200B lect # 21 (Conservation) - Integrative Biology
... particular goal Vulnerability – probability of persistence of a population or other features of an area D. Phylogenetics and conservation As we have discussed, there has been tremendous recent progress in understanding the relationships of organisms at all levels, due to two different advances, whos ...
... particular goal Vulnerability – probability of persistence of a population or other features of an area D. Phylogenetics and conservation As we have discussed, there has been tremendous recent progress in understanding the relationships of organisms at all levels, due to two different advances, whos ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
... surface of the world including forests, grassland plains, jungles, deserts, snowy terrain, and swamps. How do these biomes get formed? What are some of your favorites? On Earth, once land is formed through volcanic activity, the rock cycle, and other environmental interactions like we discussed the ...
... surface of the world including forests, grassland plains, jungles, deserts, snowy terrain, and swamps. How do these biomes get formed? What are some of your favorites? On Earth, once land is formed through volcanic activity, the rock cycle, and other environmental interactions like we discussed the ...
The relationship between biodiversity and forest ecosystem
... • hypothesis: multiple species perform the same function in many ecosystems • loss of one species results in the role filled by another with no change in goods and services • that is….biodiversity makes the system resilient to some level of species loss • evidence clear that diversity supports stabi ...
... • hypothesis: multiple species perform the same function in many ecosystems • loss of one species results in the role filled by another with no change in goods and services • that is….biodiversity makes the system resilient to some level of species loss • evidence clear that diversity supports stabi ...
Intraspecific priority effects and disease interact to alter population
... variety of mechanisms. In particular, trait variation among colonizing individuals can produce intraspecific priority effects (IPEs), where early arrivers of a single species affect the establishment or growth of later conspecifics. While we have some evidence for the importance of IPEs, we lack a gen ...
... variety of mechanisms. In particular, trait variation among colonizing individuals can produce intraspecific priority effects (IPEs), where early arrivers of a single species affect the establishment or growth of later conspecifics. While we have some evidence for the importance of IPEs, we lack a gen ...
Biodiversity and Evolution
... changes over time through changes in the genetic characteristics of populations • Natural selection – individuals with certain traits are more likely to survive and reproduce under a certain set of environmental conditions ...
... changes over time through changes in the genetic characteristics of populations • Natural selection – individuals with certain traits are more likely to survive and reproduce under a certain set of environmental conditions ...
Unsustainable Logging is a Major Threat to Forest Ecosystems
... potentially catastrophic problem because of the vital ecological services at risk, the high rate of tropical deforestation, and its growing contribution to global warming. ...
... potentially catastrophic problem because of the vital ecological services at risk, the high rate of tropical deforestation, and its growing contribution to global warming. ...
Relationships Within Ecosystems
... E. One organism benefits but the other does not benefit and is not harmed. F. parasitism ...
... E. One organism benefits but the other does not benefit and is not harmed. F. parasitism ...
William Paterson University Department of Biology
... Biology 301 is a lecture course on ecology and evolutionary biology. The topics are mainly organized into three areas: population ecology, population interactions, and population genetics. By study of the first two areas, an objective is a general understanding of population dynamics, including popu ...
... Biology 301 is a lecture course on ecology and evolutionary biology. The topics are mainly organized into three areas: population ecology, population interactions, and population genetics. By study of the first two areas, an objective is a general understanding of population dynamics, including popu ...
8th Grade First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... water, soil composition Living factors that affect the ecosystem: food sources, other population members, other species More than one individual or population in an ecosystem relies upon the same limited resource Role in an ecosystem A biotic or abiotic factor needed as a resource for survival; depl ...
... water, soil composition Living factors that affect the ecosystem: food sources, other population members, other species More than one individual or population in an ecosystem relies upon the same limited resource Role in an ecosystem A biotic or abiotic factor needed as a resource for survival; depl ...
Dens et al.
... maximum density achieved (MPD1) is 105 cfu/g. Scenario 4 assumes a base case as follows: r1 = r2 = 0.23 (3-h generation times); TMD1 = TMD2 = 10 log; a12 = 2, a21 = 1; and N10 = N20 = 102 cfu/g. While holding other factors constant, each competition model parameter is varied until MPD1 = 105 cfu/g. ...
... maximum density achieved (MPD1) is 105 cfu/g. Scenario 4 assumes a base case as follows: r1 = r2 = 0.23 (3-h generation times); TMD1 = TMD2 = 10 log; a12 = 2, a21 = 1; and N10 = N20 = 102 cfu/g. While holding other factors constant, each competition model parameter is varied until MPD1 = 105 cfu/g. ...
Landscape Ecology www.AssignmentPoint.com Landscape ecology
... rather the respective species being studied is the point of reference for what constitutes a landscape. Topological ecology at the landscape level of biological organisation (e.g. Urban et al): On the basis of ecological hierarchy theory, it is presupposed that nature is working at multiple scales ...
... rather the respective species being studied is the point of reference for what constitutes a landscape. Topological ecology at the landscape level of biological organisation (e.g. Urban et al): On the basis of ecological hierarchy theory, it is presupposed that nature is working at multiple scales ...
