1. Define habitat and describe how geologic processes influence habitats. Habitats
... Oceanic crust is much thinner than continental crust—about 5 km (3 mi) compared to 20 to 50 km (12 to 30 mi). 10. How does the density difference between continental and oceanic crust create oceans and continents? The continents can be thought of as thick blocks of crust floating on the mantle much ...
... Oceanic crust is much thinner than continental crust—about 5 km (3 mi) compared to 20 to 50 km (12 to 30 mi). 10. How does the density difference between continental and oceanic crust create oceans and continents? The continents can be thought of as thick blocks of crust floating on the mantle much ...
THE BIG EVENT Oceans Fact Sheet
... that volcanoes spewed into the atmosphere turned to water vapor, condensed, and fell as rain. And rain it did. For thousands of years, the rains fell hard and filled giant depressions—forming the world's first seas. Continental crust is less dense and thicker than the surface of the deep ocean. The ...
... that volcanoes spewed into the atmosphere turned to water vapor, condensed, and fell as rain. And rain it did. For thousands of years, the rains fell hard and filled giant depressions—forming the world's first seas. Continental crust is less dense and thicker than the surface of the deep ocean. The ...
Chapter 11 What about continental drift?
... This higher sea level floods the continental surfaces and makes possible the deposition of large areas of sedimentary deposits on top of the normally high-standing continents. The Grand Canyon provides a spectacular window into the amazing layer-cake character of these sediment deposits that in many ...
... This higher sea level floods the continental surfaces and makes possible the deposition of large areas of sedimentary deposits on top of the normally high-standing continents. The Grand Canyon provides a spectacular window into the amazing layer-cake character of these sediment deposits that in many ...
Fractured Earth - Do plumes exist?
... examine what models are presently being proposed to explain the breakup. But first, it is simpler to examine the observational data. What is it we are trying to explain? ...
... examine what models are presently being proposed to explain the breakup. But first, it is simpler to examine the observational data. What is it we are trying to explain? ...
geology of corridor h - Geological Society of Washington
... “thin skinned tectonics.” That is to say, the rocks you see today in the Valley and Ridge were deposited during the early and middle Paleozoic, and were then intensely deformed (folded, faulted, and cleaved) during the late Paleozoic Alleghanian Orogeny. Thus, the rocks of the Valley and Ridge provi ...
... “thin skinned tectonics.” That is to say, the rocks you see today in the Valley and Ridge were deposited during the early and middle Paleozoic, and were then intensely deformed (folded, faulted, and cleaved) during the late Paleozoic Alleghanian Orogeny. Thus, the rocks of the Valley and Ridge provi ...
Alfred Wegener - From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics
... to study the polar atmosphere during the expedition that lasted for two years. After returning to Germany he was offered a private p.osition in the University of Marburg where he taught astronomy and meteorology. Wegener compiled his meteorology lecture notes into a book, The Thermodynamics of the A ...
... to study the polar atmosphere during the expedition that lasted for two years. After returning to Germany he was offered a private p.osition in the University of Marburg where he taught astronomy and meteorology. Wegener compiled his meteorology lecture notes into a book, The Thermodynamics of the A ...
Ch19_PlateTectonics
... mantle, which leads to extension and breakup B) The Earth was hit by a giant asteroid at the time, pushing the plates apart C) Stresses caused by orbital forcing D) Conservative politics in Russia caused it to slide towards the right, while liberals in North America caused it to slide to the left ...
... mantle, which leads to extension and breakup B) The Earth was hit by a giant asteroid at the time, pushing the plates apart C) Stresses caused by orbital forcing D) Conservative politics in Russia caused it to slide towards the right, while liberals in North America caused it to slide to the left ...
File
... show HOW the plates move. • Back then, we had no GPS (global position satellites) nor did we know much about atomic radiation nor CONVECTION! ...
... show HOW the plates move. • Back then, we had no GPS (global position satellites) nor did we know much about atomic radiation nor CONVECTION! ...
Worksheets - Keep It Simple Science
... Seismology patterns give more evidence. The vast majority of l)............................ and ......................... occur along the plate m)........................... ...
... Seismology patterns give more evidence. The vast majority of l)............................ and ......................... occur along the plate m)........................... ...
ES 106 Laboratory # 4 - Western Oregon University
... mountains and continents, the occurrence of earthquakes, the evolution and distribution of plants and animals, as well as many other geologic processes. Using information from the ocean basins, including topography, age, and mechanisms of their evolution, Earth scientists have developed the exciting ...
... mountains and continents, the occurrence of earthquakes, the evolution and distribution of plants and animals, as well as many other geologic processes. Using information from the ocean basins, including topography, age, and mechanisms of their evolution, Earth scientists have developed the exciting ...
Plate Tectonics and Global Impacts – Tutorial Script - FOG
... the terrane accretion. In fact, this satellite image shows that there is a chain of underwater seamounts colliding with the South American coast, and over millions of years, they pile up, are scraped off, and become part of the coastal mountain system. South America is growing through volcanism and ...
... the terrane accretion. In fact, this satellite image shows that there is a chain of underwater seamounts colliding with the South American coast, and over millions of years, they pile up, are scraped off, and become part of the coastal mountain system. South America is growing through volcanism and ...
Document
... When fluid is heated, it expands, lowering the density of the heated material, causing it to rise through the cooler fluid. As it rises, leaving the vicinity of the heat source, in this case, hot magma near the earth's surface, it will cool. When it becomes more dense (because it is cooler) than the ...
... When fluid is heated, it expands, lowering the density of the heated material, causing it to rise through the cooler fluid. As it rises, leaving the vicinity of the heat source, in this case, hot magma near the earth's surface, it will cool. When it becomes more dense (because it is cooler) than the ...
