Name AP Chemistry Take Home Quiz – Due Thursday, 1/9/2014
... a. CN-(aq) is a stronger base than C2H3O2-(aq) b. HCN(aq) is a stronger acid than HC2H3O2(aq) c. The conjugate base of CN-(aq) is C2H3O2-(aq) d. The equilibrium constant will increase with an increase in temperature. e. The pH of a solution containing equimolar amounts of CN-(aq) and HC2H3O2(aq) is ...
... a. CN-(aq) is a stronger base than C2H3O2-(aq) b. HCN(aq) is a stronger acid than HC2H3O2(aq) c. The conjugate base of CN-(aq) is C2H3O2-(aq) d. The equilibrium constant will increase with an increase in temperature. e. The pH of a solution containing equimolar amounts of CN-(aq) and HC2H3O2(aq) is ...
Sulfur Metabolism and Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids
... human health. Sulfur metabolism works at the interplay between genetics and epigenetic as well as in the maintain of cell redox homeostasis. Indeed, unbalanced levels of S compounds in the body are actually under investigation as vulnerability factors and/or indicators of impaired cell oxidation sta ...
... human health. Sulfur metabolism works at the interplay between genetics and epigenetic as well as in the maintain of cell redox homeostasis. Indeed, unbalanced levels of S compounds in the body are actually under investigation as vulnerability factors and/or indicators of impaired cell oxidation sta ...
BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Problem Unit Four
... are proteins. Enzymes are important in biological systems not only because they accelerate reactions, but also because they can be regulated, i.e., they can be turned on or off, thus allowing for the reaction rate to be controlled. Enzymes also control the type of reaction which is occurring so that ...
... are proteins. Enzymes are important in biological systems not only because they accelerate reactions, but also because they can be regulated, i.e., they can be turned on or off, thus allowing for the reaction rate to be controlled. Enzymes also control the type of reaction which is occurring so that ...
Higher Human Biology Exemplar Question Paper
... (iii) Granddaughter U and her partner go on to have a son. State the percentage chance of their son having muscular dystrophy. ...
... (iii) Granddaughter U and her partner go on to have a son. State the percentage chance of their son having muscular dystrophy. ...
The Real Story Behind the Amino Acid Leucine
... healthy aging, and overall wellness. On going research is demonstrating the key role that high quality protein, including the amino acid leucine, performs in the process of muscle protein synthesis (MPS). Leucine is a branched chain amino acid that is essential to muscle health. Whey protein is an e ...
... healthy aging, and overall wellness. On going research is demonstrating the key role that high quality protein, including the amino acid leucine, performs in the process of muscle protein synthesis (MPS). Leucine is a branched chain amino acid that is essential to muscle health. Whey protein is an e ...
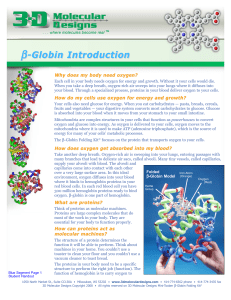
BGFK Blue Segment Student Handout
... α-globin subunits are white.) An oxygen molecule (O2) binds to the iron atom in the heme group so it can be delivered through your blood to your cells. ...
... α-globin subunits are white.) An oxygen molecule (O2) binds to the iron atom in the heme group so it can be delivered through your blood to your cells. ...
05. Clinical enzymology (1)
... A major disadvantage in the use of enzymes for the diagnosis of tissue damage is their lack of specificity to a particular tissue or cell type. Many enzymes are common to more than one tissue. ...
... A major disadvantage in the use of enzymes for the diagnosis of tissue damage is their lack of specificity to a particular tissue or cell type. Many enzymes are common to more than one tissue. ...
1 Packet #3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions How is
... Now that we have set the atomic mass of carbon-12 to 12 amu we can compare other elements to carbon-12 to determine their atomic weights. ...
... Now that we have set the atomic mass of carbon-12 to 12 amu we can compare other elements to carbon-12 to determine their atomic weights. ...
AS and A2 Biology Summary Syllabus and Word Lists
... amylose and amylopectin) and relate their structures to their roles in providing and storing energy (βglucose and cellulose are not required in this topic). 4. Describe how monosaccharides join to form disaccharides (sucrose, lactose and maltose) and polysaccharides (glycogen and amylose) through co ...
... amylose and amylopectin) and relate their structures to their roles in providing and storing energy (βglucose and cellulose are not required in this topic). 4. Describe how monosaccharides join to form disaccharides (sucrose, lactose and maltose) and polysaccharides (glycogen and amylose) through co ...
Structure_prediction_analysis_of_huntingtin_by_Phyre2_20160307
... The PDB generated from the template detailed above, is shown in cartoon format. The protein model is coloured from blue through to red from N to C terminus. The model is shown in 2 orientations, related by a 90 degree rotation in the plane of the screen. The model shows extended helical bundles whi ...
