Bacterial Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... specific protein. If DNA in the nucleus transmits ‘information’ to RNA which then specifies the sequence in which amino acids are joined to form proteins, it is reasonable to hypothesize that the information might involve the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA and RNA and, therefore, that there ...
... specific protein. If DNA in the nucleus transmits ‘information’ to RNA which then specifies the sequence in which amino acids are joined to form proteins, it is reasonable to hypothesize that the information might involve the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA and RNA and, therefore, that there ...
Bacterial Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... specific protein. If DNA in the nucleus transmits ‘information’ to RNA which then specifies the sequence in which amino acids are joined to form proteins, it is reasonable to hypothesize that the information might involve the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA and RNA and, therefore, that there ...
... specific protein. If DNA in the nucleus transmits ‘information’ to RNA which then specifies the sequence in which amino acids are joined to form proteins, it is reasonable to hypothesize that the information might involve the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA and RNA and, therefore, that there ...
Role of mathematics in chemistry
... bonds and lone pairs reflects another level of dichotomy where standard quantum mechanics, in both time-independent and dependent forms, seems ineffective and theories of subdynamics describing open systems appear as more natural tools. Chemistry as a craftsmanship has always been aware of the loose ...
... bonds and lone pairs reflects another level of dichotomy where standard quantum mechanics, in both time-independent and dependent forms, seems ineffective and theories of subdynamics describing open systems appear as more natural tools. Chemistry as a craftsmanship has always been aware of the loose ...
Chapter 4
... that the masses of element Y that combine with a fixed mass of elements X to form two or more different compounds are in the ratios of small whole numbers. • Examples: NO, NO2, N2O, N2O5, etc. ...
... that the masses of element Y that combine with a fixed mass of elements X to form two or more different compounds are in the ratios of small whole numbers. • Examples: NO, NO2, N2O, N2O5, etc. ...
Development of the Ruminant Digestive Tract
... • HCl secretion is inadequate in newborn calf to lower abomasal pH enough for pepsin activity • Calf born with few parietal cells – Number of parietal cells increase 10-fold in 72 hr – Number of parietal cells reach mature level in 31 days ...
... • HCl secretion is inadequate in newborn calf to lower abomasal pH enough for pepsin activity • Calf born with few parietal cells – Number of parietal cells increase 10-fold in 72 hr – Number of parietal cells reach mature level in 31 days ...
Ideas on Cell Respiration Demos
... cleaners. Out of this I fashioned a 3-dimensional spindle to demonstrate mitosis and meiosis phases. Unfortunately, I could not do cytokinesis with this model. This year I challenged my AP students to fashion a 3-dimensional model of meiosis which was movable through the phases. They came up with ex ...
... cleaners. Out of this I fashioned a 3-dimensional spindle to demonstrate mitosis and meiosis phases. Unfortunately, I could not do cytokinesis with this model. This year I challenged my AP students to fashion a 3-dimensional model of meiosis which was movable through the phases. They came up with ex ...
The relative molecular mass, heterogeneity and subunit composition
... (Fig. l a ) for a protein concentration of 0.1 mg/ml in a 0.1 Mborate buffer, pH 7.6 containing 0 . 2 ~ - N a C I .Only very small amounts of dissociation products of the globulin (2S, 4 s and 7 s components) were evident, while associated forms were completely absent. Proteins for sedimentation equ ...
... (Fig. l a ) for a protein concentration of 0.1 mg/ml in a 0.1 Mborate buffer, pH 7.6 containing 0 . 2 ~ - N a C I .Only very small amounts of dissociation products of the globulin (2S, 4 s and 7 s components) were evident, while associated forms were completely absent. Proteins for sedimentation equ ...
The Occurrence and Location of Teichoic Acids in
... the cell, but if they are present in the protoplast membrane or other outer regions of the cell they may be visualized as partners to the wall teichoic acids, the whole system being well suited to such functions as the transport of ions. , Both ribitol and glycerol teichoic acids are found in walls, ...
... the cell, but if they are present in the protoplast membrane or other outer regions of the cell they may be visualized as partners to the wall teichoic acids, the whole system being well suited to such functions as the transport of ions. , Both ribitol and glycerol teichoic acids are found in walls, ...
Instructor`s Guide
... bronchus (plural is bronchi): Also called a bronchial tube, it is a branch of the trachea that conveys air to the lungs. bulk flow: A term describing how substances such as air move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration, and how air is moved in and out of the lungs. cellular resp ...
... bronchus (plural is bronchi): Also called a bronchial tube, it is a branch of the trachea that conveys air to the lungs. bulk flow: A term describing how substances such as air move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration, and how air is moved in and out of the lungs. cellular resp ...
minervini
... Europe (EGEE) and China (CNGrid) Grid infrastructures The goals of the EUChinaGRID are: ...
... Europe (EGEE) and China (CNGrid) Grid infrastructures The goals of the EUChinaGRID are: ...
Lec 16 - RNA and IT`s Structure
... 1,000 to 10.000 different species of mRNA in a cell. These mRNA types differ only in the sequence of their bases and in length. When one gene (cistron) codes for a single mRNA strand the mRNA is said to be monocistronic. In many cases, however, several adjacent cistrons may transcribe an mRNA molecu ...
... 1,000 to 10.000 different species of mRNA in a cell. These mRNA types differ only in the sequence of their bases and in length. When one gene (cistron) codes for a single mRNA strand the mRNA is said to be monocistronic. In many cases, however, several adjacent cistrons may transcribe an mRNA molecu ...
File - thebiotutor.com
... – Amino acids are used to form enzymes and are used as building blocks for other things in the cell – There are 20 different amino acids. – Amino acids are join together to form long chains called Polypeptides. Polypeptides can twist and coil to form proteins 3. Lipids – Made of 1 glycerol and 3 fat ...
... – Amino acids are used to form enzymes and are used as building blocks for other things in the cell – There are 20 different amino acids. – Amino acids are join together to form long chains called Polypeptides. Polypeptides can twist and coil to form proteins 3. Lipids – Made of 1 glycerol and 3 fat ...
Metabolic Acidosis
... L-Lactic Acidosis Overproduction of L-lactic Acid • Net production of L-lactic acid occurs when the body must regenerate ATP without oxygen • 1 H+ is produced per ATP regenerated from glucose • Because a patient will need to regenerate 72 mmol of ATP per minutes, As much as 72 mmol/min of H+ can be ...
... L-Lactic Acidosis Overproduction of L-lactic Acid • Net production of L-lactic acid occurs when the body must regenerate ATP without oxygen • 1 H+ is produced per ATP regenerated from glucose • Because a patient will need to regenerate 72 mmol of ATP per minutes, As much as 72 mmol/min of H+ can be ...
Regulation of Transcription
... of a group of genes (i.e. heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e. metallothionine) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression To achieve high levels of expression, several different transcription factors binding to dif ...
... of a group of genes (i.e. heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e. metallothionine) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression To achieve high levels of expression, several different transcription factors binding to dif ...
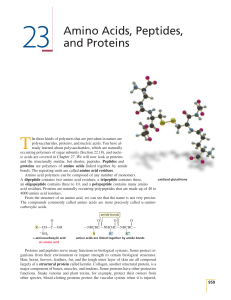
23 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... essential amino acids from our diets because we either cannot synthesize them at all or cannot synthesize them in adequate amounts. For example, we must have a dietary source of phenylalanine because we cannot synthesize benzene rings. However, we do not need tyrosine in our diets, because we can sy ...
... essential amino acids from our diets because we either cannot synthesize them at all or cannot synthesize them in adequate amounts. For example, we must have a dietary source of phenylalanine because we cannot synthesize benzene rings. However, we do not need tyrosine in our diets, because we can sy ...
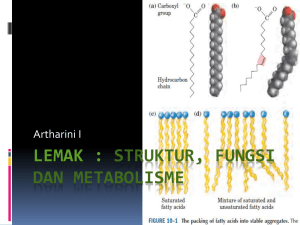
LEMAK : Struktur, Fungsi dan Metabolisme
... Usually R1 and R3 are saturated and R2 is unsaturated Natural fats are mixture of two or more simple triglycerides ...
... Usually R1 and R3 are saturated and R2 is unsaturated Natural fats are mixture of two or more simple triglycerides ...
Energy Metabolism of the Performance Horse. In
... glycogen serves as the major fuel source. The production of lactate is a possible end stage of this anaerobic pathway. ...
... glycogen serves as the major fuel source. The production of lactate is a possible end stage of this anaerobic pathway. ...
Essential Outcomes Biology
... 2) The relationships between living and non-living components of an ecosystem are in flux due to natural changes and human action. (Standard 4) Learning Goals: a) Students will explain that the amount of life an environment can support is limited. ( B 4.1) b) Students will describe how human activit ...
... 2) The relationships between living and non-living components of an ecosystem are in flux due to natural changes and human action. (Standard 4) Learning Goals: a) Students will explain that the amount of life an environment can support is limited. ( B 4.1) b) Students will describe how human activit ...
Biology Revision
... The chain is then folded to form a specific shape: The specific shape of an enzyme enables it to function. Active site of enzyme. A cleft in the protein where a specific substrate ‘fits’ ...
... The chain is then folded to form a specific shape: The specific shape of an enzyme enables it to function. Active site of enzyme. A cleft in the protein where a specific substrate ‘fits’ ...
Hydrothermal Reactions from Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate to Phenol
... On the basis of the observation of the final product phenol and intermittent formic acid and formaldehyde in the hydrothermal reactions, we propose a possible reaction mechanism for phenol formation. Scheme 1 illustrates the main process of the hydrothermal reactions (see details in Supporting Infor ...
... On the basis of the observation of the final product phenol and intermittent formic acid and formaldehyde in the hydrothermal reactions, we propose a possible reaction mechanism for phenol formation. Scheme 1 illustrates the main process of the hydrothermal reactions (see details in Supporting Infor ...
Indole Test - Farmasi Unand
... usually evolved immediately and only tubes not showing gas within 10 sec. Are sealed for longer observation ...
... usually evolved immediately and only tubes not showing gas within 10 sec. Are sealed for longer observation ...
126 EFFECT OF ULTRAVIOLET-B IRRADIATION ON FATTY ACIDS
... (Zverdanovic et al.,2009), degradation of light harvesting proteins (Jr, 2005), changing of protein profile (Abdel-Kareem, 1999), inhibition of enzymes of ...
... (Zverdanovic et al.,2009), degradation of light harvesting proteins (Jr, 2005), changing of protein profile (Abdel-Kareem, 1999), inhibition of enzymes of ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.