Submarine Earthquakes, Part I
... Once we pass the continental margin we get into some of the deepest parts of the world's oceans. In this area, the ocean floor has trenches. These trenches can be thousands of kilometers long, hundreds of kilometers wide, and extend three to four kilometers below the surrounding ocean floor. In the ...
... Once we pass the continental margin we get into some of the deepest parts of the world's oceans. In this area, the ocean floor has trenches. These trenches can be thousands of kilometers long, hundreds of kilometers wide, and extend three to four kilometers below the surrounding ocean floor. In the ...
Lesson 2 - Continental Drift Alfred Wegener.key
... But scientists now think that the Earth's surface is split up into big chunks called tectonic plates and that mountains are formed when these tectonic plates collide. The idea that the Earth's surface is not stable and is made up of parts that move was first put forward by Alfred Wegener. He propose ...
... But scientists now think that the Earth's surface is split up into big chunks called tectonic plates and that mountains are formed when these tectonic plates collide. The idea that the Earth's surface is not stable and is made up of parts that move was first put forward by Alfred Wegener. He propose ...
Chapteer 1 study guide rev
... Below are listed some Key Topics or terms to aid in focusing your study time. More topics then these may appear on the exam but these are a good place to start. Check each box as Chapter 1 you review the concept � Know the name and location of the world’s oceans � Be able to explain the diffe ...
... Below are listed some Key Topics or terms to aid in focusing your study time. More topics then these may appear on the exam but these are a good place to start. Check each box as Chapter 1 you review the concept � Know the name and location of the world’s oceans � Be able to explain the diffe ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... matched with those from another (i.e., South America and Africa). Ocean spreading has always been moving the continents towards or away from each other. About 200 million years ago during the Jurassic period, Pangea began to separate (Figure 33). Pangea's continental crust was subjected to many faul ...
... matched with those from another (i.e., South America and Africa). Ocean spreading has always been moving the continents towards or away from each other. About 200 million years ago during the Jurassic period, Pangea began to separate (Figure 33). Pangea's continental crust was subjected to many faul ...
Plate boundaries| sample answer
... in a process called folding. The uplifted land can be called fold mountains and an example is the Himalayas. Areas in which crust is created are called constructive plate boundaries. An example is a mid ocean ridge, deep under the ocean floor where land is created (Mid-Atlantic ridge has occurred du ...
... in a process called folding. The uplifted land can be called fold mountains and an example is the Himalayas. Areas in which crust is created are called constructive plate boundaries. An example is a mid ocean ridge, deep under the ocean floor where land is created (Mid-Atlantic ridge has occurred du ...
Earth_through_geological_time
... Larger crustal areas were assembled into larger blocks called cratons Cratons form the core of modern continents ...
... Larger crustal areas were assembled into larger blocks called cratons Cratons form the core of modern continents ...
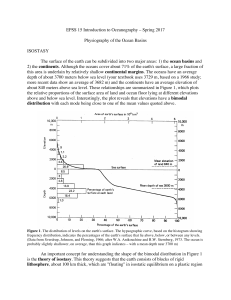
EPSS 15 Introduction to Oceanography – Spring 2017 Physiography
... rise or abyssal plains (discussed below). Important agents in this process are turbidity currents. These are short lived, gravity-induced currents consisting of mixtures of sediment and water which flow downslope as a density current. Turbidity currents are the primary means by which terrigenous (la ...
... rise or abyssal plains (discussed below). Important agents in this process are turbidity currents. These are short lived, gravity-induced currents consisting of mixtures of sediment and water which flow downslope as a density current. Turbidity currents are the primary means by which terrigenous (la ...
Plate Tectonics II: Transform Faults, Subduction Zones, and Ho
... b. Of the plate boundaries you identified above, which has the deepest earthquakes? c. Along western South America, what is the position of the earthquakes with respect to the trenches? d. What major types of geologic features are common in subduction zones? e. What geologic events are common at sub ...
... b. Of the plate boundaries you identified above, which has the deepest earthquakes? c. Along western South America, what is the position of the earthquakes with respect to the trenches? d. What major types of geologic features are common in subduction zones? e. What geologic events are common at sub ...
Chapter 2
... – Occasionally, at random intervals, the Earth's magnetic field reverses. New rock formed from magma records the orientation of Earth's magnetic field at the time the magma cools. – Studies of the sea floor revealed "stripes" of alternating magnetization parallel to the mid-oceanic ridges. This is e ...
... – Occasionally, at random intervals, the Earth's magnetic field reverses. New rock formed from magma records the orientation of Earth's magnetic field at the time the magma cools. – Studies of the sea floor revealed "stripes" of alternating magnetization parallel to the mid-oceanic ridges. This is e ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/test-bank-marine-biology-8th-edition-castro ...
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/test-bank-marine-biology-8th-edition-castro ...
Chapter 8
... • DuToit’s evidence – expanded Wegener’s ideas – Mesosaurus fossils • found on Gondwanaland (southern hemisphere) continents • a fresh/brackish water species – could not swim across Atlantic ...
... • DuToit’s evidence – expanded Wegener’s ideas – Mesosaurus fossils • found on Gondwanaland (southern hemisphere) continents • a fresh/brackish water species – could not swim across Atlantic ...
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea (/pænˈdʒiːə/) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from earlier continental units approximately 300 million years ago, and it began to break apart about 175 million years ago. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, much of Pangaea was in the southern hemisphere and surrounded by a super ocean, Panthalassa. Pangaea was the last supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists.