pricing and the law
... • Supply—the amounts of a good or service that will be offered for sale at different prices during a specified period. • Pure competition—a market structure with so many buyers and sellers that no single participant can significantly influence price. • Monopolistic competition—diverse parties exchan ...
... • Supply—the amounts of a good or service that will be offered for sale at different prices during a specified period. • Pure competition—a market structure with so many buyers and sellers that no single participant can significantly influence price. • Monopolistic competition—diverse parties exchan ...
Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Supply and Demand
... Recall from Chapter 1 that because economic models rely on assumptions, they are simplifications of reality. In some cases, the assumptions of the model may not seem to match the economic situation being analyzed. For example, the model of demand and supply assumes that we are analyzing a perfectly ...
... Recall from Chapter 1 that because economic models rely on assumptions, they are simplifications of reality. In some cases, the assumptions of the model may not seem to match the economic situation being analyzed. For example, the model of demand and supply assumes that we are analyzing a perfectly ...
Document
... the word) are zero, the industry stops growing, but does not die. This is because all factors of production are being remunerated at their opportunity cost, i.e. at the rate they would earn elsewhere in the economy. The existence of positive profits in an industry constitutes a signal that outputs ...
... the word) are zero, the industry stops growing, but does not die. This is because all factors of production are being remunerated at their opportunity cost, i.e. at the rate they would earn elsewhere in the economy. The existence of positive profits in an industry constitutes a signal that outputs ...
Elasticity Sample Questions
... Which of the following best describes price elasticity of demand? A. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the change in the quantity demanded to a change in price. B. Price elasticity of demand measures the change in price versus a change in quantity demanded. C. Price elastici ...
... Which of the following best describes price elasticity of demand? A. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the change in the quantity demanded to a change in price. B. Price elasticity of demand measures the change in price versus a change in quantity demanded. C. Price elastici ...
review mon and after
... belief that it faced demand curve D2 and acted without consideration of the other firm's behavior, the market price would likely end up being _______ and the combined economic profits of the firms would be _______. A) P1; given by the area of the rectangle bounded by 0P1CQ4 B) P1; zero C) P3; given ...
... belief that it faced demand curve D2 and acted without consideration of the other firm's behavior, the market price would likely end up being _______ and the combined economic profits of the firms would be _______. A) P1; given by the area of the rectangle bounded by 0P1CQ4 B) P1; zero C) P3; given ...
CHAPTER 1
... ►Teaching tips: Be sure students understand the graph in Figure 11-1. It may help them to understand a perfectly elastic demand curve by drawing a series of demand curves that are increasingly more elastic, but not perfectly so. With each of these curves, the response of quantity demanded to a given ...
... ►Teaching tips: Be sure students understand the graph in Figure 11-1. It may help them to understand a perfectly elastic demand curve by drawing a series of demand curves that are increasingly more elastic, but not perfectly so. With each of these curves, the response of quantity demanded to a given ...
Final Exam A
... a downward-sloping long-run average cost (LRAC) curve. an upward-sloping long-run average cost (LRAC) curve. an upward-sloping long-run marginal cost (LRMC) curve. a horizontal long-run average cost (LRAC) curve. ...
... a downward-sloping long-run average cost (LRAC) curve. an upward-sloping long-run average cost (LRAC) curve. an upward-sloping long-run marginal cost (LRMC) curve. a horizontal long-run average cost (LRAC) curve. ...
Document
... True: Differential pricing can occur in several ways: it can be negotiated; it can involve secondary markets, or periodic or random discounting. Pages 274-275 ...
... True: Differential pricing can occur in several ways: it can be negotiated; it can involve secondary markets, or periodic or random discounting. Pages 274-275 ...
Microeconomics, 4e (Perloff)
... elasticity of demand, and a negatively sloped income consumption curve is associated with a negative income elasticity of demand. The income consumption curve represents how consumption changes with an increase in income. An upward sloping income consumption curve represents an increase in consumpti ...
... elasticity of demand, and a negatively sloped income consumption curve is associated with a negative income elasticity of demand. The income consumption curve represents how consumption changes with an increase in income. An upward sloping income consumption curve represents an increase in consumpti ...
Lecture 7 - Har Wai Mun
... • Each firm has a large market share. • The firms are interdependent. Thus, the behavior of oligopoly firms depend on the behavior of other (oligopoly) firms in the industry. Before making a decision, each firm must consider how the other firms will react to its decision and influence its profit. (3 ...
... • Each firm has a large market share. • The firms are interdependent. Thus, the behavior of oligopoly firms depend on the behavior of other (oligopoly) firms in the industry. Before making a decision, each firm must consider how the other firms will react to its decision and influence its profit. (3 ...
Lecture on Household Sorting and Public Goods
... receives a price of P’ • Problem is that firm producing at optimal point (S*) will lose money because D curve shows people not willing to pay that much • But there is a social cost to not having enough bus service, so to get residents to buy the socially optimal amount, P must be lower than market p ...
... receives a price of P’ • Problem is that firm producing at optimal point (S*) will lose money because D curve shows people not willing to pay that much • But there is a social cost to not having enough bus service, so to get residents to buy the socially optimal amount, P must be lower than market p ...
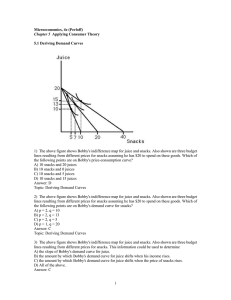
Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin)
... 12) Jason needs help getting ready for the next test in his economics course and would like to hire Maria, an economics tutor to help him. Jason is willing to pay $30 for the first hour of tutoring, $25 for the second, $20 for the third, $15 for the fourth, and $10 for the fifth. The equilibrium pr ...
... 12) Jason needs help getting ready for the next test in his economics course and would like to hire Maria, an economics tutor to help him. Jason is willing to pay $30 for the first hour of tutoring, $25 for the second, $20 for the third, $15 for the fourth, and $10 for the fifth. The equilibrium pr ...
Document
... costs (including explicit and implicit costs) • Accounting profit ignores implicit costs, so it’s higher than economic profit. ...
... costs (including explicit and implicit costs) • Accounting profit ignores implicit costs, so it’s higher than economic profit. ...
Oligopoly
... Equilibrium in the Cournot model, in which each firm correctly assumes how much its competitor will produce and sets its own production level accordingly. ...
... Equilibrium in the Cournot model, in which each firm correctly assumes how much its competitor will produce and sets its own production level accordingly. ...
MR < MC
... Industry structure in which a small number of firms produce products that are either close or perfect substitutes Cost advantages from large size may prevent the long-run adjustment to zero economic profit Undifferentiated and differentiated products Slide 5 ...
... Industry structure in which a small number of firms produce products that are either close or perfect substitutes Cost advantages from large size may prevent the long-run adjustment to zero economic profit Undifferentiated and differentiated products Slide 5 ...
Oligopoly and Strategic Pricing
... industry. (H&H Example 10.2) But it may be cheaper to buy out rivals than to force them out by predatory pricing. Firm 1 (with market power) prices at P: AC 1 < P < AC 2 , means that Firm 2 (with higher costs) cannot make a positive profit. Unless the production process exhibits decreasing costs (In ...
... industry. (H&H Example 10.2) But it may be cheaper to buy out rivals than to force them out by predatory pricing. Firm 1 (with market power) prices at P: AC 1 < P < AC 2 , means that Firm 2 (with higher costs) cannot make a positive profit. Unless the production process exhibits decreasing costs (In ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