The Effect of L-Carnitine Treatment on Lactic Acid Levels in Normal
... decraesing intramithochondrial Acetyl CoA / CoA ratio. Keywords: L-carnitine, Lactic Acid, IGT, Normal Glucose Tolerance ...
... decraesing intramithochondrial Acetyl CoA / CoA ratio. Keywords: L-carnitine, Lactic Acid, IGT, Normal Glucose Tolerance ...
The Nitrogen Cycle
... Description of the Nitrogen Cycle • N2 gas in the atmosphere must be taken in by symbiotic bacteria in the roots of plants (legumes) through nitrogen fixation. Then other bacteria change the nitrogen so it can be taken up by plants. Animals eat plants and get nitrogen. When plants and animals die, ...
... Description of the Nitrogen Cycle • N2 gas in the atmosphere must be taken in by symbiotic bacteria in the roots of plants (legumes) through nitrogen fixation. Then other bacteria change the nitrogen so it can be taken up by plants. Animals eat plants and get nitrogen. When plants and animals die, ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... Amount of energy that must be absorbed by reactants in 53. their ground states to reach the transition state so that a reaction can occur (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 54. Energy change associated with a mole of gas and ions reacting with water (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 55. The energy change whe ...
... Amount of energy that must be absorbed by reactants in 53. their ground states to reach the transition state so that a reaction can occur (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 54. Energy change associated with a mole of gas and ions reacting with water (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 55. The energy change whe ...
Molecular Machines
... US, have recently made ‘daisy-chain’ polymers in which a whole series of these units is linked together. In theory, Grubbs and colleagues estimate that a perfectly linear polymer of this sort should be 58 per cent longer in the extended state than when contracted. Over many monomer units, that diffe ...
... US, have recently made ‘daisy-chain’ polymers in which a whole series of these units is linked together. In theory, Grubbs and colleagues estimate that a perfectly linear polymer of this sort should be 58 per cent longer in the extended state than when contracted. Over many monomer units, that diffe ...
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior: The 2015 Transition
... and Behavior has improved on many metrics, but one steady outcome of our continued efforts is that the journal has shown a linear increase in submissions over the past 10 years, attesting to its popularity as a place to publish high-quality innovative research. Indeed, I would argue that Pharmacolog ...
... and Behavior has improved on many metrics, but one steady outcome of our continued efforts is that the journal has shown a linear increase in submissions over the past 10 years, attesting to its popularity as a place to publish high-quality innovative research. Indeed, I would argue that Pharmacolog ...
Preferentially biotinylate N-terminal α
... Biotinylation reagents containing N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) esters are widely used to label proteins at primary amino groups (-NH2), which exist in the side chain of lysine residues and at the N-terminus of each polypeptide. With large proteins, labeling of several lysine residues and the N-terminu ...
... Biotinylation reagents containing N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) esters are widely used to label proteins at primary amino groups (-NH2), which exist in the side chain of lysine residues and at the N-terminus of each polypeptide. With large proteins, labeling of several lysine residues and the N-terminu ...
Practice Test 2
... solutions of Ca(NO3)2 and Na2CO3 are mixed is A) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq) B) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) C) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) ----> Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 NaNO3(s) D) Ca2+(aq) + CO32 ...
... solutions of Ca(NO3)2 and Na2CO3 are mixed is A) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq) B) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) C) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) ----> Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 NaNO3(s) D) Ca2+(aq) + CO32 ...
falciparum - Griffith Research Online
... pathways critical for parasite survival and/or transmission. Malarial parasites digest the infected host’s hemoglobin to obtain free amino acids [6]. These amino acids are used to maintain osmotic pressure within infected red blood cells, for protein synthesis during parasite development and reprodu ...
... pathways critical for parasite survival and/or transmission. Malarial parasites digest the infected host’s hemoglobin to obtain free amino acids [6]. These amino acids are used to maintain osmotic pressure within infected red blood cells, for protein synthesis during parasite development and reprodu ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... response to different types of stimuli, such as electrical or chemical signals. A gated channel protein is a transport protein that opens a "gate," allowing a molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion. A stimulus causes the ...
... response to different types of stimuli, such as electrical or chemical signals. A gated channel protein is a transport protein that opens a "gate," allowing a molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion. A stimulus causes the ...
BMB 400 PART THREE - ANSWERS ANSWERS to Questions from
... in vitro, and this was a key technique in deciphering the genetic code. However, it differs from DNA and RNA polymerases in points 1 and 4. Polynucleotide phosphorylase does not use a template, but rather adds ribonucleotides to an RNA in a highly reversible reaction. The substrates (in the directio ...
... in vitro, and this was a key technique in deciphering the genetic code. However, it differs from DNA and RNA polymerases in points 1 and 4. Polynucleotide phosphorylase does not use a template, but rather adds ribonucleotides to an RNA in a highly reversible reaction. The substrates (in the directio ...
Chemistry Review ATOMS
... • The mass of atoms and molecules is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. – The # of atoms for each element in the reactants must equal the # of atoms for each element in the products in a chemical reaction. – Chemical Equations must be balanced. ...
... • The mass of atoms and molecules is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. – The # of atoms for each element in the reactants must equal the # of atoms for each element in the products in a chemical reaction. – Chemical Equations must be balanced. ...
video slide - Ionia Public Schools
... • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts Copyright ...
... • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts Copyright ...
Document
... Application of delayed extraction–matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for analysis of sphingolipids in pericardial fluid, peritoneal fluid and serum from Gaucher disease patients Takehisa Fujiwaki , , a, Seiji Yamaguchia, Masaru Tasakaa, Nobuo Sakurab and Tam ...
