Dispersal traits determine plant response to habitat
... of dispersal limitations must be separated from the effects of spatially autocorrelated environmental conditions. In this study, we explicitly aimed to overcome the obscuring effects arising from the above-mentioned methodological challenges. Therefore, we investigated the relationship between plant ...
... of dispersal limitations must be separated from the effects of spatially autocorrelated environmental conditions. In this study, we explicitly aimed to overcome the obscuring effects arising from the above-mentioned methodological challenges. Therefore, we investigated the relationship between plant ...
Unit 21.1
... • Remember: Because of natural selection every organism has a variety of adaptations that are suited to it’s specific living conditions. • The role of an organism in it’s habitat is called its niche. (what it eats, how it gets the food, what eats it, how and when it reproduces, physical conditions i ...
... • Remember: Because of natural selection every organism has a variety of adaptations that are suited to it’s specific living conditions. • The role of an organism in it’s habitat is called its niche. (what it eats, how it gets the food, what eats it, how and when it reproduces, physical conditions i ...
Chapter 51 Mini Notes
... b. Studies have shown that the differences in diet are genetic c. Only one group can detect and respond to specific odor molecules produced by the banana slugs ...
... b. Studies have shown that the differences in diet are genetic c. Only one group can detect and respond to specific odor molecules produced by the banana slugs ...
Evolutionary action of tropical animals on the reproduction of plants
... Knowledge of the syndromes of seed dispersal and types of pollination is essential for the evaluation of the functional significance of structural characters. I attempt here to contribute to the understanding of the ecological morphology of plant reproductive organs. In this field, morphology repres ...
... Knowledge of the syndromes of seed dispersal and types of pollination is essential for the evaluation of the functional significance of structural characters. I attempt here to contribute to the understanding of the ecological morphology of plant reproductive organs. In this field, morphology repres ...
Ecological benefits of the temporary nature concept
... Destruction of the habitat Destruction has an impact on non-mobile species, but the overall population afterwards is not smaller than before temporary nature. Destruction can have a more far-reaching negative impact on species that choose temporary nature for reproduction. Destruction should not be ...
... Destruction of the habitat Destruction has an impact on non-mobile species, but the overall population afterwards is not smaller than before temporary nature. Destruction can have a more far-reaching negative impact on species that choose temporary nature for reproduction. Destruction should not be ...
Journal of Biotechnology VI-2 Genomics, proteomics and
... produced ectoine as the main compatible solute for osmotic stress adaptation (Csonka, 1989; Galinski and Trüper, 1994). Our aim was to establish the best condition of osmotic downshock required for high yield of ectoine production using strain EG6 and compare it with one of the type strains H. elong ...
... produced ectoine as the main compatible solute for osmotic stress adaptation (Csonka, 1989; Galinski and Trüper, 1994). Our aim was to establish the best condition of osmotic downshock required for high yield of ectoine production using strain EG6 and compare it with one of the type strains H. elong ...
Biology 423 – Exam # 1
... 20. Pirt’s study on bioremediation with bacteria did which of the following? a) developed techniques for breaking down horse manure b) used thermophilic bacteria and bacteria active at 37 degrees c) converted almost all of the organic matter to water and oxygen d) none of the above 21. Which predic ...
... 20. Pirt’s study on bioremediation with bacteria did which of the following? a) developed techniques for breaking down horse manure b) used thermophilic bacteria and bacteria active at 37 degrees c) converted almost all of the organic matter to water and oxygen d) none of the above 21. Which predic ...
Databases
... ranging from viruses to bacteria to eukaryotes. • For each model organism, RefSeq aims to provide separate and linked records for the genomic DNA, the gene transcripts, and the proteins arising from those transcripts. ...
... ranging from viruses to bacteria to eukaryotes. • For each model organism, RefSeq aims to provide separate and linked records for the genomic DNA, the gene transcripts, and the proteins arising from those transcripts. ...
Overgrazing their welcome
... gazelles. Meanwhile, other plants, such as broom bush (markh), have been reduced in size rather than number. Animals from hares to oryx use this shrub for shade and shelter, so it is likely that the reduced size of the plant under camel grazing could lower the populations of these animals. Although ...
... gazelles. Meanwhile, other plants, such as broom bush (markh), have been reduced in size rather than number. Animals from hares to oryx use this shrub for shade and shelter, so it is likely that the reduced size of the plant under camel grazing could lower the populations of these animals. Although ...
Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... postdoc position as well as a scientific programmer position. The group is involved in establishing a new center for global molecular epidemiology focusing on the pathogenicity and systems biology of bacteria. 1 postdoc within predictive bioinformatics for molecular epidemiology - The candidate will ...
... postdoc position as well as a scientific programmer position. The group is involved in establishing a new center for global molecular epidemiology focusing on the pathogenicity and systems biology of bacteria. 1 postdoc within predictive bioinformatics for molecular epidemiology - The candidate will ...
Linking Nature`s services to ecosystems: some general ecological
... or resources may be used to maintain populations at desired levels to provide or secure this service in a cost-effective manner. For example, food-web management in lakes through stocking or removal of specific species can improve both fishing and water quality (Carpenter and Kitchell, 1993). Other ...
... or resources may be used to maintain populations at desired levels to provide or secure this service in a cost-effective manner. For example, food-web management in lakes through stocking or removal of specific species can improve both fishing and water quality (Carpenter and Kitchell, 1993). Other ...
Life Science The Life Science standards emphasize a more complex
... relationships in the living world. Students build on basic principles related to these concepts by exploring the cellular organization and the classification of organisms; the dynamic relationships among organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems; and change as a result of the transmission ...
