LT4ActivityPacket
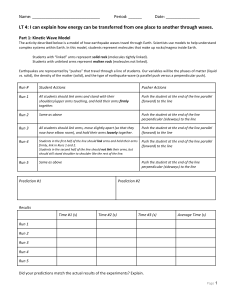
... 1. Position your slinky at the “0 cm” amplitude mark on your masking tape. 2. Create an S-wave by sliding one end of the slinky back and forth to move slowly. a. When ready to collect data, measure the amplitude of your wave, as you make a wave. b. Repeat for a total of 3 trials and record. 3. Repea ...
... 1. Position your slinky at the “0 cm” amplitude mark on your masking tape. 2. Create an S-wave by sliding one end of the slinky back and forth to move slowly. a. When ready to collect data, measure the amplitude of your wave, as you make a wave. b. Repeat for a total of 3 trials and record. 3. Repea ...
How Do Stress Forces Affect Rock?
... Accurate measurements for small, nearby earthquakes not large, distant earthquakes ...
... Accurate measurements for small, nearby earthquakes not large, distant earthquakes ...
Shallow Water Gravity Waves: A Note on the Particle Orbits
... differences in height of the surface and to the vertical acceleration of the fluid. Results obtained here are in complete agreement with those of the standard theory, but the present labor-saving method facilitates a greater and more immediate understanding of the phenomenon. Another distinct advant ...
... differences in height of the surface and to the vertical acceleration of the fluid. Results obtained here are in complete agreement with those of the standard theory, but the present labor-saving method facilitates a greater and more immediate understanding of the phenomenon. Another distinct advant ...
Earthquakes Terminology of Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory
... of the Earth. As the waves propagate, the rocks are elastically deformed by change in either volume or shape. ...
... of the Earth. As the waves propagate, the rocks are elastically deformed by change in either volume or shape. ...
seismic waves notes - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • The fact that P-waves pass through the core, but are refracted along the way, indicates that the inner core is denser than the outer core and solid. • When pressure dominates, atoms are squeezed together tightly and exist in the solid state. • If temperatures are high enough, atoms move apart enou ...
... • The fact that P-waves pass through the core, but are refracted along the way, indicates that the inner core is denser than the outer core and solid. • When pressure dominates, atoms are squeezed together tightly and exist in the solid state. • If temperatures are high enough, atoms move apart enou ...
Document
... Figures: 11.2, 11.5, 11.9, 11.1, 11.13, Table 11.3 caption, Box 11.2, 11.20, 11.26, 11.28, Box 11.3-E&F Terms: aftershock, foreshock, body wave, surface wave, P wave, S wave, elastic rebound, epicenter, focus, fault, fault creep, liquefaction, magnitude, Richter scale, seismic gaps, seismic sea wave ...
... Figures: 11.2, 11.5, 11.9, 11.1, 11.13, Table 11.3 caption, Box 11.2, 11.20, 11.26, 11.28, Box 11.3-E&F Terms: aftershock, foreshock, body wave, surface wave, P wave, S wave, elastic rebound, epicenter, focus, fault, fault creep, liquefaction, magnitude, Richter scale, seismic gaps, seismic sea wave ...
structure of lithosphere velocity heterogeneities in kamchtaka and
... Here we first present results of a Minimum 1D lithosphere-asthenosphere velocity model (up to about 200 km depth) that serves for uniform high precision earthquake location and as initial reference model for 3D tomography. The model is calculated with program VELEST that has a number of advantages, ...
... Here we first present results of a Minimum 1D lithosphere-asthenosphere velocity model (up to about 200 km depth) that serves for uniform high precision earthquake location and as initial reference model for 3D tomography. The model is calculated with program VELEST that has a number of advantages, ...
Earthquakes
... They’re Caused by a Build-up of STRESS in Earth’s Crust As tectonic plates move, they cause stress in the crust, which in turn produces folds and faults. ...
... They’re Caused by a Build-up of STRESS in Earth’s Crust As tectonic plates move, they cause stress in the crust, which in turn produces folds and faults. ...
