Plant derived medicines to treat cancer
... The sequence of the amino acids in the enzyme’s polypeptide chain(s) could be found, giving the primary structure of the polypeptide(s). The primary structure of the polypeptide is determined by the sequence of bases in the mRNA molecule that was translated into the polypeptide at the ribosome. This ...
... The sequence of the amino acids in the enzyme’s polypeptide chain(s) could be found, giving the primary structure of the polypeptide(s). The primary structure of the polypeptide is determined by the sequence of bases in the mRNA molecule that was translated into the polypeptide at the ribosome. This ...
Chapter 2
... • Matter is made up of elements • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
... • Matter is made up of elements • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
Chance and Necessity in the Selection of Nucleic Acid Catalysts
... molecules by iterative rounds of selection and amplification.3,4 This process is called in vitro selection, or SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment;3 Figure 1). The RNA receptors that result from such experiments are often referred to, at least by those who do not object ...
... molecules by iterative rounds of selection and amplification.3,4 This process is called in vitro selection, or SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment;3 Figure 1). The RNA receptors that result from such experiments are often referred to, at least by those who do not object ...
Chapter 5 Slides
... Proteins Proteins may be "conjugated" with other chemical groups • If the non-amino acid part of the protein is important to its function, it is called a prosthetic group. • Be familiar with the terms: glycoprotein, lipoprotein, nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein, metalloprotein, hemoprotein, flavoprotei ...
... Proteins Proteins may be "conjugated" with other chemical groups • If the non-amino acid part of the protein is important to its function, it is called a prosthetic group. • Be familiar with the terms: glycoprotein, lipoprotein, nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein, metalloprotein, hemoprotein, flavoprotei ...
The Copper Cycle
... Acids and Bases In general, acids are compounds that produce hydrogen ions (H+), also called protons. Acids can also be defined as substances that produce hydronium ions (H3O+), which is a hydrogen ion combined with a water molecule: H+(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq). The two equations below both represent ...
... Acids and Bases In general, acids are compounds that produce hydrogen ions (H+), also called protons. Acids can also be defined as substances that produce hydronium ions (H3O+), which is a hydrogen ion combined with a water molecule: H+(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq). The two equations below both represent ...
galanin - Personal Home Pages (at UEL)
... •Galanin is a 29 amino acid neuro-peptide has inhibitory actions •Exerts biological effects in mammals such as feeding, insulin release and growth hormone ...
... •Galanin is a 29 amino acid neuro-peptide has inhibitory actions •Exerts biological effects in mammals such as feeding, insulin release and growth hormone ...
Study of the arginine repressor in different organisms
... and are involved in activation of several catabolic pathways. The arginine repressor of Streptomyces clavuligerus participates in regulation of clavulanic acid production. The Escherichia coli repressor is involved in the site-specific DNA recombination mechanism that resolves multimeric forms of th ...
... and are involved in activation of several catabolic pathways. The arginine repressor of Streptomyces clavuligerus participates in regulation of clavulanic acid production. The Escherichia coli repressor is involved in the site-specific DNA recombination mechanism that resolves multimeric forms of th ...
Class_X–Science__term_I
... Mohan took pure water for the electrolytic decomposition of water but did not see any bubbles near the electrodes. Explain why? Rancidity is a process used for spoiling of cooked food materials like vegetables etc. When kept for long time in open. How can you prevent such process to proceed? Give an ...
... Mohan took pure water for the electrolytic decomposition of water but did not see any bubbles near the electrodes. Explain why? Rancidity is a process used for spoiling of cooked food materials like vegetables etc. When kept for long time in open. How can you prevent such process to proceed? Give an ...
03-232 Biochemistry Exam II - 2013 Name:________________________
... substrate (2 pts) The valine sidechain in the wild-type will show a non-polar (hydrophobic effect) interaction with the Phe on the substrate. This is more favourable than the interaction with the Aspartic acid in the mutant (1 pt) iii)To determine the effectiveness of drug A and drug B in inhibiting ...
... substrate (2 pts) The valine sidechain in the wild-type will show a non-polar (hydrophobic effect) interaction with the Phe on the substrate. This is more favourable than the interaction with the Aspartic acid in the mutant (1 pt) iii)To determine the effectiveness of drug A and drug B in inhibiting ...
1 - Cardiovascular Research
... We and others propose that interruptions in glucose and FA metabolism in the heart are the geneses of diabetic cardiomyopathy.8,26,38,39 Following diabetes, myocardial GLUT4 gene and protein expression are reduced.8,27 However, hyperglycaemia sustains glucose uptake by the diabetic heart, such that ...
... We and others propose that interruptions in glucose and FA metabolism in the heart are the geneses of diabetic cardiomyopathy.8,26,38,39 Following diabetes, myocardial GLUT4 gene and protein expression are reduced.8,27 However, hyperglycaemia sustains glucose uptake by the diabetic heart, such that ...
`A` LEVEL H2 CHEMISTRY ORGANIC REACTIONS SUMMARY By
... An atom contains equal number of protons and electrons and is electrically neutral. 1.1 Proton and Neutron Numbers An atom can be represented as AZX, where X is the symbol of the element. Z = number of protons = number of electrons (proton number or atomic number) A = number of protons + number of n ...
... An atom contains equal number of protons and electrons and is electrically neutral. 1.1 Proton and Neutron Numbers An atom can be represented as AZX, where X is the symbol of the element. Z = number of protons = number of electrons (proton number or atomic number) A = number of protons + number of n ...
Recombinant Mouse Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF)
... Stability: Lyophilized Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C. For long term storage it is ...
... Stability: Lyophilized Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C. For long term storage it is ...
Metabolic Flux Profiling of Reaction Modules in Liver Drug
... of specific reaction clusters, in this case xenobiotic transformation. At its core, this framework consists of an algorithm for top-down partitioning of directed graphs with non-uniform edge weight distributions. The core algorithm is further augmented with metabolic flux profiling and stoichiometri ...
... of specific reaction clusters, in this case xenobiotic transformation. At its core, this framework consists of an algorithm for top-down partitioning of directed graphs with non-uniform edge weight distributions. The core algorithm is further augmented with metabolic flux profiling and stoichiometri ...
copy_of_secstruc
... DSSP: secondary structure assignment from PDB (Kabsch-Sander, 1983) • H = alpha helix • B = residue in isolated beta-bridge • E = extended strand, participates in beta ladder • G = 3-helix (3/10 helix) • I = 5 helix (pi helix) ...
... DSSP: secondary structure assignment from PDB (Kabsch-Sander, 1983) • H = alpha helix • B = residue in isolated beta-bridge • E = extended strand, participates in beta ladder • G = 3-helix (3/10 helix) • I = 5 helix (pi helix) ...
PDF - Science Matters
... Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure function relationship in which the way something is designed and built contributes to its ability to perform specific functions; f ...
... Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure function relationship in which the way something is designed and built contributes to its ability to perform specific functions; f ...
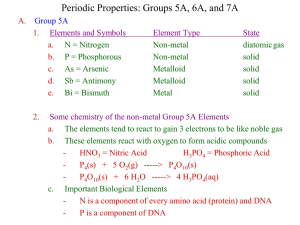
Periodic Properties II PreLab
... b. 20% of the atmosphere and 50% of the crust is O (by mass) c. These elements react with oxygen to form acidic compounds d. Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) is the largest volume chemical used in industry - S(s) + O2(g) -----> SO2(g) - SO2(g) + H2O(l) -----> H2SO3(aq) = sulfurous acid e. We will be burning S( ...
... b. 20% of the atmosphere and 50% of the crust is O (by mass) c. These elements react with oxygen to form acidic compounds d. Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) is the largest volume chemical used in industry - S(s) + O2(g) -----> SO2(g) - SO2(g) + H2O(l) -----> H2SO3(aq) = sulfurous acid e. We will be burning S( ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-12
... Aerobic metabolism provides most ATP needed for contraction At peak activity, anaerobic glycolysis needed to generate ATP Creatine phosphate; ATP and Glycogen; 15 billion thick/fiber; each one 2500 molecules of ATP/second; thousands of muscle fibers per muscle Cell 3.75 10(16) power ATP mole ...
... Aerobic metabolism provides most ATP needed for contraction At peak activity, anaerobic glycolysis needed to generate ATP Creatine phosphate; ATP and Glycogen; 15 billion thick/fiber; each one 2500 molecules of ATP/second; thousands of muscle fibers per muscle Cell 3.75 10(16) power ATP mole ...
