Comprehensive Analysis of Amino Acid and Nucleotide
... against protein databases(2-6). Here, we define pseudogenes as disabled copies of genes that do not produce a functional, full-length copy of a protein (7). Operationally, these are identified as regions of the chromosome that are similar to known proteins but contain obvious disablements (such as s ...
... against protein databases(2-6). Here, we define pseudogenes as disabled copies of genes that do not produce a functional, full-length copy of a protein (7). Operationally, these are identified as regions of the chromosome that are similar to known proteins but contain obvious disablements (such as s ...
ETimminsSchiffman_ConsPhys 961KB Feb 13 2013
... proteome. Using information from the recently published Pacific oyster genome, 1,671 proteins ...
... proteome. Using information from the recently published Pacific oyster genome, 1,671 proteins ...
The experiments provide ne~~~den~~~~t the r&rate clewage pathway... of carbon for the synthesis of $tty ack& k‘l...
... Waft, 1965; Leveille atid- Hanson, 19@5a,196&J. On- the basis of these observations, and of the presumed jm~~rmeabil~tyof m~tochon~r~ato palyanions such as citr$tte, it was proposed that e~~rarnito~h~ndria~ citrate is derived from i~trarn~~~~o~l~ia1citrate via the intermediate formation of rr-ketogl ...
... Waft, 1965; Leveille atid- Hanson, 19@5a,196&J. On- the basis of these observations, and of the presumed jm~~rmeabil~tyof m~tochon~r~ato palyanions such as citr$tte, it was proposed that e~~rarnito~h~ndria~ citrate is derived from i~trarn~~~~o~l~ia1citrate via the intermediate formation of rr-ketogl ...
Lysine-Restricted Diet as Adjunct Therapy for Pyridoxine
... single patient with PDE between the ages of 9 and 18 years, despite pyridoxine treatment (Dogan et al. 2012). Standard treatment for inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) affecting catabolic pathways of essential amino acids includes reduction in the substrate of the deficient enzyme through dietary mod ...
... single patient with PDE between the ages of 9 and 18 years, despite pyridoxine treatment (Dogan et al. 2012). Standard treatment for inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) affecting catabolic pathways of essential amino acids includes reduction in the substrate of the deficient enzyme through dietary mod ...
Preface 1 PDF
... Studies of Euglena were instrumental in establishing the contribution of the nuclear and chloroplast genome to the development of chloroplasts. As additional information became available from studies of higher plants and other algae, it became apparent that Euglena was an atypical organism; it had i ...
... Studies of Euglena were instrumental in establishing the contribution of the nuclear and chloroplast genome to the development of chloroplasts. As additional information became available from studies of higher plants and other algae, it became apparent that Euglena was an atypical organism; it had i ...
Nutrition!!!
... Complex carbohydrates (starches) are all derived from plants except for lactose (milk) and glycogen (small amounts from meat) ...
... Complex carbohydrates (starches) are all derived from plants except for lactose (milk) and glycogen (small amounts from meat) ...
pH of the electrophoresis buffer
... • OH group of cellulose interact with biomolecules and results in ‘tailing’ • water absorbing and electrical conductivity capacity of paper depends on its content (96% -cellulose) • Electro osmosis ...
... • OH group of cellulose interact with biomolecules and results in ‘tailing’ • water absorbing and electrical conductivity capacity of paper depends on its content (96% -cellulose) • Electro osmosis ...
Chapter 1 Biology: The Study of Life
... In living things adaptations evolve over time. Adaptation are inherited changes that occur over time to enable an organism to respond to stimuli and better survive IN AN ENVIRONMENT. ...
... In living things adaptations evolve over time. Adaptation are inherited changes that occur over time to enable an organism to respond to stimuli and better survive IN AN ENVIRONMENT. ...
Chapter 1 Biology: The Study of Life
... In living things adaptations evolve over time. Adaptation are inherited changes that occur over time to enable an organism to respond to stimuli and better survive IN AN ENVIRONMENT. ...
... In living things adaptations evolve over time. Adaptation are inherited changes that occur over time to enable an organism to respond to stimuli and better survive IN AN ENVIRONMENT. ...
Poster
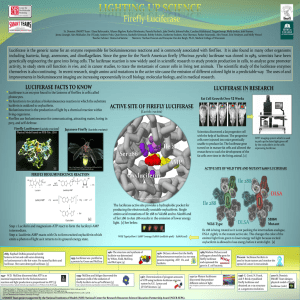
... Luciferase is the generic name for an enzyme responsible for bioluminescence reactions and is commonly associated with fireflies. It is also found in many other organisms including bacteria, fungi, anemones, and dinoflagellates. Since the gene for the North American firefly (Photinus pyralis) lucife ...
... Luciferase is the generic name for an enzyme responsible for bioluminescence reactions and is commonly associated with fireflies. It is also found in many other organisms including bacteria, fungi, anemones, and dinoflagellates. Since the gene for the North American firefly (Photinus pyralis) lucife ...
powerpoint
... III. "Spending" Energy I: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS A. DNA and RNA Structure B. DNA and RNA Function ...
... III. "Spending" Energy I: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS A. DNA and RNA Structure B. DNA and RNA Function ...
