ch_04
... representation of the law of supply. The supply curve slopes upward to the right. The slope tells us that the quantity supplied varies directly – in the same direction – with the price. ...
... representation of the law of supply. The supply curve slopes upward to the right. The slope tells us that the quantity supplied varies directly – in the same direction – with the price. ...
Q 1 /2 - Wiley
... Even if we have no capacity constraints, and constant marginal cost, a firm cannot capture all demand by cutting price. This blunts price-cutting incentives and means that the firms' own behavior does not mimic free entry ...
... Even if we have no capacity constraints, and constant marginal cost, a firm cannot capture all demand by cutting price. This blunts price-cutting incentives and means that the firms' own behavior does not mimic free entry ...
Imperfect Competition
... The big picture, before the details Numerical examples of price competition games necessarily get heavy. Before we see too many symbols and parentheses, let’s outline the big picture, including (in italics) what it takes to fully specify such a game and solve for the Nash equilibrium. 1. Each firm h ...
... The big picture, before the details Numerical examples of price competition games necessarily get heavy. Before we see too many symbols and parentheses, let’s outline the big picture, including (in italics) what it takes to fully specify such a game and solve for the Nash equilibrium. 1. Each firm h ...
University of Groningen Identification of strategic industries
... difficult, because lobby groups play an important role and the outcomes of the alternatives are characterized by a high degree of uncertainty. Adding to the complexity of this analysis is the fact that industries are generally far from isolated, but are part of different types of networks. Although ...
... difficult, because lobby groups play an important role and the outcomes of the alternatives are characterized by a high degree of uncertainty. Adding to the complexity of this analysis is the fact that industries are generally far from isolated, but are part of different types of networks. Although ...
Price Ceilings and Price Floors
... The Organic Trade Association reported sales increased from $1 billion in 1990 to $31.5 billion in 2011, more than 90% of which were sales of food products. Why, then, are organic foods more expensive than their conventional counterparts? The answer is a clear application of the theories of supply a ...
... The Organic Trade Association reported sales increased from $1 billion in 1990 to $31.5 billion in 2011, more than 90% of which were sales of food products. Why, then, are organic foods more expensive than their conventional counterparts? The answer is a clear application of the theories of supply a ...
We Sold a Million Units – The Role of Advertising Past
... pharmaceutical firms often distribute advertisements to report the percentage of doctors or dentists who use certain treatments and health products; automobile companies frequently invest in publicity to stress that certain model has been the most sold during the previous month or year; advertising ...
... pharmaceutical firms often distribute advertisements to report the percentage of doctors or dentists who use certain treatments and health products; automobile companies frequently invest in publicity to stress that certain model has been the most sold during the previous month or year; advertising ...
Slide 1
... In this equilibrium, quantity supplied and quantity demanded both equal 100 burgers. To the right, the government imposes a price ceiling of $2. Because the price ceiling is below the equilibrium price of $3, the market price equals $2. At this price, 125 burgers are demanded and only 75 are supplie ...
... In this equilibrium, quantity supplied and quantity demanded both equal 100 burgers. To the right, the government imposes a price ceiling of $2. Because the price ceiling is below the equilibrium price of $3, the market price equals $2. At this price, 125 burgers are demanded and only 75 are supplie ...
microfinance semester 1
... Refers to day to day to market supply. This kind of supply is fixed and can not be increased suddenly and also perishable goods. ...
... Refers to day to day to market supply. This kind of supply is fixed and can not be increased suddenly and also perishable goods. ...
第四章PPT
... Theresa’s consumer surplus is equal to the area of rectangle A and is the difference between the highest price she would pay—$6—and the market price of $3.50. Tom’s consumer surplus is equal to the area of rectangle B, and Terri’s consumer surplus is equal to the area of rectangle C. Total consumer ...
