Chapter 15
... • Early ideas to explain how genes work came from studying human diseases • Archibald Garrod – 1902 – Recognized that alkaptonuria is inherited via a recessive allele – Proposed that patients with the disease lacked a particular enzyme ...
... • Early ideas to explain how genes work came from studying human diseases • Archibald Garrod – 1902 – Recognized that alkaptonuria is inherited via a recessive allele – Proposed that patients with the disease lacked a particular enzyme ...
Krebs Cycle
... to CO2 with concomitant release of NADH, FADH2, and GTP - Such oxidation of acetyl groups occurs via a “cycle” rather than a “pathway”—since both the substrate and the product are identical (oxaloacetate), or simply put, the substrate ultimately cycles to itself in a series of reactions—this is in c ...
... to CO2 with concomitant release of NADH, FADH2, and GTP - Such oxidation of acetyl groups occurs via a “cycle” rather than a “pathway”—since both the substrate and the product are identical (oxaloacetate), or simply put, the substrate ultimately cycles to itself in a series of reactions—this is in c ...
A MODEL FOR THE PROTEOLYTIC REGULATION OF
... abundance of LpxC is regulated via FtsH cleavage (Sorensen et al., 1996) which has a direct effect on the cell’s generation time. In experiments conducted by Schakermann et al. (2013), they reported half life values for LpxC presumably due to FtsH activity under conditions that results in different ...
... abundance of LpxC is regulated via FtsH cleavage (Sorensen et al., 1996) which has a direct effect on the cell’s generation time. In experiments conducted by Schakermann et al. (2013), they reported half life values for LpxC presumably due to FtsH activity under conditions that results in different ...
Supplementary Figure 1
... unit. Evidently, UbS27a domains are less conserved than ribosomal S27a domains or homologs to SUMO1, despite the presence of a hypervariable loop at the N-terminus of SUMO1. Particularly indicative of a high rate of mutations or polymorphisms is the relatively large divergence between species that a ...
... unit. Evidently, UbS27a domains are less conserved than ribosomal S27a domains or homologs to SUMO1, despite the presence of a hypervariable loop at the N-terminus of SUMO1. Particularly indicative of a high rate of mutations or polymorphisms is the relatively large divergence between species that a ...
Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4)
... Titration is an analytical procedure where the amount of an unknown substance is determined by the addition of a standard solution (a solution with a known concentration) until the equivalence point is reached. The equivalence point is reached when stoichiometrically equal amounts of each reactant h ...
... Titration is an analytical procedure where the amount of an unknown substance is determined by the addition of a standard solution (a solution with a known concentration) until the equivalence point is reached. The equivalence point is reached when stoichiometrically equal amounts of each reactant h ...
Super secondary structure (Motif)
... 5. EF hand is two helices connected by a loop that contains residues to coordinate calcium ion (Ca2+) Name refers to the helices E and F in parvalbumin Loop contains 12 amino acids, 5 bind Ca++ ...
... 5. EF hand is two helices connected by a loop that contains residues to coordinate calcium ion (Ca2+) Name refers to the helices E and F in parvalbumin Loop contains 12 amino acids, 5 bind Ca++ ...
Fatty acid and phospholipid metabolism in prokaryotes
... mutagens in combination with a battery of clever selection and screening techniques [7]. Such mutations generally fall into one of two classes. Firstly, they may confer an auxotrophy on a strain, such as a requirement for unsaturated fatty acids or glycerol phosphate. Such mutants have generally los ...
... mutagens in combination with a battery of clever selection and screening techniques [7]. Such mutations generally fall into one of two classes. Firstly, they may confer an auxotrophy on a strain, such as a requirement for unsaturated fatty acids or glycerol phosphate. Such mutants have generally los ...
ENZYMES: PROPERTIES OF B
... a molecule and the type of environment in which a molecule is found (gaseous, aqueous, a lipid bilayer, etc.). An important feature of molecular modeling programs is the ability to change aspects of the molecule being studied. For example, it is possible to add, remove, and alter specific atoms and ...
... a molecule and the type of environment in which a molecule is found (gaseous, aqueous, a lipid bilayer, etc.). An important feature of molecular modeling programs is the ability to change aspects of the molecule being studied. For example, it is possible to add, remove, and alter specific atoms and ...
Peptide Chemistry and Drug Design Brochure
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2936163/ ...
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2936163/ ...
Towards Controlling the Glycoform: A Model Framework Linking
... glycans and the glycoform on the performance of biotherapeutics is not only limited to antibodies but also extends to other industrially relevant glycoproteins such as IFN-β and EPO amongst others [9]. Current Problems Resulting from Glycans and Causes of Variation A well-defined product may have co ...
... glycans and the glycoform on the performance of biotherapeutics is not only limited to antibodies but also extends to other industrially relevant glycoproteins such as IFN-β and EPO amongst others [9]. Current Problems Resulting from Glycans and Causes of Variation A well-defined product may have co ...
Gene Section CYP7A1 (cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily A, polypeptide 1)
... demonstrated a crucial role for this enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis. Mice and humans with cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase deficiency exhibit, however, different phenotypes (Norlin and Wikvall, 2007). Several mechanisms for regulation of CYP7A1 have been described (Chiang, 2004). Bile acids inhibit ...
... demonstrated a crucial role for this enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis. Mice and humans with cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase deficiency exhibit, however, different phenotypes (Norlin and Wikvall, 2007). Several mechanisms for regulation of CYP7A1 have been described (Chiang, 2004). Bile acids inhibit ...
Document
... Expression is regulated by the needs of the cell and the environment as needed (not continuously). Constitutive genes Continuously expressed. ...
... Expression is regulated by the needs of the cell and the environment as needed (not continuously). Constitutive genes Continuously expressed. ...
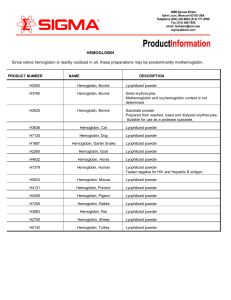
HEMOGLOBIN Since native hemoglobin is readily oxidized in air
... Hemoglobin is the major component of red blood cells, and is responsible for their red color. Its normal concentration in erythrocytes is 34%. Hemoglobin is the most important respiratory protein of vertebrates by virtue of its ability to transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues, and to facil ...
... Hemoglobin is the major component of red blood cells, and is responsible for their red color. Its normal concentration in erythrocytes is 34%. Hemoglobin is the most important respiratory protein of vertebrates by virtue of its ability to transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues, and to facil ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Observe the conversion of potential energy to kinetic (heat) energy that is evidenced by an increase in the temperature of water caused by burning a food source. • Build the molecular model of cellular respiration reactants and products to demonstrate the conservation of matter (atoms) in the proc ...
... • Observe the conversion of potential energy to kinetic (heat) energy that is evidenced by an increase in the temperature of water caused by burning a food source. • Build the molecular model of cellular respiration reactants and products to demonstrate the conservation of matter (atoms) in the proc ...
Maritimibacter alkaliphilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a genome
... designated HTCC2654T, was isolated from the western Sargasso Sea by using a dilution-toextinction culturing method. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain HTCC2654T belonged to the Roseobacter clade of the order Rhodobacterales. The 16S rRNA gene sequence similarit ...
... designated HTCC2654T, was isolated from the western Sargasso Sea by using a dilution-toextinction culturing method. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain HTCC2654T belonged to the Roseobacter clade of the order Rhodobacterales. The 16S rRNA gene sequence similarit ...
Biochemical Screening of Pyrimidine
... Orotic acid (uracil-4-carboxylic acid) has been the livers were quickly excised and placed in a chilled bath of isotonic saline solution. A 20 per cent homogenate in chilled shown under both in vivo and in vitro conditions, 0.25 M sucrose was made with the use of an all-glass Potterin both microorga ...
... Orotic acid (uracil-4-carboxylic acid) has been the livers were quickly excised and placed in a chilled bath of isotonic saline solution. A 20 per cent homogenate in chilled shown under both in vivo and in vitro conditions, 0.25 M sucrose was made with the use of an all-glass Potterin both microorga ...
IGCSE® Chemistry - Hodder Plus Home
... (c) the average mass of the isotopes of an element [1] compared with one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12 [1] (d) Ar of Cu = (63 × 69.1 + 65 × 30.9)/100 [1] = 63.6 [1] 6 (a) aluminium + chlorine → aluminium chloride [1] 2Al(s) + 3Cl2(g) → 2AlCl3(s) [1 for reactants, 1 for product ...
... (c) the average mass of the isotopes of an element [1] compared with one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12 [1] (d) Ar of Cu = (63 × 69.1 + 65 × 30.9)/100 [1] = 63.6 [1] 6 (a) aluminium + chlorine → aluminium chloride [1] 2Al(s) + 3Cl2(g) → 2AlCl3(s) [1 for reactants, 1 for product ...
nucleosome antigen - Arotec Diagnostics
... the product will bind autoantibodies to nucleosome antigen. ...
... the product will bind autoantibodies to nucleosome antigen. ...
Identification and Quantification of Oxidized Proteins
... Different forms of oxidative modification have different functional consequences * Met is highly susceptible but oxidation often does not affect protein function * Carbonyls are often associated with dysfunction but may require more stringent oxidative conditions ...
... Different forms of oxidative modification have different functional consequences * Met is highly susceptible but oxidation often does not affect protein function * Carbonyls are often associated with dysfunction but may require more stringent oxidative conditions ...
The Mole
... Atomic, molecular, and formula masses are all relative numbers. That is, they contain no units. Saying that the atomic mass of magnesium is 24 means that its atoms are twice as heavy as those of some other element (carbon) with an atomic mass of 12. It is possible, however, to assign units to atomic ...
... Atomic, molecular, and formula masses are all relative numbers. That is, they contain no units. Saying that the atomic mass of magnesium is 24 means that its atoms are twice as heavy as those of some other element (carbon) with an atomic mass of 12. It is possible, however, to assign units to atomic ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.