... Application of delayed extraction–matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for analysis of sphingolipids in pericardial fluid, peritoneal fluid and serum from Gaucher disease patients Takehisa Fujiwaki , , a, Seiji Yamaguchia, Masaru Tasakaa, Nobuo Sakurab and Tam ...
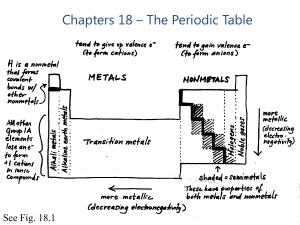
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... production for use in fertilizers, explosives, rayon, and polymers such as nylon, urea-formaldehyde resins, and acrylics. 2. Hydrazine, N2H4. Used in rockets as a propellant, and as a starting point for anti-tuberculin drugs. 3. Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and nitric acid (HNO3). Used ...
... production for use in fertilizers, explosives, rayon, and polymers such as nylon, urea-formaldehyde resins, and acrylics. 2. Hydrazine, N2H4. Used in rockets as a propellant, and as a starting point for anti-tuberculin drugs. 3. Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and nitric acid (HNO3). Used ...
biochem ch 44B [9-2
... for prevention and repair of damage done by reactive oxygen species and generation of energy RBCs only generate ATP by glycolysis – ATP used for ion transport across PM (Na+, K+, and Ca2+), phosphorylation of membrane proteins, and priming reactions of glycolysis o Glycolysis uses Rapoport-Lueberi ...
... for prevention and repair of damage done by reactive oxygen species and generation of energy RBCs only generate ATP by glycolysis – ATP used for ion transport across PM (Na+, K+, and Ca2+), phosphorylation of membrane proteins, and priming reactions of glycolysis o Glycolysis uses Rapoport-Lueberi ...
THE GENETIC PROCESS CHAPTER 4
... The discussion thus far describes the conversion of DNA information for the synthesis of proteins. The discussion is incomplete without consideration of another important process, DNA replication. Replication is the process whereby a DNA molecule duplicates to yield identical DNA molecules. The dupl ...
... The discussion thus far describes the conversion of DNA information for the synthesis of proteins. The discussion is incomplete without consideration of another important process, DNA replication. Replication is the process whereby a DNA molecule duplicates to yield identical DNA molecules. The dupl ...
Biostructures and Molecular Modelling in Drug Research
... Molecular modelling makes it possible to construct models of already known molecules, but also unknown or not yet synthesised molecules can be investigated. With molecular modelling it is possible to study the relationships between molecular structure and various properties, and to assist in design ...
... Molecular modelling makes it possible to construct models of already known molecules, but also unknown or not yet synthesised molecules can be investigated. With molecular modelling it is possible to study the relationships between molecular structure and various properties, and to assist in design ...
RNA Helicase Module in an Acetyltransferase That Modifies a
... histone. Could an ancestral acetylase have acted on RNA in the primordial RNA World? If so, there should be traces reminiscent of such a molecule in either eukaryotes or archaea. Indeed, BLAST analysis with E. coli TmcA as a query identified homologous genes containing consecutive DUF699 and Acetylt ...
... histone. Could an ancestral acetylase have acted on RNA in the primordial RNA World? If so, there should be traces reminiscent of such a molecule in either eukaryotes or archaea. Indeed, BLAST analysis with E. coli TmcA as a query identified homologous genes containing consecutive DUF699 and Acetylt ...
CHAPTER 7: Energy for Muscular Activity
... All energy in the human body is derived from the breakdown of three complex nutrients: carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The end result of the breakdown of these substances is the production of various amounts of the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the body. ATP provid ...
... All energy in the human body is derived from the breakdown of three complex nutrients: carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The end result of the breakdown of these substances is the production of various amounts of the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the body. ATP provid ...
Why does lactic acid build up in muscles?
... Why does lactic acid build up in muscles? And why does it cause soreness? January 23, 2006 As our bodies perform strenuous exercise, we begin to breathe faster as we attempt to shuttle more oxygen to our working muscles. The body prefers to generate most of its energy using aerobic methods, meaning ...
... Why does lactic acid build up in muscles? And why does it cause soreness? January 23, 2006 As our bodies perform strenuous exercise, we begin to breathe faster as we attempt to shuttle more oxygen to our working muscles. The body prefers to generate most of its energy using aerobic methods, meaning ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Energy-Releasing Pathways Anaerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the cell cytoplasm that does not use oxygen as the final electron acceptor. Aerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the mitochondria using oxygen as the final electron acceptor. ...
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Energy-Releasing Pathways Anaerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the cell cytoplasm that does not use oxygen as the final electron acceptor. Aerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the mitochondria using oxygen as the final electron acceptor. ...
Topic 3
... A person with coeliac disease has no microvilli in their small intestine. Explain why this person would find it hard to exercise. Use information from the table to help you. ...
... A person with coeliac disease has no microvilli in their small intestine. Explain why this person would find it hard to exercise. Use information from the table to help you. ...
Biotech Lect-10 - ASAB-NUST
... Microbial Biotechnology in Food and Agriculture • reduction in the reliance on chemical treatments to control weeds by engineering herbicide tolerance into crops • production of products that have high yield and enhanced nutritional value ...
... Microbial Biotechnology in Food and Agriculture • reduction in the reliance on chemical treatments to control weeds by engineering herbicide tolerance into crops • production of products that have high yield and enhanced nutritional value ...
Lecture 9
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.