Homework 5 - uc-davis economics
... (2) Each country demands all of the products that every other country produces; (3) Thus, large countries demand more imports from other countries. The gravity equation relationship does not hold in the Heckscher-Ohlin model. Explain how the logic of the gravity equation breaks down in the Heckscher ...
... (2) Each country demands all of the products that every other country produces; (3) Thus, large countries demand more imports from other countries. The gravity equation relationship does not hold in the Heckscher-Ohlin model. Explain how the logic of the gravity equation breaks down in the Heckscher ...
What Happens when the Environment Changes: Comparative
... profits. We are not in long run equilibrium any more. As entry becomes possible, new firms will enter the market, and the price will fall to 16. Think of an immediate jump to the new short run equilibrium (X = 40, px = 20), followed by a gradual movement along the new demand curve as entry occurs an ...
... profits. We are not in long run equilibrium any more. As entry becomes possible, new firms will enter the market, and the price will fall to 16. Think of an immediate jump to the new short run equilibrium (X = 40, px = 20), followed by a gradual movement along the new demand curve as entry occurs an ...
Economics 101 L - Iowa State University, Department of Economics
... What is the maximum price that someone is willing to pay for the last unit available? 2 POINTS From Demand equation: Price = 900 – (20*8) = $740 ...
... What is the maximum price that someone is willing to pay for the last unit available? 2 POINTS From Demand equation: Price = 900 – (20*8) = $740 ...
Beyond Excess Competition: A New Theory of Implicit Mercantilism
... Each successive monopolist as a seller, either upstream or downstream, is required to behave as a competitive buyer.2 That is, the same economic agent behaves as a monopolist seller, but at the same moment behaves as a competitive buyer, at each and every market point successively related upward and ...
... Each successive monopolist as a seller, either upstream or downstream, is required to behave as a competitive buyer.2 That is, the same economic agent behaves as a monopolist seller, but at the same moment behaves as a competitive buyer, at each and every market point successively related upward and ...
Presentation - Market Design Inc.
... Theorem. If intercept drawn independently from the same distribution, seller’s revenue is maximized by – awarding good to those with highest values if constant hazard rate – shifting quantity toward high demanders if increasing hazard rate ...
... Theorem. If intercept drawn independently from the same distribution, seller’s revenue is maximized by – awarding good to those with highest values if constant hazard rate – shifting quantity toward high demanders if increasing hazard rate ...
A.P. Microeconomics In Class Review #1 Economic Principles & Systems
... units (households & firms) • Macro: study decisions of nation as whole (govts, banking system) ...
... units (households & firms) • Macro: study decisions of nation as whole (govts, banking system) ...
Many small boats are made of fibreglass, which is derived from
... a. The rise in the price of crude oil increases production costs for individual firms and thus shifts the industry supply curve up, as shown in Figure 1. The typical firm’s initial marginal-cost curve is MC1 and its average-total-cost curve is ATC1. In the initial equilibrium, the industry supply cu ...
... a. The rise in the price of crude oil increases production costs for individual firms and thus shifts the industry supply curve up, as shown in Figure 1. The typical firm’s initial marginal-cost curve is MC1 and its average-total-cost curve is ATC1. In the initial equilibrium, the industry supply cu ...
Supply and Demand Infographic Supplemental Activity
... teach it to say “supply and demand.”) The supply and demand infographic highlights basic concepts such as the laws of supply and demand, changes in demand and supply versus changes in the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied, the determinants of demand and supply, and market equilibrium. Supp ...
... teach it to say “supply and demand.”) The supply and demand infographic highlights basic concepts such as the laws of supply and demand, changes in demand and supply versus changes in the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied, the determinants of demand and supply, and market equilibrium. Supp ...
Chapter 6 Self-Paced Book Work
... ____ 10. Deficiency payments are part of a federal program to assist a. farmers. c. consumers. b. senior citizens. d. college students. ____ 11. Prices perform the allocation function well because they do all of the following EXCEPT a. provide neutrality, favoring neither the producer or consumer. ...
... ____ 10. Deficiency payments are part of a federal program to assist a. farmers. c. consumers. b. senior citizens. d. college students. ____ 11. Prices perform the allocation function well because they do all of the following EXCEPT a. provide neutrality, favoring neither the producer or consumer. ...
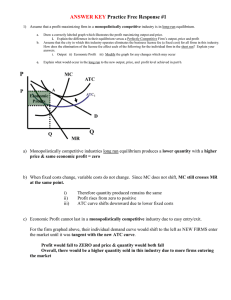
ANSWER KEY Practice Free Response
... Assume that the city in which this industry operates eliminates the business license fee (a fixed cost) for all firms in this industry. How does the elimination of the license fee affect each of the following for the individual firm in the short run? Explain your answers. i. Output ii) Economic Prof ...
... Assume that the city in which this industry operates eliminates the business license fee (a fixed cost) for all firms in this industry. How does the elimination of the license fee affect each of the following for the individual firm in the short run? Explain your answers. i. Output ii) Economic Prof ...
basic supply and demand - Fairfield Public Schools
... Law of demand: All else equal, as prices falls, the quantity demanded rises and as price rises, the quantity demanded falls. ...
... Law of demand: All else equal, as prices falls, the quantity demanded rises and as price rises, the quantity demanded falls. ...
Consumer Equilibrium and Market Demand Chapter 4
... is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
... is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
Ch. 4: Consumer Equilibrium and Market Demand
... is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
... is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
Chapter 4 The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
... ANSWER: 1. Demand increases - Equilibrium price increases - Equilibrium quantity increases 2. Supply decreases - Equilibrium price increases - Equilibrium quantity decreases 3. Supply increases - Equilibrium price decreases - Equilibrium quantity increases 4. Demand increases - Equilibrium price inc ...
... ANSWER: 1. Demand increases - Equilibrium price increases - Equilibrium quantity increases 2. Supply decreases - Equilibrium price increases - Equilibrium quantity decreases 3. Supply increases - Equilibrium price decreases - Equilibrium quantity increases 4. Demand increases - Equilibrium price inc ...
Chapter 2 – Supply and Demand
... Determinants of Supply. ◦ Technology –Positive relationship. ◦ Weather – Positive relationship. ◦ Factor Prices – Negative relationship. Ex: Price of raw peanut goes up due to a long dry summer that hammers raw peanut production. What will happen to the supply of peanut butter? ...
... Determinants of Supply. ◦ Technology –Positive relationship. ◦ Weather – Positive relationship. ◦ Factor Prices – Negative relationship. Ex: Price of raw peanut goes up due to a long dry summer that hammers raw peanut production. What will happen to the supply of peanut butter? ...
Example #1
... 13. Imagine this is the final for Econ 101. You have managed to achieve 50/100 and 70/100 on the first two midterms, which each make up 25% of your grade. The remaining 50% is decided by the final. To get 80% for the course, how much would you need to earn on the final exam out of a hundred possibl ...
... 13. Imagine this is the final for Econ 101. You have managed to achieve 50/100 and 70/100 on the first two midterms, which each make up 25% of your grade. The remaining 50% is decided by the final. To get 80% for the course, how much would you need to earn on the final exam out of a hundred possibl ...
II. SUPPLY AND DEMAND
... 1. Demanders of corn -- the consumers a. Law of demand -- all other things remaining the same, the higher the price of a good, the less is the quantity demanded of that good. b. The demand schedule and curve -- tabular and graphical representation of the negative relationship (downward slope) betwee ...
... 1. Demanders of corn -- the consumers a. Law of demand -- all other things remaining the same, the higher the price of a good, the less is the quantity demanded of that good. b. The demand schedule and curve -- tabular and graphical representation of the negative relationship (downward slope) betwee ...
Unit 1 _ ppt1 _ Economics Refresher 2014
... allowed to move freely – government may set some price controls Prices set by a law differ from the equilibrium price This creates inefficiencies in the market as a ...
... allowed to move freely – government may set some price controls Prices set by a law differ from the equilibrium price This creates inefficiencies in the market as a ...
CHAPTER THREE DEMAND AND SUPPLY • Demand law • Supply
... Draw demand and supply curves Calculate elasticity Differences between change in demand quantity and change in demand Differences between change in supply quantity and change in supply ...
... Draw demand and supply curves Calculate elasticity Differences between change in demand quantity and change in demand Differences between change in supply quantity and change in supply ...
Exercises to complete the Equilibrium discussion MULTIPLE
... 5) Refer to Figure 4.1. If the government will not allow landlords to charge more than $400 for an apartment, which of the following will happen? 5) _______ A) B) C) D) ...
... 5) Refer to Figure 4.1. If the government will not allow landlords to charge more than $400 for an apartment, which of the following will happen? 5) _______ A) B) C) D) ...
Economics 200Y: 2nd Mid Term Name
... losses. Do these government subsidies in bad times increase the long run average income of farmers? (4) (a) If each shareholder’s utility function is not a function of the …rm’s output decisions, then each shareholder’s utility is only a¤ected through the …rm’s e¤ect on shareholder’s wealth. And sin ...
... losses. Do these government subsidies in bad times increase the long run average income of farmers? (4) (a) If each shareholder’s utility function is not a function of the …rm’s output decisions, then each shareholder’s utility is only a¤ected through the …rm’s e¤ect on shareholder’s wealth. And sin ...
Project on Supply and Demand
... Part IV: Predicted Future Market Equilibrium for iPhones Economists do not only use supply and demand to explain how prices are set for products at the moment, they can also use the laws of supply and demand to make predictions of what will happen to the market for a given product. Consider the foll ...
... Part IV: Predicted Future Market Equilibrium for iPhones Economists do not only use supply and demand to explain how prices are set for products at the moment, they can also use the laws of supply and demand to make predictions of what will happen to the market for a given product. Consider the foll ...