Earth`s Magnetic Field Magnetic Field of the Earth
... magnetization adds to the induced field •! this produces a positive magnetic anomaly •! in strips that formed during reversed polarity, the remnant magnetization subtracts from the induced field •! this produces a negative magnetic anomaly •! when the anomalies are contoured, the effect is to produc ...
... magnetization adds to the induced field •! this produces a positive magnetic anomaly •! in strips that formed during reversed polarity, the remnant magnetization subtracts from the induced field •! this produces a negative magnetic anomaly •! when the anomalies are contoured, the effect is to produc ...
Chapter 17 – Plate Tectonics
... as a single landmass called Pangaea. A. Pangaea began to break up 200 million years ago and began drifting apart B. The process is still occurring. 3. Wegener’s evidence for continental drift went beyond the “puzzle fit” the map-makers had seen and includes: A. Rocks B. Fossils C. Climatic Data ES C ...
... as a single landmass called Pangaea. A. Pangaea began to break up 200 million years ago and began drifting apart B. The process is still occurring. 3. Wegener’s evidence for continental drift went beyond the “puzzle fit” the map-makers had seen and includes: A. Rocks B. Fossils C. Climatic Data ES C ...
Document
... Attempts were made to explain mountains by crustal cooling and contraction of Earth. However, even then evidence existed that the continents had moved. By 1950, submarine data had beg;un to show astonishing sea floor features. This eventually lead to “sea floor spreading” and “plate tectonics”, the ...
... Attempts were made to explain mountains by crustal cooling and contraction of Earth. However, even then evidence existed that the continents had moved. By 1950, submarine data had beg;un to show astonishing sea floor features. This eventually lead to “sea floor spreading” and “plate tectonics”, the ...
plate tectonics
... valley. Two continents are separated by a valley that downdrops and eventually floods ...
... valley. Two continents are separated by a valley that downdrops and eventually floods ...
iNOB
... largest area of the marine ecosystem. It reaches from coasts to the middle of the ocean. The living things that survive in the open ocean need to have a way to float or swim in ocean water. ...
... largest area of the marine ecosystem. It reaches from coasts to the middle of the ocean. The living things that survive in the open ocean need to have a way to float or swim in ocean water. ...
What happens when plates diverge - KMS 8th Grade Science
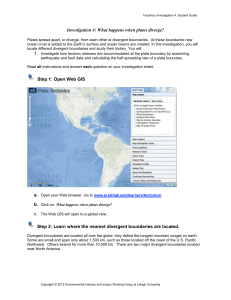
... a. Open your Web browser. Go to www.ei.lehigh.edu/learners/tectonics/ b. Click on: What happens when plates diverge? c. The Web GIS will open to a global view. Step 2: Learn where the nearest divergent boundaries are located. Divergent boundaries are located all over the globe; they define the longe ...
... a. Open your Web browser. Go to www.ei.lehigh.edu/learners/tectonics/ b. Click on: What happens when plates diverge? c. The Web GIS will open to a global view. Step 2: Learn where the nearest divergent boundaries are located. Divergent boundaries are located all over the globe; they define the longe ...
Evolution of the East African and related orogens, and the assembly
... Orogeny (800–650 Ma; Stern, 1994) represents a distinct series of events within the Pan-African of central Gondwana, responsible for the assembly of greater Gondwana. Collectively, paleomagnetic and age data indicate that another later event at 550 Ma (Kuunga Orogeny) may represent the final suturin ...
... Orogeny (800–650 Ma; Stern, 1994) represents a distinct series of events within the Pan-African of central Gondwana, responsible for the assembly of greater Gondwana. Collectively, paleomagnetic and age data indicate that another later event at 550 Ma (Kuunga Orogeny) may represent the final suturin ...
Baltica upside down: A new plate tectonic model for Rodinia and the
... The late Precambrian basin evolution in these two regions also varies considerably with respect to tectonic setting, depositional age and environment, basin thickness, lithology, and igneous activity (Kumpulainen and Nystuen, 1985), and the overall conclusion must be that the Precambrian geology of ...