A Review on Bio-butyric Acid Production and its Optimization
... activities of PTB and independent lactate dehydrogenase (iLDH), and increased activities of PTA and LDH (Zhu and Yang, 2003). In butyrate-producing strains, PTA, AK, PTB, BK, iLDH, and LDH are the main enzymes relevant to acetate, butyrate, and lactate production. Their products distribution is affe ...
... activities of PTB and independent lactate dehydrogenase (iLDH), and increased activities of PTA and LDH (Zhu and Yang, 2003). In butyrate-producing strains, PTA, AK, PTB, BK, iLDH, and LDH are the main enzymes relevant to acetate, butyrate, and lactate production. Their products distribution is affe ...
Chem 350 – thermo problems Key 1. How many meters of stairway
... The unfolding of a protein is like the melting of an organic crystal in several ways. In a crystal, individual units, e.g. individual urea molecules, are packed very close to each other, forming a lattice. As urea molecules are uncharged, a urea crystal must be held together by van der Waals interac ...
... The unfolding of a protein is like the melting of an organic crystal in several ways. In a crystal, individual units, e.g. individual urea molecules, are packed very close to each other, forming a lattice. As urea molecules are uncharged, a urea crystal must be held together by van der Waals interac ...
and related proteins three-dimensional structure in a large family of
... yses combining sequence alignment with a structural superposition of a few members of the family of proteins have been carried out forother homologous families, notably globins (Lesk & Chothia, 1980), serine proteases (Greer, 1990), and, very recently, subtilisin-like proteins (Siezen et al., 1991). ...
... yses combining sequence alignment with a structural superposition of a few members of the family of proteins have been carried out forother homologous families, notably globins (Lesk & Chothia, 1980), serine proteases (Greer, 1990), and, very recently, subtilisin-like proteins (Siezen et al., 1991). ...
Raman Spectroscopy
... visible and ultraviolet region which lie between 8000 2000 Å (800-200 nm) as already mentioned above. In these cases, the light energy absorbed is stored within the substance and then used for bringing about the reaction. A large number of different types of reactions can be brought about by exposur ...
... visible and ultraviolet region which lie between 8000 2000 Å (800-200 nm) as already mentioned above. In these cases, the light energy absorbed is stored within the substance and then used for bringing about the reaction. A large number of different types of reactions can be brought about by exposur ...
Mass Spectrometry-Grade Endoproteinases
... Reduction and alkylation of cystine residues using dithiothreitol (DTT) and iodoacetamide, respectively, will minimize the appearance of unknown masses from disulfide bond formation and side-chain modification, improving detection of cysteine-containing peptides. Alkylation with iodoacetamide increa ...
... Reduction and alkylation of cystine residues using dithiothreitol (DTT) and iodoacetamide, respectively, will minimize the appearance of unknown masses from disulfide bond formation and side-chain modification, improving detection of cysteine-containing peptides. Alkylation with iodoacetamide increa ...
Cis-trans peptide variations in structurally similar proteins.
... The values of ω are associated with the other backbone dihedrals and a strict correlation was observed with the adjacent φ angle (Esposito et al. 2005). A strong association between the side chain and backbone conformation has also been noted for the cis conformation (Pal and Chakrabarti 1999). Loca ...
... The values of ω are associated with the other backbone dihedrals and a strict correlation was observed with the adjacent φ angle (Esposito et al. 2005). A strong association between the side chain and backbone conformation has also been noted for the cis conformation (Pal and Chakrabarti 1999). Loca ...
Reaction Mechanisms of Mononuclear Non
... in 1992, and pursued graduate studies at Iowa State University of Science and Technology with Professor James H. Espenson (Ph.D., 1996). Following an NIH postdoctoral fellowship with Professor Harry B. Gray at Caltech, he joined the faculty of the University of California, Los Angeles. In 2003, he m ...
... in 1992, and pursued graduate studies at Iowa State University of Science and Technology with Professor James H. Espenson (Ph.D., 1996). Following an NIH postdoctoral fellowship with Professor Harry B. Gray at Caltech, he joined the faculty of the University of California, Los Angeles. In 2003, he m ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.