Economics Topic Wise Reference Material for
... Ans. – MRT/MOC of a good along a PPC is defined as the amount of one good that needs to be sacrificed per unit increase in production of the other good. Q.5 what is the problem of “what to produce” ? Ans.-It is the problem of selection of different goods and their quantities with available resources ...
... Ans. – MRT/MOC of a good along a PPC is defined as the amount of one good that needs to be sacrificed per unit increase in production of the other good. Q.5 what is the problem of “what to produce” ? Ans.-It is the problem of selection of different goods and their quantities with available resources ...
Financial Collateral and Macroeconomic Amplification∗
... their investment in physical capital to meet borrowers’ higher demand for credit, so that these can expand their capital investment further. In turn, the response of total production – which increases in borrowers’real assets, ceteris paribus –is ampli…ed, relative to situations in which bankers’fea ...
... their investment in physical capital to meet borrowers’ higher demand for credit, so that these can expand their capital investment further. In turn, the response of total production – which increases in borrowers’real assets, ceteris paribus –is ampli…ed, relative to situations in which bankers’fea ...
By How Much Does GDP Rise If the Government Buys More Output?
... and work or between consumption this year and in any future year. Military spending is the obvious example. If instead the government provided consumers with goods and services they would have purchased anyway, the resulting multiplier would be lower. In the extreme case, where the government purcha ...
... and work or between consumption this year and in any future year. Military spending is the obvious example. If instead the government provided consumers with goods and services they would have purchased anyway, the resulting multiplier would be lower. In the extreme case, where the government purcha ...
Principles Of Economics
... The sample quiz provided for each chapter has two sections: multiple-choice and nonmultiple choice. The multiple-choice section is designed to be given after a student reads the chapter but before material is covered in class. The multiple-choice questions test mainly knowledge (the first level of l ...
... The sample quiz provided for each chapter has two sections: multiple-choice and nonmultiple choice. The multiple-choice section is designed to be given after a student reads the chapter but before material is covered in class. The multiple-choice questions test mainly knowledge (the first level of l ...
T.Y.B.A. Economics Paper - IV
... combination. The kinked shape of the demand curve is based on the assumption that the competitors react differently to a rise in price or to a fall in price. It is also assumed that when an individual seller increases the price of his product other sellers will not increase their prices so that the ...
... combination. The kinked shape of the demand curve is based on the assumption that the competitors react differently to a rise in price or to a fall in price. It is also assumed that when an individual seller increases the price of his product other sellers will not increase their prices so that the ...
By How Much Does GDP Rise If the Government Buys More Output?
... and work or between consumption this year and in any future year. Military spending is the obvious example. If instead the government provided consumers with goods and services they would have purchased anyway, the resulting multiplier would be lower. In the extreme case, where the government purcha ...
... and work or between consumption this year and in any future year. Military spending is the obvious example. If instead the government provided consumers with goods and services they would have purchased anyway, the resulting multiplier would be lower. In the extreme case, where the government purcha ...
norface08 Alho 8162004 en
... The productivity effect emerges because labour can be allocated to its most productive use and the productivity of the outsourced labour is thereby enhanced. The price effect is derived from the fact that the price of the output, the cost of which is reduced, will also go down. The job effect simply ...
... The productivity effect emerges because labour can be allocated to its most productive use and the productivity of the outsourced labour is thereby enhanced. The price effect is derived from the fact that the price of the output, the cost of which is reduced, will also go down. The job effect simply ...
The Interest Rate Effect on Private Saving: Alternative Perspectives
... levels would lead to higher levels of saving. Or, the effect of the interest rate on saving may differ depending on macroeconomic or demographical conditions or policy environment. Examining the link between the interest rate and saving is important. In the short term, whether policy interest rates ...
... levels would lead to higher levels of saving. Or, the effect of the interest rate on saving may differ depending on macroeconomic or demographical conditions or policy environment. Examining the link between the interest rate and saving is important. In the short term, whether policy interest rates ...
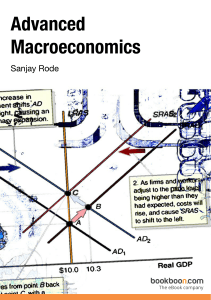
Advanced Macroeconomics - Juridica – Kolegji Evropian
... international factors affecting macroeconomics. Words fall short to express my deep sense of gratitude to my research guide, Dr. Neeraj Hatekar, Professor, Department of Economics, University of Mumbai, Mumbai, India. His continuous support in my research was a source of inspiration. He taught me va ...
... international factors affecting macroeconomics. Words fall short to express my deep sense of gratitude to my research guide, Dr. Neeraj Hatekar, Professor, Department of Economics, University of Mumbai, Mumbai, India. His continuous support in my research was a source of inspiration. He taught me va ...
Chapter 22 - Samuel Moon Jung
... Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 22 Aggregate Demand and Supply Analysis 22.1 Aggregate Demand 1) The aggregate demand curve is the total quantity of an economy's A) intermediate goods demanded at different inflation rates. B) intermediate goods demanded at a part ...
... Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 22 Aggregate Demand and Supply Analysis 22.1 Aggregate Demand 1) The aggregate demand curve is the total quantity of an economy's A) intermediate goods demanded at different inflation rates. B) intermediate goods demanded at a part ...
ExamView Pro - ec1001june2009.tst
... 5. According to a utilitarian, total social utility will be maximized when marginal pounds are distributed to the people with the a. greatest need. b. highest total utility from their income. c. most productive labor resources. d. highest marginal utility of income. 6. In the long run, large and con ...
... 5. According to a utilitarian, total social utility will be maximized when marginal pounds are distributed to the people with the a. greatest need. b. highest total utility from their income. c. most productive labor resources. d. highest marginal utility of income. 6. In the long run, large and con ...
THE MIT DICTIONARY OF MODERN ECONOMICS
... less than fourteen people must inevitably be open to criticism and that they will have omitted something, somewhere which others will see as being far more important than many of the entries chosen. To this end all criticism and suggestions for improvement are welcomed. For the moment, we believe th ...
... less than fourteen people must inevitably be open to criticism and that they will have omitted something, somewhere which others will see as being far more important than many of the entries chosen. To this end all criticism and suggestions for improvement are welcomed. For the moment, we believe th ...
8 the economy at full employment: the classical model
... 34) The marginal product of labor is assumed to decrease as more labor is employed because A) each extra hour is less skilled than the previous hour. B) the more labor employed, the more productive the workers become. C) capital and technology are fixed at any particular point in time. D) labor is a ...
... 34) The marginal product of labor is assumed to decrease as more labor is employed because A) each extra hour is less skilled than the previous hour. B) the more labor employed, the more productive the workers become. C) capital and technology are fixed at any particular point in time. D) labor is a ...
Forward Guidance and Macroeconomic Outcomes Since the Financial Crisis ∗ Jeffrey R. Campbell
... term premia that is absent from log-linearized New Keynesian (NK) models in which the expectations theory of the term structure holds good and real rates should not be affected much beyond the duration of price stickiness. These findings raise questions about the use of standard NK models for ident ...
... term premia that is absent from log-linearized New Keynesian (NK) models in which the expectations theory of the term structure holds good and real rates should not be affected much beyond the duration of price stickiness. These findings raise questions about the use of standard NK models for ident ...
Slides - University of Alberta
... used to incorporate a possible "refuge" for the lemming at very low densities. when lemmings are so dispersed, then they must become very hard to locate for the stoat. ...
... used to incorporate a possible "refuge" for the lemming at very low densities. when lemmings are so dispersed, then they must become very hard to locate for the stoat. ...
The Interaction between Household and Firm Dynamics and the
... during recessions, when lower than anticipated in‡ation increases the real value of debt burdens. This feature cannot be evaluated adequately with the standard assumption of one-period debt. Second, ...
... during recessions, when lower than anticipated in‡ation increases the real value of debt burdens. This feature cannot be evaluated adequately with the standard assumption of one-period debt. Second, ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES Robert E. Hall Working Paper 15496
... because monetary policy had driven short-term safe interest rates down to zero without heading off the contraction. Fiscal policy, including increases in federal purchases and in state and local purchases financed by federal grants, has become an important part of the government’s response to a seve ...
... because monetary policy had driven short-term safe interest rates down to zero without heading off the contraction. Fiscal policy, including increases in federal purchases and in state and local purchases financed by federal grants, has become an important part of the government’s response to a seve ...
OnlineAppendix
... + sr = 0.66. The rest of GDP corresponds to profits paid to intangible capital, p = 1%. The Allocation of Labor: The equilibrium allocation of labor between production and research is pinned down in equation (12) by the choices of parameters above and our calibrated innovation intensity of the econo ...
... + sr = 0.66. The rest of GDP corresponds to profits paid to intangible capital, p = 1%. The Allocation of Labor: The equilibrium allocation of labor between production and research is pinned down in equation (12) by the choices of parameters above and our calibrated innovation intensity of the econo ...
Monetary Policy According to HANK ∗ Greg Kaplan Benjamin Moll
... 2010). The most compelling corroboration of this behavior is perhaps the quasiexperimental evidence that uncovers (i) an aggregate quarterly marginal propensity to consume out of unanticipated, transitory, small government transfers of around 25 percent (Johnson et al., 2006; Parker et al., 2013) an ...
... 2010). The most compelling corroboration of this behavior is perhaps the quasiexperimental evidence that uncovers (i) an aggregate quarterly marginal propensity to consume out of unanticipated, transitory, small government transfers of around 25 percent (Johnson et al., 2006; Parker et al., 2013) an ...
"Monetary Policy According to HANK"
... The most compelling corroboration of this behavior is perhaps the quasi-experimental evidence that uncovers (i) an aggregate quarterly marginal propensity to consume out of unanticipated, transitory, small government transfers of around 25 percent (Johnson et al., 2006; Parker et al., 2013) and (ii) ...
... The most compelling corroboration of this behavior is perhaps the quasi-experimental evidence that uncovers (i) an aggregate quarterly marginal propensity to consume out of unanticipated, transitory, small government transfers of around 25 percent (Johnson et al., 2006; Parker et al., 2013) and (ii) ...