Ch 2 Sec 3: Monitoring Earthquakes
... 1. map faults- Geologists use the data from seismic waves to map faults, which are often hidden by a thick layer of rock or soil. When wave encounters a fault it reflects off of it so scientists detect reflected waves to determine where faults are located. This practice helps geologists determine th ...
... 1. map faults- Geologists use the data from seismic waves to map faults, which are often hidden by a thick layer of rock or soil. When wave encounters a fault it reflects off of it so scientists detect reflected waves to determine where faults are located. This practice helps geologists determine th ...
Wearing Down Earth`s Surface
... • Remember that tectonic plates move very_______________. Sometimes rocks move along easily with the plates, but they can also jam up against a plate or between two_______________. Over time, stress builds up within the rock at the plates_______________ against each other. ...
... • Remember that tectonic plates move very_______________. Sometimes rocks move along easily with the plates, but they can also jam up against a plate or between two_______________. Over time, stress builds up within the rock at the plates_______________ against each other. ...
Seismographs - Ring of Fire Science
... and S waves at three stations. Scientists determining the distance they were from the focus of an earthquake would first write down the exact time the S waves arrived at the first station, which was 10:45 a.m. They would subtract the exact time the P waves arrived, which was 10:17 a.m. from the S wa ...
... and S waves at three stations. Scientists determining the distance they were from the focus of an earthquake would first write down the exact time the S waves arrived at the first station, which was 10:45 a.m. They would subtract the exact time the P waves arrived, which was 10:17 a.m. from the S wa ...
Monitoring the Earth from space And earthquakes
... indicates its location and the current time. All GPS satellites synchronize operations so that these repeating signals are transmitted at the same instant. The signals, moving at the speed of light, arrive at a GPS receiver at slightly different times because some satellites are farther away than ot ...
... indicates its location and the current time. All GPS satellites synchronize operations so that these repeating signals are transmitted at the same instant. The signals, moving at the speed of light, arrive at a GPS receiver at slightly different times because some satellites are farther away than ot ...
A Proposed `Megathrust Megaswath` OBS Deployment In
... the deadliest ever on US soil. It is famous for a 40-m wave run up at Scotch Cap where it wiped away a concrete lighthouse, and for the tsunami that killed 165 people, mostly in Hawaii. This earthquake initially had a magnitude of 7.4, but it is now seen as a type example of a ‘tsunami earthquake’ a ...
... the deadliest ever on US soil. It is famous for a 40-m wave run up at Scotch Cap where it wiped away a concrete lighthouse, and for the tsunami that killed 165 people, mostly in Hawaii. This earthquake initially had a magnitude of 7.4, but it is now seen as a type example of a ‘tsunami earthquake’ a ...
Why Do Earthquakes Happen?
... On the maps below, each dot marks the locations of a magnitude 4 or larger earthquake. The earthquakes were recorded over a five-year time period. ...
... On the maps below, each dot marks the locations of a magnitude 4 or larger earthquake. The earthquakes were recorded over a five-year time period. ...
The Focus and Epicenter of an Earthquake
... spreading ridge centers more than 150,000 quakes strong enough to be felt are recorded each year ...
... spreading ridge centers more than 150,000 quakes strong enough to be felt are recorded each year ...
Investigation of tectonics and statistical analysis of earthquake
... the light of the theory of plate tectonics (plate - tectonic) has taken a clear face, so that on a global scale in the series Mountains is often mentioned as a classic example of the collision of continent - continent, which was aimed at the continental margin of the Pacific Ocean. [3]. Zagros is on ...
... the light of the theory of plate tectonics (plate - tectonic) has taken a clear face, so that on a global scale in the series Mountains is often mentioned as a classic example of the collision of continent - continent, which was aimed at the continental margin of the Pacific Ocean. [3]. Zagros is on ...
Chapter 10: Earthquakes & The Earth’s Interior
... produced by the rapid release of energy Energy ...
... produced by the rapid release of energy Energy ...
Chapter 9: Earthquakes
... b) Each degree of magnitude is 32 times greater than the one before c) 5.5 – 6.5 = 32 times stronger 5.5 – 7.5 1025 times stronger (322) 2. Moment magnitude Scale a) looks at fault size b) measures how much movement occurred c) how stiff are the rocks? d) the number is an average of several seismic ...
... b) Each degree of magnitude is 32 times greater than the one before c) 5.5 – 6.5 = 32 times stronger 5.5 – 7.5 1025 times stronger (322) 2. Moment magnitude Scale a) looks at fault size b) measures how much movement occurred c) how stiff are the rocks? d) the number is an average of several seismic ...
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude October 20th
... Prior to 1935 the estimation of the intensity of an earthquake was base on a qualitative and subjective interpretation of the Mercalli Intensity Scale. Charles Richter (1935) devised a quantitative method based on the amplitude of the largest waves recorded on a seismogram. The size of the amp ...
... Prior to 1935 the estimation of the intensity of an earthquake was base on a qualitative and subjective interpretation of the Mercalli Intensity Scale. Charles Richter (1935) devised a quantitative method based on the amplitude of the largest waves recorded on a seismogram. The size of the amp ...
Is There An Earthquake Migration Global Pattern?
... Manually collected data is used as the basis for automation and consolidation of probable seismic migration using the Flinn-Engdahl region as accurately as possible. It was observed that the pairs of consequent events over magnitude are well correlated. Only migration 4, manually collected, showed i ...
... Manually collected data is used as the basis for automation and consolidation of probable seismic migration using the Flinn-Engdahl region as accurately as possible. It was observed that the pairs of consequent events over magnitude are well correlated. Only migration 4, manually collected, showed i ...
The Northridge Earthquake
... Seismic waves, felt as the shaking motion when an earthquake occurs, are generated when energy is released during an earthquake. The difference in time is takes for the two primary types of seismic body waves—P waves and S waves—to travel to and be recorded by a seismometer, is used to determine whe ...
... Seismic waves, felt as the shaking motion when an earthquake occurs, are generated when energy is released during an earthquake. The difference in time is takes for the two primary types of seismic body waves—P waves and S waves—to travel to and be recorded by a seismometer, is used to determine whe ...
Name Determining Earthquake Probabilities
... 3. The statewide probability map suggests that overall, there is a 99% chance of a damaging M=(6.7 or greater) earthquake occurring somewhere in the state in the next 30 years. Should resources for ...
... 3. The statewide probability map suggests that overall, there is a 99% chance of a damaging M=(6.7 or greater) earthquake occurring somewhere in the state in the next 30 years. Should resources for ...
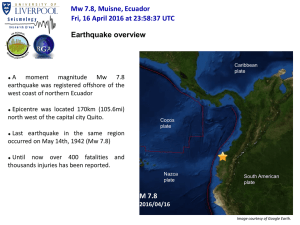
Mw 7.8, Muisne, Ecuador Fri, 16 April 2016 at 23:58:37 UTC USGS
... Above: Graph displaying the total energy release over time for the rupture. Most of the energy was released after 20 seconds of the beginning of the earthquake ...
... Above: Graph displaying the total energy release over time for the rupture. Most of the energy was released after 20 seconds of the beginning of the earthquake ...
THE INTENSITY OF EARTHQUAKE IN INDIA ABSTRACT An
... to initiate the necessary steps for the mitigation and prevention of adverse affects of seismic disasters. It may be mentioned that the occurrences of earthquakes cannot be precisely predicted because till now no suitable technique for earthquake prediction could be developed as the seismic events a ...
... to initiate the necessary steps for the mitigation and prevention of adverse affects of seismic disasters. It may be mentioned that the occurrences of earthquakes cannot be precisely predicted because till now no suitable technique for earthquake prediction could be developed as the seismic events a ...
Unit 1 student handout
... Example: The database records an average of 57.2 earthquakes of magnitude 2.0-2.9 each year in the San Francisco area. The MRI (1/57.2) is 0.017 years, which is equivalent to an average of one earthquake every 6 days. Your turn: What is the approximate MRI in days for earthquakes in the San Francisc ...
... Example: The database records an average of 57.2 earthquakes of magnitude 2.0-2.9 each year in the San Francisco area. The MRI (1/57.2) is 0.017 years, which is equivalent to an average of one earthquake every 6 days. Your turn: What is the approximate MRI in days for earthquakes in the San Francisc ...
Earthquake Prediction through Animal Behavior: A Review
... Numerous observations also exist of animals displaying panic in the few seconds prior to the onset of strong ground shaking in American case.(Tributsch, 1982) lists many such examples, including dogs barking, nervous cats jumping out of windows, birds screaming, rats running out of their holes, bees ...
... Numerous observations also exist of animals displaying panic in the few seconds prior to the onset of strong ground shaking in American case.(Tributsch, 1982) lists many such examples, including dogs barking, nervous cats jumping out of windows, birds screaming, rats running out of their holes, bees ...
GEO1011
... In a deserted area, it doesn’t matter if there are strong earthquakes. In a region with a dam or a nuclear power plant, even a small earthquake can be a catastrophe. The seismic risk takes into account the type of building etc in the area in addition to the vibrations caused by earthquakes. ...
... In a deserted area, it doesn’t matter if there are strong earthquakes. In a region with a dam or a nuclear power plant, even a small earthquake can be a catastrophe. The seismic risk takes into account the type of building etc in the area in addition to the vibrations caused by earthquakes. ...
At least 5,000 people are estimated to have died, and thousands of
... left homeless. Hardest hit with the badly constructed high-rise apartment blocks built to pre-cast concrete *** which have sprung up in recent years. They were the first collapse on their occupants and they are now being blamed for the high death toll as there’re few which withstood the tremors. Man ...
... left homeless. Hardest hit with the badly constructed high-rise apartment blocks built to pre-cast concrete *** which have sprung up in recent years. They were the first collapse on their occupants and they are now being blamed for the high death toll as there’re few which withstood the tremors. Man ...
EARTHQUAKES
... rock similar to peridotite in roughly the same proportions as the rocks thought to make up Earth’s core and mantle. ...
... rock similar to peridotite in roughly the same proportions as the rocks thought to make up Earth’s core and mantle. ...
File
... the size of the largest seismic waves generated by a quake that is used to describe its magnitude. – Each successive number in the scale represents an increase in seismic-wave size, or amplitude, of a factor of 10. – Each increase in magnitude corresponds to about a 32-fold increase in seismic energ ...
... the size of the largest seismic waves generated by a quake that is used to describe its magnitude. – Each successive number in the scale represents an increase in seismic-wave size, or amplitude, of a factor of 10. – Each increase in magnitude corresponds to about a 32-fold increase in seismic energ ...
Waves_Seismograms
... – Travel just below or along the ground’s surface – Slower than body waves; rolling and side-to-side movement – Especially damaging to buildings ...
... – Travel just below or along the ground’s surface – Slower than body waves; rolling and side-to-side movement – Especially damaging to buildings ...
Earthquakes - Perry Local Schools
... An earthquake is “a sudden movement of the Earth, caused by the abrupt release of strain that has accumulated over a long time” (Shedlock and Pakiser). Earthquakes occur far more often than most people think. However, few of these earthquakes are strong enough to be felt by humans. Even fewer have t ...
... An earthquake is “a sudden movement of the Earth, caused by the abrupt release of strain that has accumulated over a long time” (Shedlock and Pakiser). Earthquakes occur far more often than most people think. However, few of these earthquakes are strong enough to be felt by humans. Even fewer have t ...
Earthquake prediction

Earthquake prediction is a branch of the science of seismology concerned with the specification of the time, location, and magnitude of future earthquakes within stated confidence limits but with sufficient precision that a warning can be issued. Of particular importance is the prediction of hazardous earthquakes likely to cause loss of life or damage to infrastructure. Earthquake prediction is sometimes distinguished from earthquake forecasting, which can be defined as the probabilistic assessment of general earthquake hazard, including the frequency and magnitude of damaging earthquakes in a given area over years or decades. It can be further distinguished from earthquake warning systems, which upon detection of an earthquake, provide a real-time warning to regions that might be affected.In the 1970s, scientists were optimistic that a practical method for predicting earthquakes would soon be found, but by the 1990s continuing failure led many to question whether it was even possible. Demonstrably successful predictions of large earthquakes have not occurred and the few claims of success are controversial. Extensive searches have reported many possible earthquake precursors, but, so far, such precursors have not been reliably identified across significant spatial and temporal scales While some scientists still hold that, given enough resources, prediction might be possible, many others now maintain that earthquake prediction is inherently impossible.