Chapter 3
... and used in gene therapy to treat cystic fibrosis, cancer, and potentially other diseases. allele - One of two or more alternative forms of a gene located at the corresponding site (locus) on homologous chromosomes. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color ...
... and used in gene therapy to treat cystic fibrosis, cancer, and potentially other diseases. allele - One of two or more alternative forms of a gene located at the corresponding site (locus) on homologous chromosomes. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color ...
Incomplete Dominance & Codominance
... Punnett squares - probability diagram illustrating the possible offspring of a mating. Ss X Ss ...
... Punnett squares - probability diagram illustrating the possible offspring of a mating. Ss X Ss ...
Distinguishing endogenous versus exogenous DNA
... In the late 1990s it was reported that human DNA existed on the Shroud of Turin, and although in a generally degraded state, certain regions were sufficiently intact to clone and sequence three genes from bloodstained fibers: human betaglobin, amelogenin X and amelogenin Y. An unknown variable in su ...
... In the late 1990s it was reported that human DNA existed on the Shroud of Turin, and although in a generally degraded state, certain regions were sufficiently intact to clone and sequence three genes from bloodstained fibers: human betaglobin, amelogenin X and amelogenin Y. An unknown variable in su ...
Cloning of genes from genomic DNA: Part 3
... We will use restriction enzymes to cleave off the ends of the PCR products. The oligonucleotide primers used in the PCR reaction were designed to include either an XbaI or a HindIII restriction site in their sequence. In addition, we will cut our genomic DNA with the enzymes and run a little bit of ...
... We will use restriction enzymes to cleave off the ends of the PCR products. The oligonucleotide primers used in the PCR reaction were designed to include either an XbaI or a HindIII restriction site in their sequence. In addition, we will cut our genomic DNA with the enzymes and run a little bit of ...
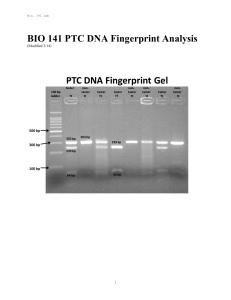
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... interesting, but not nearly as interesting a being able to experimentally “see” the difference between both forms of the gene. One way to tell the difference between the PAV and AVI alleles is to take advantage of the C to T change at nucleotide position 785. The nucleotide sequence surrounding this ...
... interesting, but not nearly as interesting a being able to experimentally “see” the difference between both forms of the gene. One way to tell the difference between the PAV and AVI alleles is to take advantage of the C to T change at nucleotide position 785. The nucleotide sequence surrounding this ...
Report on tested replacement component for β
... have determined the quality of DNA by measuring the A260/280 ratio as well as PCR amplification. In general, as also noted by Popa et al. (2007), the absorbance value did not have any impact on amplification. For the most part, DNA extracted from specimens collected in this study, amplified the full ...
... have determined the quality of DNA by measuring the A260/280 ratio as well as PCR amplification. In general, as also noted by Popa et al. (2007), the absorbance value did not have any impact on amplification. For the most part, DNA extracted from specimens collected in this study, amplified the full ...
Seminal Proteins
... the same concentrations of PCR fragment (figure 1). Two activities was identifies in band shift PAGE; the first is the classic DNase activity, and the second is a slight DNA retardation activity. Single and double stained Band shift PAGE assay: Although band shift PAGEs were originally designed to d ...
... the same concentrations of PCR fragment (figure 1). Two activities was identifies in band shift PAGE; the first is the classic DNase activity, and the second is a slight DNA retardation activity. Single and double stained Band shift PAGE assay: Although band shift PAGEs were originally designed to d ...
Recombinant DNA Techniques Laboratory Bi 431/531
... • Goal is to sequence the lux genes in environmentally isolated bacteria • Each person will isolate their own strain • Procedure is Ex III in Winfrey et al. • PB plates will be used instead of LBS • Each person will streak two PB plates from the provided sea creature ...
... • Goal is to sequence the lux genes in environmentally isolated bacteria • Each person will isolate their own strain • Procedure is Ex III in Winfrey et al. • PB plates will be used instead of LBS • Each person will streak two PB plates from the provided sea creature ...
COAS_B1_Ch08 Nucleic acids
... deoxyribose ring. The end of the molecule where the phosphate is bonded to carbon 5 is called the 5 end, while the other is the 3 end. two strands of a DNA molecule are linked to each other by weak hydrogen bonds between the • The bases. A always bonds with T, and C always bonds with G. A and T ar ...
... deoxyribose ring. The end of the molecule where the phosphate is bonded to carbon 5 is called the 5 end, while the other is the 3 end. two strands of a DNA molecule are linked to each other by weak hydrogen bonds between the • The bases. A always bonds with T, and C always bonds with G. A and T ar ...
2 - Griffith Research Online
... products regardless of whether the reducing agent was present, although rates of reaction were approximately 2-fold greater in the presence of DTT, presumably due to protection of the enzyme from oxidation. The specificities of hFEN1-catalysed reactions were monitored by denaturing reversed phase HP ...
... products regardless of whether the reducing agent was present, although rates of reaction were approximately 2-fold greater in the presence of DTT, presumably due to protection of the enzyme from oxidation. The specificities of hFEN1-catalysed reactions were monitored by denaturing reversed phase HP ...
mendelian genetics guided notes
... 1. Rule of Unit Factors – each organism has 2 alleles that control each trait Ex. 1 allele comes from mom and 1 allele comes from dad 2. Rule of Dominance – In cases in which 2 or more alleles for a single trait exist, one allele may be dominant (mask) to the recessive one Ex. Dominant = TT or Tt R ...
... 1. Rule of Unit Factors – each organism has 2 alleles that control each trait Ex. 1 allele comes from mom and 1 allele comes from dad 2. Rule of Dominance – In cases in which 2 or more alleles for a single trait exist, one allele may be dominant (mask) to the recessive one Ex. Dominant = TT or Tt R ...
Supplementary Information (doc 7548K)
... Supplementary Table 1 | Clinical characteristics of CG-SH cell line and AML patients. Data include FAB, French-American-British classification of AML, and mutational status of nucleophosmin gene (NPM1), internal tandem duplications of FLT3 gene (FLT3-3-ITD) and point mutations in DNMT3A (R882H). Ave ...
... Supplementary Table 1 | Clinical characteristics of CG-SH cell line and AML patients. Data include FAB, French-American-British classification of AML, and mutational status of nucleophosmin gene (NPM1), internal tandem duplications of FLT3 gene (FLT3-3-ITD) and point mutations in DNMT3A (R882H). Ave ...
High-throughput genotyping
... • The most simple and common type of polymorphism • Highly abundant; every 1000 bp along human genome • Most SNPs do not affect on cell function • some SNPs could predispose people to disease or • influence the individual’s response to a drug ...
... • The most simple and common type of polymorphism • Highly abundant; every 1000 bp along human genome • Most SNPs do not affect on cell function • some SNPs could predispose people to disease or • influence the individual’s response to a drug ...
Lecture slides
... cubic spline function As reference one can use an artificial “median array” for a set of arrays or use a log-normal distribution, which is a good approximation. ...
... cubic spline function As reference one can use an artificial “median array” for a set of arrays or use a log-normal distribution, which is a good approximation. ...
ch. 12 Biotechnology-notes-ppt
... Campbell, Reece, Mitchell, and Taylor, ©2003. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. • Unless otherwise noted, illustrations are ...
... Campbell, Reece, Mitchell, and Taylor, ©2003. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. • Unless otherwise noted, illustrations are ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.