Module 5 - Earthquakes - IST Akprind Yogyakarta
... • How much can surface and subsurface material contribute to earthquake damages? Like many other physical phenomena, the answer is, "It depends." Thick sequences of unconsolidated sediments, such as sand, mud, and artificial fill, greatly magnify ground shaking during an earthquake. Ground shaking t ...
... • How much can surface and subsurface material contribute to earthquake damages? Like many other physical phenomena, the answer is, "It depends." Thick sequences of unconsolidated sediments, such as sand, mud, and artificial fill, greatly magnify ground shaking during an earthquake. Ground shaking t ...
Earthquakes
... • Body waves – originate from the focus of the earthquake – P waves (primary waves) are compression waves that push and pull rock as they travel • Cause particles to move back & forth • Move through solids, liquids and gases • 1st waves to arrive ...
... • Body waves – originate from the focus of the earthquake – P waves (primary waves) are compression waves that push and pull rock as they travel • Cause particles to move back & forth • Move through solids, liquids and gases • 1st waves to arrive ...
Earth Materials
... At the outer-inner core boundary P waves move faster through solid than liquid Therefore the inner core must be solid Earthquakes ...
... At the outer-inner core boundary P waves move faster through solid than liquid Therefore the inner core must be solid Earthquakes ...
Seism shop
... Fund for providing facilities and generous funding to make this event possible. The Seismology Student Workshop is an event designed by graduate students, for graduate students. We aim to foster a convivial environment where young researchers connect with peers in their field and present active rese ...
... Fund for providing facilities and generous funding to make this event possible. The Seismology Student Workshop is an event designed by graduate students, for graduate students. We aim to foster a convivial environment where young researchers connect with peers in their field and present active rese ...
The Ultimate Wave Tahiti Classroom Poster
... at the interface between an island and the open ocean, is a magic zone where the energy of waves breaking in shallow water helps support a rich diversity of life. coral reefs are structures built by living organisms—a synergy of plant and animal life. how is my community like a coral reef? How might ...
... at the interface between an island and the open ocean, is a magic zone where the energy of waves breaking in shallow water helps support a rich diversity of life. coral reefs are structures built by living organisms—a synergy of plant and animal life. how is my community like a coral reef? How might ...
Plate tectonics NB Name
... Base your answer/s to the following question/s on the diagram on the left, which shows a cutaway view of Earth in which the interior layers are visible. The paths of the earthquake/seismic waves generated at point X are also shown. A, B, C, and D are locations of seismic stations on Earth’s surface, ...
... Base your answer/s to the following question/s on the diagram on the left, which shows a cutaway view of Earth in which the interior layers are visible. The paths of the earthquake/seismic waves generated at point X are also shown. A, B, C, and D are locations of seismic stations on Earth’s surface, ...
The Focus and Epicenter of an Earthquake
... travel times for Pand S-waves. The farther away a seismograph is from the focus of an earthquake, the longer the interval between the arrivals of the Pand S- waves ...
... travel times for Pand S-waves. The farther away a seismograph is from the focus of an earthquake, the longer the interval between the arrivals of the Pand S- waves ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... plates. This indicates that most active faults occur at tectonic plate boundaries as a result of plate motion. 3. Why are surface waves more destructive to buildings than P waves or S waves are? Surface waves are more destructive to buildings than P waves and S waves are because the energy of surfac ...
... plates. This indicates that most active faults occur at tectonic plate boundaries as a result of plate motion. 3. Why are surface waves more destructive to buildings than P waves or S waves are? Surface waves are more destructive to buildings than P waves and S waves are because the energy of surfac ...
Start at "A View From Above" 1. What evidence do you see on the
... 11. Watch the paths taken by P and S waves in this planet model; be sure to consider the speed of the P wave in different materials. Sketch the layers of this planet and label them as solid or liquid. Solid then liquid ...
... 11. Watch the paths taken by P and S waves in this planet model; be sure to consider the speed of the P wave in different materials. Sketch the layers of this planet and label them as solid or liquid. Solid then liquid ...
Earthquakes and Earth`s Interior Summary
... Abrupt movements of faults that release elastically stored energy cause earthquakes – Elastic Rebound. Earthquake vibrations are measured with seismometers. Energy released at an earthquake’s focus radiates outward as body waves, which are of two kinds: P waves (Primary waves, which are compressiona ...
... Abrupt movements of faults that release elastically stored energy cause earthquakes – Elastic Rebound. Earthquake vibrations are measured with seismometers. Energy released at an earthquake’s focus radiates outward as body waves, which are of two kinds: P waves (Primary waves, which are compressiona ...
Types of seismic waveS
... Secondary waves (S-waves) are shear waves that are transverse in nature. These waves arrive at seismograph stations after the faster moving P waves during an earthquake and displace the ground perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Depending on the propagational direction, the wave can take ...
... Secondary waves (S-waves) are shear waves that are transverse in nature. These waves arrive at seismograph stations after the faster moving P waves during an earthquake and displace the ground perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Depending on the propagational direction, the wave can take ...
AICE Environmental Management GIZMOS Class Code
... Both P and S waves are known as body waves because they travel through solid rock below Earth’s surface. When these waves reach the surface, their effects combine in surface waves, which shake the ground back and forth, up and down, and side to side. Surface waves account for the largest wiggles on ...
... Both P and S waves are known as body waves because they travel through solid rock below Earth’s surface. When these waves reach the surface, their effects combine in surface waves, which shake the ground back and forth, up and down, and side to side. Surface waves account for the largest wiggles on ...
Top 10 Earthquakes since 1900
... Shear (transverse) waves – think rope Particles move perpendicular to the direction the energy wave is traveling S-waves slower than p-waves (2-5 km/sec) High density material faster wave speed Only travel through solids (can’t shear liquid or gas) ...
... Shear (transverse) waves – think rope Particles move perpendicular to the direction the energy wave is traveling S-waves slower than p-waves (2-5 km/sec) High density material faster wave speed Only travel through solids (can’t shear liquid or gas) ...
Earth`s Changing Surface
... • Think about the slinky again. Instead of pulling it just out, think about pulling it out and up and down. • S waves shake structures violently. They cannot move through liquids, only solids. ...
... • Think about the slinky again. Instead of pulling it just out, think about pulling it out and up and down. • S waves shake structures violently. They cannot move through liquids, only solids. ...
Free Surface Multiple Removal Theory - M-OSRP
... Green’s theorem requires the wavefield P and its normal derivative Pn on the measurement surface as the input. In marine exploration, an over/under cable has been used to obtain data at two depths. We study some practical issues when performing Green’s theorem for wave separation using over/under ca ...
... Green’s theorem requires the wavefield P and its normal derivative Pn on the measurement surface as the input. In marine exploration, an over/under cable has been used to obtain data at two depths. We study some practical issues when performing Green’s theorem for wave separation using over/under ca ...
Conservation of Energy and Momentum
... Waves have characteristic properties that do not depend on the type of wave. 39. Waves carry _____________________ from one place to another. There is no net movement of matter. 40. Waves in mechanical media (mechanical waves), such as in springs and ropes, and on the earth (seismic waves), can be i ...
... Waves have characteristic properties that do not depend on the type of wave. 39. Waves carry _____________________ from one place to another. There is no net movement of matter. 40. Waves in mechanical media (mechanical waves), such as in springs and ropes, and on the earth (seismic waves), can be i ...
Surface wave inversion

Inversion is the set of methods used to infer properties through physical measurements. Surface wave inversion is the method by which elastic properties, density, and thickness of layers in the subsurface are attained through analysis of surface wavedispersion. The entire inversion process requires the gathering of seismic data, the creation of dispersion curves, and finally the inference of subsurface properties.























