
Document
... a. In a closed economy with no government spending or taxes (G=T=0), the level of consumption expenditure is C = A + mpc Y while investment expenditure is given by I = B – ieir Firms in the short run set the price level P = 1. We can then write the demand for liquid assets as: M = Y - iemr Solve ...
... a. In a closed economy with no government spending or taxes (G=T=0), the level of consumption expenditure is C = A + mpc Y while investment expenditure is given by I = B – ieir Firms in the short run set the price level P = 1. We can then write the demand for liquid assets as: M = Y - iemr Solve ...
Second quiz with answers
... in terms of these two quantities if you had the real numbers. Given what the report says, which component is causing the unemployment rate to decline? ...
... in terms of these two quantities if you had the real numbers. Given what the report says, which component is causing the unemployment rate to decline? ...
Chapter19 - Web.UVic.ca
... b) Potential GDP is the level of output produced when all factors of production are being used at their normal rates. Output can exceed potential when labour works overtime or when capital and land are used more intensively than normal. c) A recessionary output gap only requires Y to be below Y*. It ...
... b) Potential GDP is the level of output produced when all factors of production are being used at their normal rates. Output can exceed potential when labour works overtime or when capital and land are used more intensively than normal. c) A recessionary output gap only requires Y to be below Y*. It ...
總體經濟學 期末考 日期:97
... pursued a policy of steady money growth. 6. The time between when a recession begins and when the central bank lowers interest rates to stimulate aggregate demand is an example of an: (A) inside lag of monetary policy. (C) inside lag of fiscal policy. (B) outside lag of monetary policy. (D) outside ...
... pursued a policy of steady money growth. 6. The time between when a recession begins and when the central bank lowers interest rates to stimulate aggregate demand is an example of an: (A) inside lag of monetary policy. (C) inside lag of fiscal policy. (B) outside lag of monetary policy. (D) outside ...
Monetary Policy
... – Influences both the nominal and real interest rate – To affect a nominal interest rate does some kind of open market operation to change it – By changing the quantity of money that the Fed achieves its target for the Federal Funds rate – The expected inflation rate does not change every time the F ...
... – Influences both the nominal and real interest rate – To affect a nominal interest rate does some kind of open market operation to change it – By changing the quantity of money that the Fed achieves its target for the Federal Funds rate – The expected inflation rate does not change every time the F ...
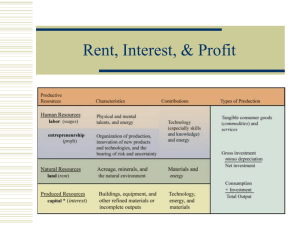
Rent, Interest, and Profit
... How does economic rent explain suburban sprawl? Why is land in Lake Oswego so expensive? Why is land in Western Oregon worth more than land in Eastern Oregon? Complete Student Workbook Activity 50 ...
... How does economic rent explain suburban sprawl? Why is land in Lake Oswego so expensive? Why is land in Western Oregon worth more than land in Eastern Oregon? Complete Student Workbook Activity 50 ...
Spring 2014
... C. The Frisch elasticity of labor supply is defined to be the elasticity of hours worked to the wage rate holding the marginal utility of wealth (the Lagrange multiplier for the budget constraint) constant. Derive the Frisch elasticity for your decentralized economy for each of the two utility funct ...
... C. The Frisch elasticity of labor supply is defined to be the elasticity of hours worked to the wage rate holding the marginal utility of wealth (the Lagrange multiplier for the budget constraint) constant. Derive the Frisch elasticity for your decentralized economy for each of the two utility funct ...
Institute of Business Management Semester II Course Instructor
... Q#3 a) What determines the position of the FE line? Give two examples of changes in the economy that would shift the FE line to the right. b). What relationship does the IS curve capture? Derive the IS curve graphically and show why it slopes as it does. Give two examples of changes in the economy t ...
... Q#3 a) What determines the position of the FE line? Give two examples of changes in the economy that would shift the FE line to the right. b). What relationship does the IS curve capture? Derive the IS curve graphically and show why it slopes as it does. Give two examples of changes in the economy t ...
Document
... b. potential output exceeds actual output. c. the output gap is zero. d. actual output exceeds potential output. ...
... b. potential output exceeds actual output. c. the output gap is zero. d. actual output exceeds potential output. ...
Lecture 3. Measuring Macroeconomic Variables
... change in the price level. Using the GDP deflator to measure the price level, and using the measures in the upper panel of Table 2.4, inflation over the time from year 1 to year 2 is measured as a percentage rate of change: ...
