Biodiversity Exam
... b. a hot climate area with numerous types of species c. an area, regardless of climate, with various numbers of ecosystems. Protists (protozoa, algae, etc.) are: a. Prokaryotes b. Eukaryotes ...
... b. a hot climate area with numerous types of species c. an area, regardless of climate, with various numbers of ecosystems. Protists (protozoa, algae, etc.) are: a. Prokaryotes b. Eukaryotes ...
Biology Test
... A. the way the organism uses the range of physical and biological conditions in which it lives B. all the physical and biological factors in the organism’s environment C. the range of temperatures that the organisms need to survive D. a full description of the place and organism lives ...
... A. the way the organism uses the range of physical and biological conditions in which it lives B. all the physical and biological factors in the organism’s environment C. the range of temperatures that the organisms need to survive D. a full description of the place and organism lives ...
Slide 1
... Department of Horticultural Sciences HFSB 409 and Centeq 120A 845-2937 or 229-8746 [email protected] ...
... Department of Horticultural Sciences HFSB 409 and Centeq 120A 845-2937 or 229-8746 [email protected] ...
File - Pedersen Science
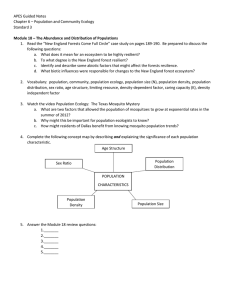
... a. What does it mean for an ecosystem to be highly resilient? b. To what degree is the New England forest resilient? c. Identify and describe some abiotic factors that might affect the forests resilience. d. What biotic influences were responsible for changes to the New England forest ecosystem? 2. ...
... a. What does it mean for an ecosystem to be highly resilient? b. To what degree is the New England forest resilient? c. Identify and describe some abiotic factors that might affect the forests resilience. d. What biotic influences were responsible for changes to the New England forest ecosystem? 2. ...
File - Pedersen Science
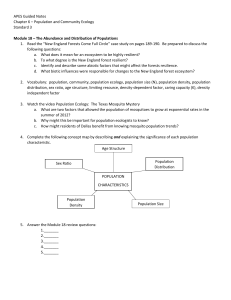
... a. What does it mean for an ecosystem to be highly resilient? b. To what degree is the New England forest resilient? c. Identify and describe some abiotic factors that might affect the forests resilience. d. What biotic influences were responsible for changes to the New England forest ecosystem? 2. ...
... a. What does it mean for an ecosystem to be highly resilient? b. To what degree is the New England forest resilient? c. Identify and describe some abiotic factors that might affect the forests resilience. d. What biotic influences were responsible for changes to the New England forest ecosystem? 2. ...
chapt20_lecture_anim
... Genetic Variation and Evolution • Genetic variation – Differences in alleles of genes found within individuals in a population – Raw material for natural selection ...
... Genetic Variation and Evolution • Genetic variation – Differences in alleles of genes found within individuals in a population – Raw material for natural selection ...
Universität Bonn - M. Sc. Plant Sciences
... Das Modul ist folgendem Studiengang/folgenden Studiengängen zugeordnet M. Sc. (Plant Science) Inhalte des Moduls The lab course will deal with the phylogenetic information stored over 500 million years of land plant evolution, stored in the genomes of living plants. Molecular techniques, mainly DNA ...
... Das Modul ist folgendem Studiengang/folgenden Studiengängen zugeordnet M. Sc. (Plant Science) Inhalte des Moduls The lab course will deal with the phylogenetic information stored over 500 million years of land plant evolution, stored in the genomes of living plants. Molecular techniques, mainly DNA ...
Introduction to Biotechnology
... It can happen from weeks 10-13 after the last period This is a better technique than amniocentesis because that can only happen from weeks 15-18 ...
... It can happen from weeks 10-13 after the last period This is a better technique than amniocentesis because that can only happen from weeks 15-18 ...
Lecture 3
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Understanding populations
... members are more common in a crowded population than in a sparse population. Density independent: when deaths are equally likely in a crowded or sparse population. ...
... members are more common in a crowded population than in a sparse population. Density independent: when deaths are equally likely in a crowded or sparse population. ...
Document
... and twigs. They have the lowest reproduction rate among all small birds (1 chick/year). But they care for their young. The decline of their numbers corresponds with the introduction of rats, cats and logging in the island. ...
... and twigs. They have the lowest reproduction rate among all small birds (1 chick/year). But they care for their young. The decline of their numbers corresponds with the introduction of rats, cats and logging in the island. ...
Download chapter 3
... highly degraded and fragmented habitats. In many cases, it is not clear how to define separate populations, since this requires knowledge of mechanisms for gene flow within and between populations for the different species, which can only be generally characterized at this point. Throughout the MVP ...
... highly degraded and fragmented habitats. In many cases, it is not clear how to define separate populations, since this requires knowledge of mechanisms for gene flow within and between populations for the different species, which can only be generally characterized at this point. Throughout the MVP ...
Chapter 20 PowerPoint
... Genetic Variation and Evolution • Genetic variation – Differences in alleles of genes found within individuals in a population – Raw material for natural selection ...
... Genetic Variation and Evolution • Genetic variation – Differences in alleles of genes found within individuals in a population – Raw material for natural selection ...
FUNGI - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... 8. Explain how the exponential growth equation is different than the logistic growth equation. 9. What are the axes we use to display population growth patterns? ...
... 8. Explain how the exponential growth equation is different than the logistic growth equation. 9. What are the axes we use to display population growth patterns? ...
7E - gcisd
... Evolution refers to the permanent genetic change (change in gene frequencies) in population of individuals. ...
... Evolution refers to the permanent genetic change (change in gene frequencies) in population of individuals. ...
Defining Biodiversity
... ecosystems (Convention on Biological Diversity). Components include: Genetic Diversity: Genetic diversity refers to the variability in the genetic makeup among individuals within a population. Species Diversity: Species diversity refers to the range of species native to a particular geographical are ...
... ecosystems (Convention on Biological Diversity). Components include: Genetic Diversity: Genetic diversity refers to the variability in the genetic makeup among individuals within a population. Species Diversity: Species diversity refers to the range of species native to a particular geographical are ...
Chapter 15 Evolution
... Darwin’s theory of natural selection remains the central theme of evolution Scientists of today know that natural selection is not the only mechanism of evolution Evolution occurs at the population level, with genes as the raw material. ...
... Darwin’s theory of natural selection remains the central theme of evolution Scientists of today know that natural selection is not the only mechanism of evolution Evolution occurs at the population level, with genes as the raw material. ...
Populations
... 1. Give one example for each of the following types of limiting factors. a. density-dependent b. density-independent 2. What is meant by the term “carrying capacity”? 3. Give an example of a. interspecific competition b. intraspecific competition 4. How might overcrowding lead to a reduction in popu ...
... 1. Give one example for each of the following types of limiting factors. a. density-dependent b. density-independent 2. What is meant by the term “carrying capacity”? 3. Give an example of a. interspecific competition b. intraspecific competition 4. How might overcrowding lead to a reduction in popu ...