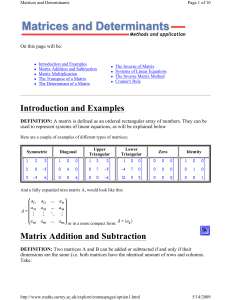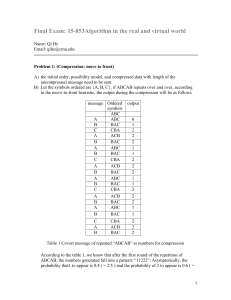
Lecture 4 Divide and Conquer Maximum/minimum Median finding
... number (the median corresponds to k = dn/2e). Given an array A[1, 2, . . . , n], one algorithm for selecting the kth smallest element is simply to sort A then return A[dn/2e]. This takes Θ(n log n) time using, say, MergeSort. How could we hope to do better? Well, suppose we had a black box that gave ...
... number (the median corresponds to k = dn/2e). Given an array A[1, 2, . . . , n], one algorithm for selecting the kth smallest element is simply to sort A then return A[dn/2e]. This takes Θ(n log n) time using, say, MergeSort. How could we hope to do better? Well, suppose we had a black box that gave ...
Sample examinations Linear Algebra (201-NYC-05) Autumn 2010 1. Given
... b. e2 and e3 belong to H , since each side of the equation defining H is zero, but e2 + e3 does not belong to H , because the left side of the equation defining H is zero and the right side is 1. Therefore, H is not closed under addition. ...
... b. e2 and e3 belong to H , since each side of the equation defining H is zero, but e2 + e3 does not belong to H , because the left side of the equation defining H is zero and the right side is 1. Therefore, H is not closed under addition. ...












![Lecture 16: Properties of S Matrices. Shifting Reference Planes. [ ] [ ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015297123_1-06ba65488176253b7cf35ea4664b2760-300x300.png)