EXAM REVIEW Chapter41 - (per 3) and wed 4/24 (per 2,6)
... • Red imported fire ants (RIFAs) did not evolve in North America, so there are few predators, parasites, or pathogens to hold them in check • Global climate change is expected to help RIFAs extend their range in the US ...
... • Red imported fire ants (RIFAs) did not evolve in North America, so there are few predators, parasites, or pathogens to hold them in check • Global climate change is expected to help RIFAs extend their range in the US ...
chapter 6 - Lisle CUSD 202
... natural selection will enable humans to develop lungs that can detoxify pollutants? (a) A theory is part of the process that scientists follow when investigating scientific evidence in order to explain their observations. For a theory to be validated it has to be accepted by the scientific community ...
... natural selection will enable humans to develop lungs that can detoxify pollutants? (a) A theory is part of the process that scientists follow when investigating scientific evidence in order to explain their observations. For a theory to be validated it has to be accepted by the scientific community ...
Interpretive Context and Application of the Biological Condition
... observed in the field for certain assemblages (e.g., DELT anomalies in fish). As with other aspects of function, assessment approaches range greatly in complexity. The most common approach for state and tribal programs is to forego complex and demanding direct measures of organism function (such as ...
... observed in the field for certain assemblages (e.g., DELT anomalies in fish). As with other aspects of function, assessment approaches range greatly in complexity. The most common approach for state and tribal programs is to forego complex and demanding direct measures of organism function (such as ...
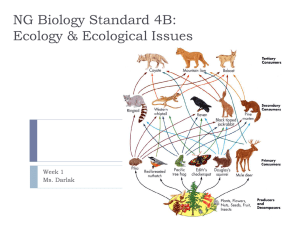
BioB4Symbiosis - Darlak4Science
... Some species of barnacles Many of the bacteria living in our large intestine. Epiphytes ...
... Some species of barnacles Many of the bacteria living in our large intestine. Epiphytes ...
Ecological Succession
... • As the rocks breaks apart, water freezes and thaws on the cracks, which breaks up the rocks further. • When the lichens die, they accumulate in the cracks. • Then mosses begin to grow and die, leading to the creation of fertile soil. • Fertile soil is made up of the broken rocks, decayed organis ...
... • As the rocks breaks apart, water freezes and thaws on the cracks, which breaks up the rocks further. • When the lichens die, they accumulate in the cracks. • Then mosses begin to grow and die, leading to the creation of fertile soil. • Fertile soil is made up of the broken rocks, decayed organis ...
File - AP Biology
... 1. Which of the following is not an observation or inference upon which natural selection is based? a. There is heritable variation among individuals. b. Poorly adapted individuals leave less offspring. c. The size of populations fluctuates over time. d. Individuals whose inherited characteristics b ...
... 1. Which of the following is not an observation or inference upon which natural selection is based? a. There is heritable variation among individuals. b. Poorly adapted individuals leave less offspring. c. The size of populations fluctuates over time. d. Individuals whose inherited characteristics b ...
Practice Exam 1
... 18. Recall the example of the introduction of rabbits to Australia. Although initially promising, efforts to control the rabbit population with the myxoma virus were not successful. This was because (circle all that apply) a. All rabbits have a natural resistence to the myxoma virus. b. The virulenc ...
... 18. Recall the example of the introduction of rabbits to Australia. Although initially promising, efforts to control the rabbit population with the myxoma virus were not successful. This was because (circle all that apply) a. All rabbits have a natural resistence to the myxoma virus. b. The virulenc ...
Big Idea 1: Multiple Choice Big Idea 1A Which of the following is not
... 1. Which of the following is not an observation or inference upon which natural selection is based? a. There is heritable variation among individuals. b. Poorly adapted individuals leave less offspring. c. The size of populations fluctuates over time. d. Individuals whose inherited characteristics b ...
... 1. Which of the following is not an observation or inference upon which natural selection is based? a. There is heritable variation among individuals. b. Poorly adapted individuals leave less offspring. c. The size of populations fluctuates over time. d. Individuals whose inherited characteristics b ...
Population Ecology
... Exponential growth is a useful model when studying populations that are introduced into a new, unfilled, environment Recovery after a catastrophe Exponential Growth: dN/dt =rmax •N rmax is the maximum rate of population growth for the ...
... Exponential growth is a useful model when studying populations that are introduced into a new, unfilled, environment Recovery after a catastrophe Exponential Growth: dN/dt =rmax •N rmax is the maximum rate of population growth for the ...
7-1-10 - Food Chain
... the food chain so they meet the above scenarios. You do that by using the + button or – button to add or remove organisms or by changing the organisms from healthy to diseased. Click on the BAR CHART tab and click play. Also make sure that you reset your food chart before making any new changes to t ...
... the food chain so they meet the above scenarios. You do that by using the + button or – button to add or remove organisms or by changing the organisms from healthy to diseased. Click on the BAR CHART tab and click play. Also make sure that you reset your food chart before making any new changes to t ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.