File
... 4.4 Market Effects of Changes in Demand A change in demand occurs when a variable other than the price of the product changes. When demand changes, people want to buy more or less of a product at the same price. Since the price of the good has not changed, the demand curve must have shifted. An incr ...
... 4.4 Market Effects of Changes in Demand A change in demand occurs when a variable other than the price of the product changes. When demand changes, people want to buy more or less of a product at the same price. Since the price of the good has not changed, the demand curve must have shifted. An incr ...
Chapter 4: Supply and Demand
... supply interact to bring about equilibrium • Show the effect of a shift in demand and supply on equilibrium price and quantity • State the limitations of demand and supply analysis ...
... supply interact to bring about equilibrium • Show the effect of a shift in demand and supply on equilibrium price and quantity • State the limitations of demand and supply analysis ...
ch 4 ppt slides
... supply interact to bring about equilibrium • Show the effect of a shift in demand and supply on equilibrium price and quantity • State the limitations of demand and supply analysis ...
... supply interact to bring about equilibrium • Show the effect of a shift in demand and supply on equilibrium price and quantity • State the limitations of demand and supply analysis ...
all together
... • The incidence of a tax does not depend on whether the tax is levied on buyers or sellers • It depends on the price elasticities of supply and demand. • The burden falls on the side of the market that is less elastic ...
... • The incidence of a tax does not depend on whether the tax is levied on buyers or sellers • It depends on the price elasticities of supply and demand. • The burden falls on the side of the market that is less elastic ...
MBA651_Supply and Demand I_ALL_QUESTIONS
... service employees discover a new and better way to prepare a field before planting. They teach it to all farmers, who use it to increase the amount of corn that they grow on each acre of land. Adjust this graph to show the effect that this discovery has on the market for corn. Correct Answer: ...
... service employees discover a new and better way to prepare a field before planting. They teach it to all farmers, who use it to increase the amount of corn that they grow on each acre of land. Adjust this graph to show the effect that this discovery has on the market for corn. Correct Answer: ...
Supply and Demand: An Introduction
... 4. An increased preference by demanders for the good or service 5. An increase in the population of potential ...
... 4. An increased preference by demanders for the good or service 5. An increase in the population of potential ...
Chapter 4 Test Bank
... 22. A severe freeze has once again damaged the Florida orange crop. The impact on the market for orange juice will be a leftward shift of: A. the supply curve. B. the demand curve, as consumers try to economize because of the shortage. C. both the supply and demand curves. D. the supply curve and a ...
... 22. A severe freeze has once again damaged the Florida orange crop. The impact on the market for orange juice will be a leftward shift of: A. the supply curve. B. the demand curve, as consumers try to economize because of the shortage. C. both the supply and demand curves. D. the supply curve and a ...
Economics: Demand and Consumer Behavior
... Inversely, since good B gives less marginal utility per Peso, I would most probably consume less of good B until the marginal utility (per Peso) of good B rises until it is the same as that of good A. ...
... Inversely, since good B gives less marginal utility per Peso, I would most probably consume less of good B until the marginal utility (per Peso) of good B rises until it is the same as that of good A. ...
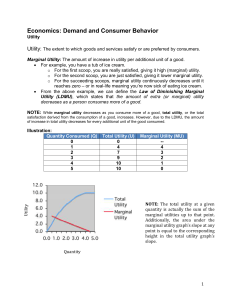
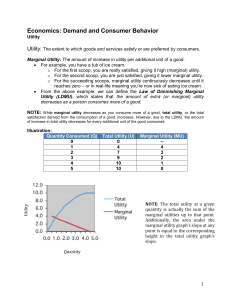
Economics: Demand and Consumer Behavior Utility Utility: The
... Inversely, since good B gives less marginal utility per Peso, I would most probably consume less of good B until the marginal utility (per Peso) of good B rises until it is the same as that of good A. ...
... Inversely, since good B gives less marginal utility per Peso, I would most probably consume less of good B until the marginal utility (per Peso) of good B rises until it is the same as that of good A. ...