... Theresa’s consumer surplus is equal to the area of rectangle A and is the difference between the highest price she would pay—$6—and the market price of $3.50. Tom’s consumer surplus is equal to the area of rectangle B, and Terri’s consumer surplus is equal to the area of rectangle C. Total consumer ...
Chapter 3 - Tucker Web Site
... Understanding the price system is a crucial milestone on your quest to learn the economic way of thinking and analyze real-world economic issues. There are two sides to a market: the market demand curve and the market supply curve. The location of the demand curve shifts when changes occur in such n ...
... Understanding the price system is a crucial milestone on your quest to learn the economic way of thinking and analyze real-world economic issues. There are two sides to a market: the market demand curve and the market supply curve. The location of the demand curve shifts when changes occur in such n ...
Complementary Monopolies and Bargaining
... over 400,000 buyers and purchasing agents who evaluate suppliers, review product quality, and negotiate supply contracts.3 The main results of the analysis are as follows. First, I consider the two-stage game when the downstream market is perfectly competitive. I show that the strategic game in sup ...
... over 400,000 buyers and purchasing agents who evaluate suppliers, review product quality, and negotiate supply contracts.3 The main results of the analysis are as follows. First, I consider the two-stage game when the downstream market is perfectly competitive. I show that the strategic game in sup ...
Q d
... • A competitive market has many buyers and sellers, each of whom has little or no influence on the market price. • Economists use the supply and demand model to analyze competitive markets. • The downward-sloping demand curve reflects the Law of Demand, which states that the quantity buyers demand o ...
... • A competitive market has many buyers and sellers, each of whom has little or no influence on the market price. • Economists use the supply and demand model to analyze competitive markets. • The downward-sloping demand curve reflects the Law of Demand, which states that the quantity buyers demand o ...
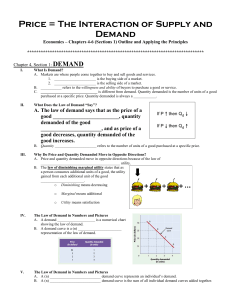
Price = The Interaction of Supply and Demand
... Moving to Equilibrium Supply and demand work together to determine price. For example, they work together to determine the price of corn at an auction (see example on the presentation). A _______________ occurs when the quantity supplied of a good is greater than the quantity demanded. Surpluses ...
... Moving to Equilibrium Supply and demand work together to determine price. For example, they work together to determine the price of corn at an auction (see example on the presentation). A _______________ occurs when the quantity supplied of a good is greater than the quantity demanded. Surpluses ...
Demand and Supply
... When price < equilibrium price, then quantity demanded > the quantity supplied. There is excess demand or a shortage. Suppliers will raise the price due to too many buyers chasing too few goods, thereby moving toward equilibrium. ...
... When price < equilibrium price, then quantity demanded > the quantity supplied. There is excess demand or a shortage. Suppliers will raise the price due to too many buyers chasing too few goods, thereby moving toward equilibrium. ...
An improvement in technology lowers the cost of producing DVD
... b. The decline in the price of stereos increases consumer surplus from area A to A + B + C + D, an increase in the amount B + C + D. Prior to the shift in supply, producer surplus was areas B + E (the area above the supply curve and below the price). After the shift in supply, producer surplus is ar ...
... b. The decline in the price of stereos increases consumer surplus from area A to A + B + C + D, an increase in the amount B + C + D. Prior to the shift in supply, producer surplus was areas B + E (the area above the supply curve and below the price). After the shift in supply, producer surplus is ar ...
File
... The Price of Admission: • Compare the box office price for a recent Justin Timberlake concert in Miami, Florida, to the StubHub.com price for seats in the same location: $88.50 versus $155. • Why is there such a big difference in prices? For major events, buying tickets from the box office means wai ...
... The Price of Admission: • Compare the box office price for a recent Justin Timberlake concert in Miami, Florida, to the StubHub.com price for seats in the same location: $88.50 versus $155. • Why is there such a big difference in prices? For major events, buying tickets from the box office means wai ...