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 13:
... The bacteria used to measure GAD activity were grown in a minimal media containing L-glutamate as carbon source (Labidi et al. 1996) instead of proline because GAD was shown in E. coli to be induced by glutamate (Fonda 1985). Enzymatic analysis showed a significant reduction of the activities in the ...
... The bacteria used to measure GAD activity were grown in a minimal media containing L-glutamate as carbon source (Labidi et al. 1996) instead of proline because GAD was shown in E. coli to be induced by glutamate (Fonda 1985). Enzymatic analysis showed a significant reduction of the activities in the ...
Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants
... by the prominent role of inorganic N in many arable soils and the dependence of many crop plants on this N source. It was also, naturally, motivated by the abundance of inorganic N fertilizers for agricultural use. After the widely discussed human perturbation of the global carbon (C) cycle, anthrop ...
... by the prominent role of inorganic N in many arable soils and the dependence of many crop plants on this N source. It was also, naturally, motivated by the abundance of inorganic N fertilizers for agricultural use. After the widely discussed human perturbation of the global carbon (C) cycle, anthrop ...
CHAPTER 6
... acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acetyl-CoA survives two cycles completely, but half of what's left exits the cycle on each turn after that. ...
... acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acetyl-CoA survives two cycles completely, but half of what's left exits the cycle on each turn after that. ...
What Is the Chemical Logic of the TCA Cycle?
... acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acetyl-CoA survives two cycles completely, but half of what's left exits the cycle on each turn after that. ...
... acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acetyl-CoA survives two cycles completely, but half of what's left exits the cycle on each turn after that. ...
chapter 15: answers to selected problems
... Sample Problem 15.5, we found that breaking down myristic acid requires 6 beta oxidation cycles and produces 7 molecules of acetyl-CoA: 6 cycles of beta oxidation produce 6 NADH + 6 FADH2 7 citric acid cycles produce 21 NADH + 7 FADH2 + 7 ATP We make a total of 6 + 21 = 27 molecules of NADH. 27 NADH ...
... Sample Problem 15.5, we found that breaking down myristic acid requires 6 beta oxidation cycles and produces 7 molecules of acetyl-CoA: 6 cycles of beta oxidation produce 6 NADH + 6 FADH2 7 citric acid cycles produce 21 NADH + 7 FADH2 + 7 ATP We make a total of 6 + 21 = 27 molecules of NADH. 27 NADH ...
biosynthesis
... 2. Transport FA into the cytoplasma of target cell - FA are released into the circulation (albumin bound NEFA) - transport through the cell membrane ...
... 2. Transport FA into the cytoplasma of target cell - FA are released into the circulation (albumin bound NEFA) - transport through the cell membrane ...
Enzymes - Science Prof Online
... Series of chemical reactions that regulate the concentration of substances within the organism. • Has order, like an assembly line. • Molecules are altered in a series of steps. • Use many smaller steps rather than one big step. ...
... Series of chemical reactions that regulate the concentration of substances within the organism. • Has order, like an assembly line. • Molecules are altered in a series of steps. • Use many smaller steps rather than one big step. ...
5. Stoichiometry - Sakshi Education
... What ever the method a compound is prepared, it contains the same elements combined in a fixed ratio by weight Eg: CO2 can be prepared by many ways i.e., by combining of carbon with oxygen or by heating lime stone etc., but what ever the method CO2 is prepared; The ratio of carbon and oxygen by mass ...
... What ever the method a compound is prepared, it contains the same elements combined in a fixed ratio by weight Eg: CO2 can be prepared by many ways i.e., by combining of carbon with oxygen or by heating lime stone etc., but what ever the method CO2 is prepared; The ratio of carbon and oxygen by mass ...
Lect 6 - BIDD - National University of Singapore
... • The number of possible structures that proteins may possess is extremely large, as highlighted by the Levinthal paradox • The physical basis of protein structural stability is not fully understood. • The primary sequence may not fully specify the tertiary structure. – chaperones ...
... • The number of possible structures that proteins may possess is extremely large, as highlighted by the Levinthal paradox • The physical basis of protein structural stability is not fully understood. • The primary sequence may not fully specify the tertiary structure. – chaperones ...
SEPARATION OF MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANES OF
... involved in oxidative phosphorylation (1), carbohydrate metabolism (2), protein metabolism (3), ...
... involved in oxidative phosphorylation (1), carbohydrate metabolism (2), protein metabolism (3), ...
Enzymes
... • Virtually all chemical reactions have an energy barrier separating the reactants and the products. • This barrier, called the free energy of activation, is the energy difference between that of the reactants and a high-energy intermediate that occurs during the formation of product. • For example, ...
... • Virtually all chemical reactions have an energy barrier separating the reactants and the products. • This barrier, called the free energy of activation, is the energy difference between that of the reactants and a high-energy intermediate that occurs during the formation of product. • For example, ...
The Additive Screen MD1-11
... There are 24 unique reagents supplied in the kit. The concentrations of the reagents have been designed to allow minimum dilution of the sample drop, and are sufficiently concentrated that vapour diffusion experiments can be carried out in as little as a 2.5µl drop. All additives have to be added to ...
... There are 24 unique reagents supplied in the kit. The concentrations of the reagents have been designed to allow minimum dilution of the sample drop, and are sufficiently concentrated that vapour diffusion experiments can be carried out in as little as a 2.5µl drop. All additives have to be added to ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.