... The late Precambrian basin evolution in these two regions also varies considerably with respect to tectonic setting, depositional age and environment, basin thickness, lithology, and igneous activity (Kumpulainen and Nystuen, 1985), and the overall conclusion must be that the Precambrian geology of ...
History of Ocean Basins
... Whereas 29 per cent of the Earth's surface is land, it would be more appropriate here to include the continental shelves and the slopes to the 1000-m isobath with the continents, leaving the remainder as oceanic. This results in 40 per cent continental and 60 per cent oceanic crust. I n 1955 I discu ...
... Whereas 29 per cent of the Earth's surface is land, it would be more appropriate here to include the continental shelves and the slopes to the 1000-m isobath with the continents, leaving the remainder as oceanic. This results in 40 per cent continental and 60 per cent oceanic crust. I n 1955 I discu ...
CHAPTER 2
... Coverage of plate tectonics is required early in introductory Geology as context for the mineralogy, petrology, structure, internal processes, and Earth history that follow. Some instructors prefer a detailed treatment early, while others like a brief discussion in the first or second lecture follow ...
... Coverage of plate tectonics is required early in introductory Geology as context for the mineralogy, petrology, structure, internal processes, and Earth history that follow. Some instructors prefer a detailed treatment early, while others like a brief discussion in the first or second lecture follow ...
Oceanic ridges - HCC Learning Web
... He postulated that all landmasses were originally united into a supercontinent named Pangaea. Fig. 2.2, p. 29 ...
... He postulated that all landmasses were originally united into a supercontinent named Pangaea. Fig. 2.2, p. 29 ...
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
... He postulated that all landmasses were originally united into a supercontinent named Pangaea. Fig. 2.2, p. 29 ...
... He postulated that all landmasses were originally united into a supercontinent named Pangaea. Fig. 2.2, p. 29 ...
EGU2017-2525
... Zoning of the Arctic territories has been conducted taking into account the Earth’s crust types, age of consolidated basement, and features of geological structure of the sedimentary cover. Developed legend for the zoning scheme incorporates five main groups of elements: continental and oceanic crus ...
... Zoning of the Arctic territories has been conducted taking into account the Earth’s crust types, age of consolidated basement, and features of geological structure of the sedimentary cover. Developed legend for the zoning scheme incorporates five main groups of elements: continental and oceanic crus ...
Magma Type and Plate Margins
... Some of this basic magma will cool the the fractures feeding up to the surface. What rock and structure will form? ...
... Some of this basic magma will cool the the fractures feeding up to the surface. What rock and structure will form? ...
Chapter 4 Marine Sedimentation
... Authigenic minerals are those formed in place and include manganese nodules and many other minerals that precipitate in the sediments Although most volcanic activity in the ocean is concentrated at the ridges, isolated volcanoes can form seamounts and guyots ...
... Authigenic minerals are those formed in place and include manganese nodules and many other minerals that precipitate in the sediments Although most volcanic activity in the ocean is concentrated at the ridges, isolated volcanoes can form seamounts and guyots ...
Plate Boundarieskouts
... Plate and the North American Plate and it separates the African Plate from the South American Plate. ...
... Plate and the North American Plate and it separates the African Plate from the South American Plate. ...
3rd NW Review Notes
... within Earth that drives tectonic plate movement, shifting tectonic plates that cause earthquakes and volcanoes, weathering and erosion, and human interaction with the Earth’s surface. ...
... within Earth that drives tectonic plate movement, shifting tectonic plates that cause earthquakes and volcanoes, weathering and erosion, and human interaction with the Earth’s surface. ...
The Task
... Identify the types of plate boundaries and how the plates move at these boundaries. Seafloor spreading: summarize how Seafloor Spreading creates new crust and select appropriate media on Discoveryeducation.com to accompany that summary. Where does seafloor spreading occur (at what type of plate bo ...