... The PDB generated from the template detailed above, is shown in cartoon format. The protein model is coloured from blue through to red from N to C terminus. The model is shown in 2 orientations, related by a 90 degree rotation in the plane of the screen. The model shows extended helical bundles whi ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... •Insensitive to Cyanide, Azide or CO •Sensitive to SHAM (salicylhydroxamic acid,) •Also found in fungi, trypanosomes & Plasmodium ...
... •Insensitive to Cyanide, Azide or CO •Sensitive to SHAM (salicylhydroxamic acid,) •Also found in fungi, trypanosomes & Plasmodium ...
C 4 plants
... yields energy – Used to pump H+ across the thylakoid membrane – Protons move from stroma into the thylakoid space • Flow of H+ back across the thylakoid membrane – Energizes ATP synthase, which – Enzymatically produces ATP from ADP + Pi • This method of producing ATP is called chemiosmosis • Photosy ...
... yields energy – Used to pump H+ across the thylakoid membrane – Protons move from stroma into the thylakoid space • Flow of H+ back across the thylakoid membrane – Energizes ATP synthase, which – Enzymatically produces ATP from ADP + Pi • This method of producing ATP is called chemiosmosis • Photosy ...
VITAMINS-5
... • PLP plays a vital role in the function of approximately 100 enzymes that catalyze essential chemical reactions in the human body • Coenzyme for • glycogen phosphorylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the release of glucose from stored glycogen • generating glucose from amino acids • Synthesis of • Neur ...
... • PLP plays a vital role in the function of approximately 100 enzymes that catalyze essential chemical reactions in the human body • Coenzyme for • glycogen phosphorylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the release of glucose from stored glycogen • generating glucose from amino acids • Synthesis of • Neur ...
physical setting chemistry
... known, while graphite is a very soft substance. Diamond has a rigid network of bonded atoms. Graphite has atoms bonded in thin layers that are held together by weak forces. Recent experiments have produced new forms of solid carbon called fullerenes. One fullerene, C60, is a spherical, cagelike mole ...
... known, while graphite is a very soft substance. Diamond has a rigid network of bonded atoms. Graphite has atoms bonded in thin layers that are held together by weak forces. Recent experiments have produced new forms of solid carbon called fullerenes. One fullerene, C60, is a spherical, cagelike mole ...
The Permeability Properties of Rat Liver Lysosomes to Nucleosides
... whereas some smaller but less hydrophobic molecules probably cannot. It seems likely therefore that nucleic acids are broken down by lysosomal enzymes to the nucleosides, which then escape intact from the lysosome. It is extremely unlikely that nucleotides could pass across the lysosomal membrane [m ...
... whereas some smaller but less hydrophobic molecules probably cannot. It seems likely therefore that nucleic acids are broken down by lysosomal enzymes to the nucleosides, which then escape intact from the lysosome. It is extremely unlikely that nucleotides could pass across the lysosomal membrane [m ...
Respiratory System Short
... Recall that aerobic respiration is cellular respiration (ATP production) that uses oxygen while anaerobic respiration is cellular respiration (ATP production) that does not require oxygen. Our cells are capable of carrying out either type, but aerobic respiration produces far more ATP (up to 19 time ...
... Recall that aerobic respiration is cellular respiration (ATP production) that uses oxygen while anaerobic respiration is cellular respiration (ATP production) that does not require oxygen. Our cells are capable of carrying out either type, but aerobic respiration produces far more ATP (up to 19 time ...
Crossing borders to bind proteins—a new concept in protein
... molecule to have a dissociation constant that is three orders of magnitude lower than that of the small molecule ligand, the polypeptide needs to contribute less than 20 kJ mol−1 of binding energy at room temperature [16]. That amount of binding energy corresponds to a few hydrophobic contacts betwe ...
... molecule to have a dissociation constant that is three orders of magnitude lower than that of the small molecule ligand, the polypeptide needs to contribute less than 20 kJ mol−1 of binding energy at room temperature [16]. That amount of binding energy corresponds to a few hydrophobic contacts betwe ...
Study Questions for Test # 2
... What is a condensation reaction? A hydrolysis reaction? Which of these is involved with the formation of macromolecules? Which is responsible for the digestion/breakdown of macromolecules? By which are macromolecules produced? In what ways are all 20 amino acids similar? In what way do all 20 differ ...
... What is a condensation reaction? A hydrolysis reaction? Which of these is involved with the formation of macromolecules? Which is responsible for the digestion/breakdown of macromolecules? By which are macromolecules produced? In what ways are all 20 amino acids similar? In what way do all 20 differ ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical
... 4) Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO 2 and water release free energy? A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules are higher energy bonds than those in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electro ...
... 4) Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO 2 and water release free energy? A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules are higher energy bonds than those in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electro ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... final common pathway for oxidation of fuel molecules provides intermediates for biosynthesis ...
... final common pathway for oxidation of fuel molecules provides intermediates for biosynthesis ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.