... change in the price level. Using the GDP deflator to measure the price level, and using the measures in the upper panel of Table 2.4, inflation over the time from year 1 to year 2 is measured as a percentage rate of change: ...
Final Exam
... determined without first knowing productivity. Thus, the neoclassical theory falls into a circular reasoning (10 points). (b) Invisible Hand: the notion of efficient allocation of capital across different industries and efficient allocation of resources across different times points are meaningless ...
... determined without first knowing productivity. Thus, the neoclassical theory falls into a circular reasoning (10 points). (b) Invisible Hand: the notion of efficient allocation of capital across different industries and efficient allocation of resources across different times points are meaningless ...
Use the information below to answer the following two questions:
... 18) How much private investment spending is crowded out by the government deficit? a. $0 b. $200 c. $400 d. $1000 ...
... 18) How much private investment spending is crowded out by the government deficit? a. $0 b. $200 c. $400 d. $1000 ...
100學年度基礎學科會考
... (B) increase because demand is elastic in this range. (C) decrease because demand is elastic in this range. (D) decrease because demand is inelastic in this range. ( ) 3. In the figure above, moving from production at point d to production at point a requires (A) technological change. (B) a decrease ...
... (B) increase because demand is elastic in this range. (C) decrease because demand is elastic in this range. (D) decrease because demand is inelastic in this range. ( ) 3. In the figure above, moving from production at point d to production at point a requires (A) technological change. (B) a decrease ...
14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Spring 06 Quiz 3
... expected, are equal to zero, so the real and the nominal interest rates are equal. Assume initially that Y = Y 0e = Yn = Yn0 , r = r0e = rn , T = G = T 0e = T̄ . In words, output, current and expected, is equal to the natural level of output, which is itself constant. The real interest rate, current ...
... expected, are equal to zero, so the real and the nominal interest rates are equal. Assume initially that Y = Y 0e = Yn = Yn0 , r = r0e = rn , T = G = T 0e = T̄ . In words, output, current and expected, is equal to the natural level of output, which is itself constant. The real interest rate, current ...
Discussion of The Design of Monetary and Fiscal Policy: A Global Perspective
... Sveen and Weinke argue that Carlstrom and Fuerst too optimistic. Kimball shows that anything that makes a firms marginal cost more sensitive to its own output increases price stickiness. Carlstrom and Fuerst assume a single economy wide market for capital. If assume that capital is firm specific, pr ...
... Sveen and Weinke argue that Carlstrom and Fuerst too optimistic. Kimball shows that anything that makes a firms marginal cost more sensitive to its own output increases price stickiness. Carlstrom and Fuerst assume a single economy wide market for capital. If assume that capital is firm specific, pr ...
Production and Growth
... • In the United States over the past century, average income as measured by real GDP per person has grown by about 2 percent per year. ...
... • In the United States over the past century, average income as measured by real GDP per person has grown by about 2 percent per year. ...
Problem Set 4 (Chapters 10-11) Essay Questions Izmir University of Economics
... A) the price level in a given period expressed as a percentage of the price level in the base period, which is by definition equal to zero B) the inflation rate in a given period compared to the inflation rate in the base period, which is by definition equal to zero C) the price level in a given per ...
... A) the price level in a given period expressed as a percentage of the price level in the base period, which is by definition equal to zero B) the inflation rate in a given period compared to the inflation rate in the base period, which is by definition equal to zero C) the price level in a given per ...
Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics ECON 102
... 1) Suppose that Ahmet has just graduated from university and looking for a job. However, as a first-time job seeker he lacks the sufficient knowledge for finding the company that has the job that is available and suitable for him. Thus, he is currently unemployed. What kind of unemployment is descri ...
... 1) Suppose that Ahmet has just graduated from university and looking for a job. However, as a first-time job seeker he lacks the sufficient knowledge for finding the company that has the job that is available and suitable for him. Thus, he is currently unemployed. What kind of unemployment is descri ...
Midterm
... European Central Bank raises the short-term interest rate, all else equal. 14. According to the uncovered interest rate parity, the dollar dereciates when the European Central Bank is expected to raise the short-term interest rate, all else equal. 15. A permanent reduction in money supply in the Eur ...
... European Central Bank raises the short-term interest rate, all else equal. 14. According to the uncovered interest rate parity, the dollar dereciates when the European Central Bank is expected to raise the short-term interest rate, all else equal. 15. A permanent reduction in money supply in the Eur ...














![Lecture25(Ch21[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008219352_1-9f95e5a074002ea83218cbb8cead45d4-300x300.png)







