models – Limits to exponential growth • Population Density (the number of individuals per unit of land area or water volume) increases as well • Competition follows as nutrients and resources are used up • The limit to population size that a particular environment can support is ...
the usefulness of ecological niche concepts in understanding plant
... is the differential utilisation of resources among species so that they can avoid competition and be able to coexist (MacArthur & Wilson, 1967; MacArthur, 1972; Schoener, 1986; Chesson, 2000). If there is no such differentiation, then it will follow the Competitive Exclusion Principle or ‘Gause’s Pr ...
... is the differential utilisation of resources among species so that they can avoid competition and be able to coexist (MacArthur & Wilson, 1967; MacArthur, 1972; Schoener, 1986; Chesson, 2000). If there is no such differentiation, then it will follow the Competitive Exclusion Principle or ‘Gause’s Pr ...
Schiel—Algal interactions on subtidal reefs
... Periodicity of reproduction and recruitment The fertility of plants and the appearance of recruits are both distinctly seasonal (Fig. 2). Ecklonia is reproductive for the longest period of the year, with some members of shallow populations possessing fertile sori from May to late November (Novaczek ...
... Periodicity of reproduction and recruitment The fertility of plants and the appearance of recruits are both distinctly seasonal (Fig. 2). Ecklonia is reproductive for the longest period of the year, with some members of shallow populations possessing fertile sori from May to late November (Novaczek ...
Evolution: the source of Earth`s biodiversity Genetic variation
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
19-Population ecology
... existence,” which states that individuals will compete (with members of their own or other species) for limited resources. The successful ones are more likely to survive and pass on the traits that made them successful to the next generation at a greater rate (natural selection). To model the realit ...
... existence,” which states that individuals will compete (with members of their own or other species) for limited resources. The successful ones are more likely to survive and pass on the traits that made them successful to the next generation at a greater rate (natural selection). To model the realit ...
New Workloads Demand Flexible Approach to Storage
... Massive virtualization, datacenter consolidation, and the ability to deploy a growing number of virtualized applications on powerful multicore CPUs have increased the risk profile within the datacenter. These datacenter trends require renewed focus on storage network availability. In this regard, ha ...
... Massive virtualization, datacenter consolidation, and the ability to deploy a growing number of virtualized applications on powerful multicore CPUs have increased the risk profile within the datacenter. These datacenter trends require renewed focus on storage network availability. In this regard, ha ...
Section 4: Population Samplings
... Physical environment factors include food, shelter, water supply, space availability, and (for plants) soil and light. One of these factors may severely limit population size, even if the others are not as constrained. The Law of the Minimum states that population growth is limited by the resource i ...
... Physical environment factors include food, shelter, water supply, space availability, and (for plants) soil and light. One of these factors may severely limit population size, even if the others are not as constrained. The Law of the Minimum states that population growth is limited by the resource i ...
Full-Text PDF
... environment creates diversity in communities of organisms, as well as it affects their stability, dynamics and pattern generation [21] (pp. 7–8) and [22]. However these spatial effects have been long ignored by most ecologists because of the difficulties they pose for modeling. Rather a common assum ...
... environment creates diversity in communities of organisms, as well as it affects their stability, dynamics and pattern generation [21] (pp. 7–8) and [22]. However these spatial effects have been long ignored by most ecologists because of the difficulties they pose for modeling. Rather a common assum ...
Population Ecology - Rochester Community Schools
... • Carrying capacity: the maximum number of organisms in a population that an environment can support for the long term Carrying capacity is limited by the energy, water, oxygen, and nutrients available (resources). ...
... • Carrying capacity: the maximum number of organisms in a population that an environment can support for the long term Carrying capacity is limited by the energy, water, oxygen, and nutrients available (resources). ...
Oecologia (1992) 92:58-64 ?-;- Oecologia ? Springer-Verlag 1992
... actions between two species of Tribolium beetles (Park 1948). These studies were influential at the time in helping might competition imagine how interspecific ecologists function in nature, and they are still widely discussed in on comgeneral ecology textbooks as model experiments petition (for exa ...
... actions between two species of Tribolium beetles (Park 1948). These studies were influential at the time in helping might competition imagine how interspecific ecologists function in nature, and they are still widely discussed in on comgeneral ecology textbooks as model experiments petition (for exa ...
Comparative Population Ecology of Eleven Species
... energy constraints cause the smallest species to move among rich patches in a coarsegrained manner. Patterns of similarities and differences among closely related (congeneric and confamilial) species suggested that evolutionary constraints sometimes, but not always, limited variation in life history ...
... energy constraints cause the smallest species to move among rich patches in a coarsegrained manner. Patterns of similarities and differences among closely related (congeneric and confamilial) species suggested that evolutionary constraints sometimes, but not always, limited variation in life history ...
Immigration and the Maintenance of Local Species Diversity
... This equilibrium is feasible if P̂i 1 0 for all species, which, from equation (6a), requires 0 ! Vˆ ! 1/r1, where species 1 is again defined as the species with the highest basic reproductive rate r. But P̂i is a monotonic increasing function of Vˆ that varies from 0 to 1` when Vˆ increases from 0 t ...
... This equilibrium is feasible if P̂i 1 0 for all species, which, from equation (6a), requires 0 ! Vˆ ! 1/r1, where species 1 is again defined as the species with the highest basic reproductive rate r. But P̂i is a monotonic increasing function of Vˆ that varies from 0 to 1` when Vˆ increases from 0 t ...
Species interaction mechanisms maintain grassland
... overyielding (Vandermeer 1981, Loreau 2004). Species overyield when interspecific interactions are less detrimental or more favorable than intraspecific interactions. That is, a species overyields when there is less competition or when there are more positive interactions in mixture than in monocultur ...
... overyielding (Vandermeer 1981, Loreau 2004). Species overyield when interspecific interactions are less detrimental or more favorable than intraspecific interactions. That is, a species overyields when there is less competition or when there are more positive interactions in mixture than in monocultur ...
Diversity effects beyond species richness: evidence from intertidal macroalgal assemblages Francisco Arenas
... are not evenly distributed, neither in biomass or spatially. The importance of diversity effects beyond species richness has not been fully explored (Giller et al. 2004), hindering our ability to extrapolate from experimental studies to natural systems. Even the predicted positive effects of species ...
... are not evenly distributed, neither in biomass or spatially. The importance of diversity effects beyond species richness has not been fully explored (Giller et al. 2004), hindering our ability to extrapolate from experimental studies to natural systems. Even the predicted positive effects of species ...
Chapter04 - Duluth High School
... species whose impact on its community or ecosystem is much larger and more influential than would be expected from mere abundance. Often, many species are intricately interconnected so that it is difficult to tell which is the essential component. ...
... species whose impact on its community or ecosystem is much larger and more influential than would be expected from mere abundance. Often, many species are intricately interconnected so that it is difficult to tell which is the essential component. ...
Invasional meltdown 6 years later: important
... 2005). Experiments showed that digestion by these two mammal species increased germination probability and speed. Furthermore, the succulents provide an energy- and water-rich food source to the rats and rabbits during the summer dry season. This study does not prove a population impact on any of th ...
... 2005). Experiments showed that digestion by these two mammal species increased germination probability and speed. Furthermore, the succulents provide an energy- and water-rich food source to the rats and rabbits during the summer dry season. This study does not prove a population impact on any of th ...
The impact of nonlinear functional responses on the long
... k gik ðtÞ This condition is such that no individual can increase its energy intake by putting more effort into a different prey. The sum in (6) is over all species k which are predators of j: The competition strength aik is set equal to one only for i ¼ k; and is smaller than 1 otherwise. For this m ...
... k gik ðtÞ This condition is such that no individual can increase its energy intake by putting more effort into a different prey. The sum in (6) is over all species k which are predators of j: The competition strength aik is set equal to one only for i ¼ k; and is smaller than 1 otherwise. For this m ...
C. E. Timothy Paine – Curriculum Vitae
... clustering of functionally dissimilar species, whereas habitat filtering has the converse effect. We used these predictions to assess the relative effects of habitat filtering and niche differentiation on recruit community assembly over spatial (5- and 30-m neighborhoods) and temporal (20-yr) scales ...
... clustering of functionally dissimilar species, whereas habitat filtering has the converse effect. We used these predictions to assess the relative effects of habitat filtering and niche differentiation on recruit community assembly over spatial (5- and 30-m neighborhoods) and temporal (20-yr) scales ...
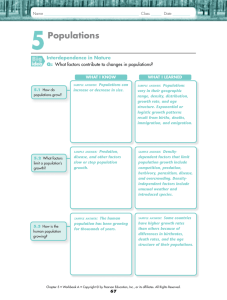
Populations
... Lesson 5.1 • Workbook A • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Lesson 5.1 • Workbook A • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
Evolution, Biological Communities, and Species Interactions
... Galápagos Islands, 900 km (540 mi) off the their understanding of molecular genetics to coast of Ecuador. The harsh, volcanic put together a modern synthesis of evolulandscape of these remote islands (see tion that clarifies these details. page 74) held an extraordinary assemblage An overwhelming ma ...
... Galápagos Islands, 900 km (540 mi) off the their understanding of molecular genetics to coast of Ecuador. The harsh, volcanic put together a modern synthesis of evolulandscape of these remote islands (see tion that clarifies these details. page 74) held an extraordinary assemblage An overwhelming ma ...
Extension on Evolution
... Latin, “eating together”) involve one species feeding in, on, or around another species. For example, one species may associate with another species that, by virtue of its own feeding behavior, makes food more accessible. The brown-headed cowbird owes its name to its habit of following herds of graz ...
... Latin, “eating together”) involve one species feeding in, on, or around another species. For example, one species may associate with another species that, by virtue of its own feeding behavior, makes food more accessible. The brown-headed cowbird owes its name to its habit of following herds of graz ...