... relationships in the living world. Students build on basic principles related to these concepts by exploring the cellular organization and the classification of organisms; the dynamic relationships among organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems; and change as a result of the transmission ...
The Geographical Ecology of Mammals
... to study population dynamics and community structure and from using patterns in space or time to infer processes past and Journal of Mammalogy, 80(2):329-332, ...
... to study population dynamics and community structure and from using patterns in space or time to infer processes past and Journal of Mammalogy, 80(2):329-332, ...
Fine-scale community and genetic structure are tightly linked in
... recombinant genotypes). A key result of this experiment was that the rate of decline in species diversity over time (Shannon index) was least pronounced in the most genetically diverse communities. After 5 years of growth, the genetically diverse communities retained the greatest species diversity. ...
... recombinant genotypes). A key result of this experiment was that the rate of decline in species diversity over time (Shannon index) was least pronounced in the most genetically diverse communities. After 5 years of growth, the genetically diverse communities retained the greatest species diversity. ...
The role of metapopulations in conservation
... introduced for the metapopulation is 370---960 km2 . All reserves are enclosed with electrical fences, to protect the wild dogs and to minimize conflict with livestock farmers. Fences act as important barriers to the movements of the dogs, so that there is little emigration and even less immigration ...
... introduced for the metapopulation is 370---960 km2 . All reserves are enclosed with electrical fences, to protect the wild dogs and to minimize conflict with livestock farmers. Fences act as important barriers to the movements of the dogs, so that there is little emigration and even less immigration ...
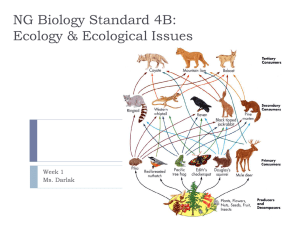
BioB4Symbiosis - Darlak4Science
... Northern pike (it’s a fish) feed on another fish, the yellow perch. An increase in the yellow perch population causes an increase in the northern pike population. The BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico has harmed many aquatic organisms that live in the Gulf region. A new strain of influenza (the flu ...
... Northern pike (it’s a fish) feed on another fish, the yellow perch. An increase in the yellow perch population causes an increase in the northern pike population. The BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico has harmed many aquatic organisms that live in the Gulf region. A new strain of influenza (the flu ...
The Great Divergence: When Did Diversity on
... mainly through pollination of stationary plants, although gamete transfer by collembolans has been documented for mosses (Cronberg et al. 2006), and may well occur much more widely in other groups, including fungi. In the sea, gamete transfer by animal vectors could, in principle, have evolved in ma ...
... mainly through pollination of stationary plants, although gamete transfer by collembolans has been documented for mosses (Cronberg et al. 2006), and may well occur much more widely in other groups, including fungi. In the sea, gamete transfer by animal vectors could, in principle, have evolved in ma ...
habitat selection in woodland nearctic
... occupying only physical, three-dimensional space and not casting a shadow upon the resource dimensions of the local environment. This may occur, for example, in migration “waves,” when large numbers of birds can be found at a site, often apparently not feeding (although evidence remains anecdotal). ...
... occupying only physical, three-dimensional space and not casting a shadow upon the resource dimensions of the local environment. This may occur, for example, in migration “waves,” when large numbers of birds can be found at a site, often apparently not feeding (although evidence remains anecdotal). ...
A Field Experiment Demonstrating Plant Life
... heritability for both life span (annual vs. biennial) and flowering phenology among our genotypes (table A1, available online; Johnson and Agrawal 2005; Johnson et al. 2009a). In previous single-generation experiments, we found natural selection on plant life-history traits and evidence that life-hi ...
... heritability for both life span (annual vs. biennial) and flowering phenology among our genotypes (table A1, available online; Johnson and Agrawal 2005; Johnson et al. 2009a). In previous single-generation experiments, we found natural selection on plant life-history traits and evidence that life-hi ...
Section 4.1 Summary – pages 91-99
... A population is a group of organisms, all of the same species, that live in a specific area. A healthy population will grow and die at a steady rate unless it runs out of food or space, or is attacked in some way by disease or predators. Scientists study changes in populations in a variety of ways. ...
... A population is a group of organisms, all of the same species, that live in a specific area. A healthy population will grow and die at a steady rate unless it runs out of food or space, or is attacked in some way by disease or predators. Scientists study changes in populations in a variety of ways. ...
The interplay of pollinator diversity, pollination services
... production volume and c. 70% of major global crops rely on animal pollination (Klein et al. 2007). Overall, crop visitation rates decline with increasing distance from pollinator habitats, as demonstrated in a meta-analysis of 16 case studies in tropical and temperate regions illustrating the potent ...
... production volume and c. 70% of major global crops rely on animal pollination (Klein et al. 2007). Overall, crop visitation rates decline with increasing distance from pollinator habitats, as demonstrated in a meta-analysis of 16 case studies in tropical and temperate regions illustrating the potent ...
Does eutrophication-driven evolution change aquatic ecosystems?
... eutrophic sections of the lake [9]. Eutrophication also reduced the intensity of sexual selection in stickleback of the Baltic Sea via multiple pathways. In this species, expression of male nuptial coloration and courtship activity are influenced by the outcome of male–male contest competition. Domi ...
... eutrophic sections of the lake [9]. Eutrophication also reduced the intensity of sexual selection in stickleback of the Baltic Sea via multiple pathways. In this species, expression of male nuptial coloration and courtship activity are influenced by the outcome of male–male contest competition. Domi ...