Answers to the Problems – Chapter 3
... In reason number 1, the article drastically confuses “a change in demand,” that is, a shift of the demand curve, and “a change in the quantity demanded,” that is, a movement along the demand curve. The article states that “a relatively strong U.S. economy continues to fuel strong demand for gasoline ...
... In reason number 1, the article drastically confuses “a change in demand,” that is, a shift of the demand curve, and “a change in the quantity demanded,” that is, a movement along the demand curve. The article states that “a relatively strong U.S. economy continues to fuel strong demand for gasoline ...
Demand, Supply and Market
... which households supply their savings, for interest or for claims to future profits, to firms that demand funds to buy capital goods. ...
... which households supply their savings, for interest or for claims to future profits, to firms that demand funds to buy capital goods. ...
chapter 3 - Choose your book for Principles of Economics, by Fred
... The supply curve is an upward-sloping line starting at the point 20 brooms per month and $1 per broom. For each $1 increase in the price of a broom, the quantity of ...
... The supply curve is an upward-sloping line starting at the point 20 brooms per month and $1 per broom. For each $1 increase in the price of a broom, the quantity of ...
EOA611S-Unit 2
... Consumers usually prefer more of something to less of it. This preference for greater quantity is reflected in the indifference curves. Higher ID’s curves represent larger quantities of goods than lower ID’s curves. The slope represent the rate at which the consumer is willing to substitute one good ...
... Consumers usually prefer more of something to less of it. This preference for greater quantity is reflected in the indifference curves. Higher ID’s curves represent larger quantities of goods than lower ID’s curves. The slope represent the rate at which the consumer is willing to substitute one good ...
Chapter 3: The Market System
... can now buy only 8 hamburgers. The higher price reduces your real income, or purchasing power, which has the tendency to induce you to purchase fewer units of the good. The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded can be shown by a demand schedule for any specific commodity. Exhibit ...
... can now buy only 8 hamburgers. The higher price reduces your real income, or purchasing power, which has the tendency to induce you to purchase fewer units of the good. The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded can be shown by a demand schedule for any specific commodity. Exhibit ...
Document
... Topic: Demand in Product / Output Markets Skill: Conceptual AACSB: Reflective Thinking ...
... Topic: Demand in Product / Output Markets Skill: Conceptual AACSB: Reflective Thinking ...
Lecture 2: Demand, Supply & Markets
... What would happen to present demand, if buyers expected future changes in: price, income, taxes, or other factors? Suppose bad weather ruins the summer rice crop, will consumers expect to pay higher prices and bid up prices? They might increase quantity demanded at the same time because they expect ...
... What would happen to present demand, if buyers expected future changes in: price, income, taxes, or other factors? Suppose bad weather ruins the summer rice crop, will consumers expect to pay higher prices and bid up prices? They might increase quantity demanded at the same time because they expect ...
Chapter 3 - Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
... The model of supply and demand is the economics profession’s greatest contribution to human understanding because it explains the operation of the markets on which we depend for nearly everything that we eat, drink, or consume. The model is so powerful and so widely used that to many people it is ec ...
... The model of supply and demand is the economics profession’s greatest contribution to human understanding because it explains the operation of the markets on which we depend for nearly everything that we eat, drink, or consume. The model is so powerful and so widely used that to many people it is ec ...
Week 6 Chapter 5 & 6: Main lecture on Revenue and Production
... • Now we have to examine what we get for an additional unit ...
... • Now we have to examine what we get for an additional unit ...
Government Influences on Markets
... Blocking rent adjustments that bring the quantity of housing demanded into equality with the quantity supplied doesn’t end scarcity. So when the law prevents the rent from adjusting and blocks the price mechanism from allocating scarce housing, some other allocation mechanism must be used. If that m ...
... Blocking rent adjustments that bring the quantity of housing demanded into equality with the quantity supplied doesn’t end scarcity. So when the law prevents the rent from adjusting and blocks the price mechanism from allocating scarce housing, some other allocation mechanism must be used. If that m ...