... Identify the types of plate boundaries and how the plates move at these boundaries. Seafloor spreading: summarize how Seafloor Spreading creates new crust and select appropriate media on Discoveryeducation.com to accompany that summary. Where does seafloor spreading occur (at what type of plate bo ...
Divergent boundaries
... Transform boundaries. As the giant plates move, diverging [pulling apart] or converging [coming together] along their borders, tremendous energies are unleashed resulting in tremors that transform Earth’s surface. While all the plates appear to be moving at different relative speeds and independentl ...
... Transform boundaries. As the giant plates move, diverging [pulling apart] or converging [coming together] along their borders, tremendous energies are unleashed resulting in tremors that transform Earth’s surface. While all the plates appear to be moving at different relative speeds and independentl ...
Paleomagnetism
... • It is NOT the motion of the Earth’s pole, but the position of the continent relative to the pole • As if the paleomagnetic pole had moved slowly along this path toward the present pole • APW path can be determined for each continent ...
... • It is NOT the motion of the Earth’s pole, but the position of the continent relative to the pole • As if the paleomagnetic pole had moved slowly along this path toward the present pole • APW path can be determined for each continent ...
Plate Tectonics
... tremors that transform Earth’s surface. •While all the plates appear to be moving at different relative speeds and independently of each other, the whole jigsaw puzzle of plates is interconnected. •No single plate can move without affecting others, and the activity of one can influence another thous ...
... tremors that transform Earth’s surface. •While all the plates appear to be moving at different relative speeds and independently of each other, the whole jigsaw puzzle of plates is interconnected. •No single plate can move without affecting others, and the activity of one can influence another thous ...
Chapter 11
... spreading, and the all-inclusive plate tectonics theory. What was Alfred Wegener's role? In 1912, German geophysicist and meteorologist Alfred Wegener publicly presented in a lecture his idea that Earth's landmasses migrate. His book, Origin of the Continents and Oceans, appeared in 1915. Wegener to ...
... spreading, and the all-inclusive plate tectonics theory. What was Alfred Wegener's role? In 1912, German geophysicist and meteorologist Alfred Wegener publicly presented in a lecture his idea that Earth's landmasses migrate. His book, Origin of the Continents and Oceans, appeared in 1915. Wegener to ...
The Oceans and Atmosphere
... Many form near oceanic ridges May emerge as an island May sink and form flat-topped seamounts called guyots Mid-ocean ...
... Many form near oceanic ridges May emerge as an island May sink and form flat-topped seamounts called guyots Mid-ocean ...
1 Evolution of continental crust through two Wilson
... The tectonic load placed on the Iapetan continental margin by Appalachian deformation is reflected in foreland-basin subsidence. Magnitudes of tectonic thickening of the crust and foreland subsidence require lithospheric adjustments, and resolution of lithospheric structures is essential to understa ...
... The tectonic load placed on the Iapetan continental margin by Appalachian deformation is reflected in foreland-basin subsidence. Magnitudes of tectonic thickening of the crust and foreland subsidence require lithospheric adjustments, and resolution of lithospheric structures is essential to understa ...
Plate tectonics
... giant continent known as Pangaea. Pangaea was a supercontinent that Wegener proposed to have existed 220 million years ago. When it started to break up, the continents slowly drifted apart as they moved through the oceanic crust. He backed up his claims with evidence such as the shapes of coastline ...
... giant continent known as Pangaea. Pangaea was a supercontinent that Wegener proposed to have existed 220 million years ago. When it started to break up, the continents slowly drifted apart as they moved through the oceanic crust. He backed up his claims with evidence such as the shapes of coastline ...
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea (/pænˈdʒiːə/) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from earlier continental units approximately 300 million years ago, and it began to break apart about 175 million years ago. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, much of Pangaea was in the southern hemisphere and surrounded by a super ocean, Panthalassa. Pangaea was the last supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists.