What is similarity and homology? What is a good match? How does
... Similarity and homology Two very important basic concepts: • Similarity: Degree of likeness between two sequences, usually expressed as a percentage of similar (or identical) residues over a given length of the alignment. Can usually be easily calculated. • Homology: Statement about common evolut ...
... Similarity and homology Two very important basic concepts: • Similarity: Degree of likeness between two sequences, usually expressed as a percentage of similar (or identical) residues over a given length of the alignment. Can usually be easily calculated. • Homology: Statement about common evolut ...
UNIT 1 NUTRITION, FEEDING, DIGESTION
... Generally all proteins are made from about 20 different amino acids in various combinations. However, it is not necessary to supply.al1 the 20 amino acids. Some can be formed in the body, using other amino acids but others have to be supplied through diet because they are not formed in the body. The ...
... Generally all proteins are made from about 20 different amino acids in various combinations. However, it is not necessary to supply.al1 the 20 amino acids. Some can be formed in the body, using other amino acids but others have to be supplied through diet because they are not formed in the body. The ...
Co-translational Folding
... Biosynthetic folding, proceeding through a series of intermediate structures (I1, I2, I3), avoids certain kinetic traps, such as Mi in the Figure, which are encountered during refolding of denatured protein. In the absence of cotranslational folding (Iu1 , Iu2 , Iu3 ), the fully synthesized polypept ...
... Biosynthetic folding, proceeding through a series of intermediate structures (I1, I2, I3), avoids certain kinetic traps, such as Mi in the Figure, which are encountered during refolding of denatured protein. In the absence of cotranslational folding (Iu1 , Iu2 , Iu3 ), the fully synthesized polypept ...
Common Pet Food Ingredients
... Beef & bone meal is a byproduct made from beef parts which are not suitable for human consumption. It can incorporate the entire cow, including the bone -- although the quality cuts of meat are always removed before beef & bone meal is made. Beef Broth: Beef broth is obtained by cooking beef, inclu ...
... Beef & bone meal is a byproduct made from beef parts which are not suitable for human consumption. It can incorporate the entire cow, including the bone -- although the quality cuts of meat are always removed before beef & bone meal is made. Beef Broth: Beef broth is obtained by cooking beef, inclu ...
Probing the origins of glutathione biosynthesis through biochemical
... juncea) provided information about the active site architecture of a group 3 enzyme [16], but no functional studies examining the contributions of active-site residues for either these or any GCLs have been reported. Identification of amino acid residues that alter the kinetic properties of SynGCL i ...
... juncea) provided information about the active site architecture of a group 3 enzyme [16], but no functional studies examining the contributions of active-site residues for either these or any GCLs have been reported. Identification of amino acid residues that alter the kinetic properties of SynGCL i ...
Genetic Disorders Leading to Hypoglycaemia
... Hypoglycaemia is common in clinical practice and can be a manifestation of many underlying conditions. It is a biochemical finding and not a diagnosis. Therefore an understanding of the molecular mechanisms that lead to hypoglycaemia is important. At a genetic level, hypoglycaemia can be due to many ...
... Hypoglycaemia is common in clinical practice and can be a manifestation of many underlying conditions. It is a biochemical finding and not a diagnosis. Therefore an understanding of the molecular mechanisms that lead to hypoglycaemia is important. At a genetic level, hypoglycaemia can be due to many ...
Use of mitochondrial electron transport mutants
... sylvestris mutant, CMSII, relating to the role of mitochondrial redox state in leaf metabolism and defence. Leaf mitochondria play key roles in photosynthesis, e.g. glycine decarboxylation in C3 plants and malate decarboxylation in certain C4 plants. Moreover, leaf mitochondrial function will depend ...
... sylvestris mutant, CMSII, relating to the role of mitochondrial redox state in leaf metabolism and defence. Leaf mitochondria play key roles in photosynthesis, e.g. glycine decarboxylation in C3 plants and malate decarboxylation in certain C4 plants. Moreover, leaf mitochondrial function will depend ...
Molecular and Structural Characterization of
... and 60 kD (TaGlu1b) that correspond to the two bands of the natural glucosidases purified from wheat shoots (Sue et al., 2000b). The same difference in mobility was evident with the N-His-tagged glucosidases (Fig. 3A). The precise Mr of N-His-tagged TaGlu1a and TaGlu1b was determined by mass spectro ...
... and 60 kD (TaGlu1b) that correspond to the two bands of the natural glucosidases purified from wheat shoots (Sue et al., 2000b). The same difference in mobility was evident with the N-His-tagged glucosidases (Fig. 3A). The precise Mr of N-His-tagged TaGlu1a and TaGlu1b was determined by mass spectro ...
UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase controls the activity of proceeding
... in almost 100% UDP-Glc.6 In the cellular context, the hydrolysis of the energy-rich pyrophosphate by phosphatases or pyrophosphate dependent proton pumps drives the biosynthesis pathway toward the UDP-sugars. USP is encoded by a single copy gene in Arabidopsis (At5g52560). Attempts to obtain homozyg ...
... in almost 100% UDP-Glc.6 In the cellular context, the hydrolysis of the energy-rich pyrophosphate by phosphatases or pyrophosphate dependent proton pumps drives the biosynthesis pathway toward the UDP-sugars. USP is encoded by a single copy gene in Arabidopsis (At5g52560). Attempts to obtain homozyg ...
pdf-download
... corresponding back reaction. One example is the racemic resolution of amino acids like methionine to the desired enantiopure L-compounds. Another class of enzymes that can be found regularly in commercialised processes are the so-called oxidoreductases, enzymes that perform oxidation or reduction re ...
... corresponding back reaction. One example is the racemic resolution of amino acids like methionine to the desired enantiopure L-compounds. Another class of enzymes that can be found regularly in commercialised processes are the so-called oxidoreductases, enzymes that perform oxidation or reduction re ...
Propionate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... Aerobic, glucose-limited chemostat of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS 8066 cometabolized propionate when this compound was added t o the reservoir medium. Co-metabolism of propionate led to an increase of the biomass and protein yields. Attempts to grow 5. cerevisiae on propionate as a sole source of c ...
... Aerobic, glucose-limited chemostat of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS 8066 cometabolized propionate when this compound was added t o the reservoir medium. Co-metabolism of propionate led to an increase of the biomass and protein yields. Attempts to grow 5. cerevisiae on propionate as a sole source of c ...
Chapter 2 - Carbon dioxide assimilation and respiration
... photosynthesis, that contrasted with the vast majority of other vascular plants. These included an unusual leaf anatomy, substantially higher rates of photosynthesis and growth, higher temperature and light optima for photosynthesis, a much higher water use efficiency, and a very low CO2 compensatio ...
... photosynthesis, that contrasted with the vast majority of other vascular plants. These included an unusual leaf anatomy, substantially higher rates of photosynthesis and growth, higher temperature and light optima for photosynthesis, a much higher water use efficiency, and a very low CO2 compensatio ...
Here
... An organic compound consists of molecules made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. There can be other atoms – for example, nitrogen, sulfur. 1. Acetylsalicylic acid, the common mild pain reliever, is a derivative of the natural product, salicin, obtained from willow bark. 2. Morphine, obt ...
... An organic compound consists of molecules made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. There can be other atoms – for example, nitrogen, sulfur. 1. Acetylsalicylic acid, the common mild pain reliever, is a derivative of the natural product, salicin, obtained from willow bark. 2. Morphine, obt ...
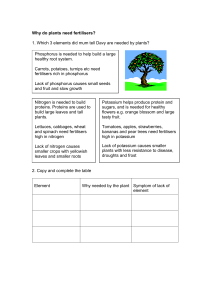
Fertilisers
... phosphate(( NH4)3 PO4 ) and potassium chloride (KCl). Some examples of brand name fertilisers are listed in the table along with their NPK ...
... phosphate(( NH4)3 PO4 ) and potassium chloride (KCl). Some examples of brand name fertilisers are listed in the table along with their NPK ...
Glucose Utilization of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle
... (ATP) that are required, and adequate oxygenation is necessary for the efficient production of these energy stores. Work in our laboratory [6, 7] has demonstrated that skeletal muscle fiber groups from fetal and neonatal rhesus monkeys {Macaca mulatto) have a higher oxygen consumption and CO2 produc ...
... (ATP) that are required, and adequate oxygenation is necessary for the efficient production of these energy stores. Work in our laboratory [6, 7] has demonstrated that skeletal muscle fiber groups from fetal and neonatal rhesus monkeys {Macaca mulatto) have a higher oxygen consumption and CO2 produc ...
INTRODUCTION
... mitochondrial compartments, many associate with partner polypeptides and with prosthetic groups to produce complexes. In the case of the respiratory chain complexes and ATP there is the added complication in that these are made up not only of nuclear encoded proteins but ones coded on mtDNA and made ...
... mitochondrial compartments, many associate with partner polypeptides and with prosthetic groups to produce complexes. In the case of the respiratory chain complexes and ATP there is the added complication in that these are made up not only of nuclear encoded proteins but ones coded on mtDNA and made ...
Cytochrome P450 - Spektrum der Wissenschaft
... NADH-dependent ferredoxin reductase (FdR). It was shown by southern hybridisation that the three genes of the P450 system are localised on the native plasmid pAC450 of A. sp. EB104. They are organised in a single operon together with a putative transcription regulator of the AraC/XylS family. To exp ...
... NADH-dependent ferredoxin reductase (FdR). It was shown by southern hybridisation that the three genes of the P450 system are localised on the native plasmid pAC450 of A. sp. EB104. They are organised in a single operon together with a putative transcription regulator of the AraC/XylS family. To exp ...
Cisplatin in vivo influence on lipid content of chromatin on rat brain
... drug cisplatin. It was known for a long time that cell nuclei are sites for active metabolism of lipids, because lipids exchanged different enzymes, that supported the necessary level of individual phospholipids or neutral lipids fraction [7, 8, 10, 12, 17]. Cisplatin interacting with nuclei may dam ...
... drug cisplatin. It was known for a long time that cell nuclei are sites for active metabolism of lipids, because lipids exchanged different enzymes, that supported the necessary level of individual phospholipids or neutral lipids fraction [7, 8, 10, 12, 17]. Cisplatin interacting with nuclei may dam ...
Intestinal Protein digestion in vitro Assay
... • Lipase: release not less than 2 uEq of acid/min/mg • ‘Contains many enzymes, including amylase, trypsin, lipase, ribonuclease and protease. The National Formulary (N.F.) and the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) specify amylase, protease and lipase only ...
... • Lipase: release not less than 2 uEq of acid/min/mg • ‘Contains many enzymes, including amylase, trypsin, lipase, ribonuclease and protease. The National Formulary (N.F.) and the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) specify amylase, protease and lipase only ...
Internal Assessment: Fermentation Biology Higher Level
... “at a higher concentration the collisions are greater.” (Clark, 2002) As yeast contains certain types of enzymes, the effect of substrate concentration in enzymes is as follows: “As the concentration of substrate increases, the rate of reaction will increase as well” (Damon, McGonegal, & Ward, 2009) ...
... “at a higher concentration the collisions are greater.” (Clark, 2002) As yeast contains certain types of enzymes, the effect of substrate concentration in enzymes is as follows: “As the concentration of substrate increases, the rate of reaction will increase as well” (Damon, McGonegal, & Ward, 2009) ...
FEMS Microbiology Ecology 28:
... diameter) of the inoculum. Inoculated £asks and uninoculated controls were incubated at 28³C on a rotary shaker (150 rpm) in the dark. To inhibit any potential bacterial contaminant, all media were supplemented with 30 and 100 Wg ml31 of chloramphenicol and streptomycin sulfate, respectively. At eac ...
... diameter) of the inoculum. Inoculated £asks and uninoculated controls were incubated at 28³C on a rotary shaker (150 rpm) in the dark. To inhibit any potential bacterial contaminant, all media were supplemented with 30 and 100 Wg ml31 of chloramphenicol and streptomycin sulfate, respectively. At eac ...
Chapter One
... tried to divide a sample of water into infin itesimally small portions, we would eventually end up with a s ingle molecule of water containing two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. If we tried to break this molecule into its individual atom~, we would no longer have water. A molecule is therefore ...
... tried to divide a sample of water into infin itesimally small portions, we would eventually end up with a s ingle molecule of water containing two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. If we tried to break this molecule into its individual atom~, we would no longer have water. A molecule is therefore ...
Cell-Free Phospholipid Biosynthesis by Gene
... coding for the GPAT and LPAAT enzymes, respectively, were expressed by in vitro transcription translation (IVTT) in the presence of SUVs. Spontaneously assembled proteoliposomes containing synthesized GPAT and LPAAT proteins were isolated by ultracentrifugation (floatation method) and the protein co ...
... coding for the GPAT and LPAAT enzymes, respectively, were expressed by in vitro transcription translation (IVTT) in the presence of SUVs. Spontaneously assembled proteoliposomes containing synthesized GPAT and LPAAT proteins were isolated by ultracentrifugation (floatation method) and the protein co ...
Structure of the ordered hydration of amino acids
... molecular-dynamics (MD) simulations (Halle & Persson, 2013), which can also provide estimates of hydration thermodynamics (Cui et al., 2013; Hu & Lill, 2014). In this paper, we studied the hydration of proteins in crystal structures at the detailed level of individual amino-acid residues. A similar ...
... molecular-dynamics (MD) simulations (Halle & Persson, 2013), which can also provide estimates of hydration thermodynamics (Cui et al., 2013; Hu & Lill, 2014). In this paper, we studied the hydration of proteins in crystal structures at the detailed level of individual amino-acid residues. A similar ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.