Chapter 24, Monopoly
... firm’s technology has economies-ofscale large enough for it to supply the whole market at a lower average total production cost than is possible with more than one firm in the market. ...
... firm’s technology has economies-ofscale large enough for it to supply the whole market at a lower average total production cost than is possible with more than one firm in the market. ...
FREE Sample Here
... Comment on the above statement. Ans: It is true that social sciences are not the same as natural sciences. Experiments have been used successfully to tell us more about the world we live in. There are limits that social scientists should be aware of, but to dismiss the use of experimental analysis e ...
... Comment on the above statement. Ans: It is true that social sciences are not the same as natural sciences. Experiments have been used successfully to tell us more about the world we live in. There are limits that social scientists should be aware of, but to dismiss the use of experimental analysis e ...
Document
... If the price falls to $1, consumer surplus increases to include the green area. At a zero price, consumer surplus increases to the entire area under the D curve. ...
... If the price falls to $1, consumer surplus increases to include the green area. At a zero price, consumer surplus increases to the entire area under the D curve. ...
Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin)
... Answer: Because the monopoly does control the market, the monopoly sets the price at the maximum level that sells all the output the monopoly produces. This maximum price is determined from the demand for the product. The downward sloping market demand curve shows that the only way to increase the q ...
... Answer: Because the monopoly does control the market, the monopoly sets the price at the maximum level that sells all the output the monopoly produces. This maximum price is determined from the demand for the product. The downward sloping market demand curve shows that the only way to increase the q ...
A Single-Price Monopoly`s Output and Price Decision
... Efficient Regulation of a Natural Monopoly When demand and cost conditions create natural monopoly, the quantity produced is less than the efficient quantity. How can government regulate natural monopoly so that it produces the efficient quantity. Marginal cost pricing rule is a regulation that sets ...
... Efficient Regulation of a Natural Monopoly When demand and cost conditions create natural monopoly, the quantity produced is less than the efficient quantity. How can government regulate natural monopoly so that it produces the efficient quantity. Marginal cost pricing rule is a regulation that sets ...
as a PDF
... pure rate of return that exists throughout the entire time structure of production, including all loan markets, and on the other hand, by the total quantity of present money (in terms of future money) ...
... pure rate of return that exists throughout the entire time structure of production, including all loan markets, and on the other hand, by the total quantity of present money (in terms of future money) ...
Free-Riding in Distribution Systems
... that geographic market and not just X alone; we could say that the advertising campaign gives rise to informational externalities9. X is therefore left bearing the entire cost of the advertising campaign, but reaping only part of the rewards10. Furthermore, the amount spent on advertising will incr ...
... that geographic market and not just X alone; we could say that the advertising campaign gives rise to informational externalities9. X is therefore left bearing the entire cost of the advertising campaign, but reaping only part of the rewards10. Furthermore, the amount spent on advertising will incr ...
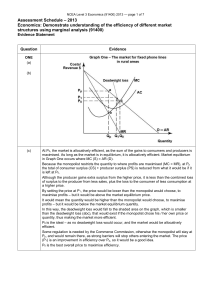
Assessment Schedule – 2013
... NCEA Level 3 Economics (91400) 2013 — page 7 of 7 barriers to entry. ...
... NCEA Level 3 Economics (91400) 2013 — page 7 of 7 barriers to entry. ...
What is a market?
... Most tennis rackets are intended to do the same thing-hit the ball over the net. But a tennis player can choose from a wide assortment of rackets. There are different shapes, materials, weights, handle sizes, and types of strings. You can buy a prestrung racket for less than $15. Or you can spend mo ...
... Most tennis rackets are intended to do the same thing-hit the ball over the net. But a tennis player can choose from a wide assortment of rackets. There are different shapes, materials, weights, handle sizes, and types of strings. You can buy a prestrung racket for less than $15. Or you can spend mo ...
Econs Webquest - 11s402
... Due to the announcement of the Budget 2011, Singaporeans are given many benefits, including a rise in disposable incomes due to tax ...
... Due to the announcement of the Budget 2011, Singaporeans are given many benefits, including a rise in disposable incomes due to tax ...
Economic Efficiency, Government Price Setting, and Taxes
... Producer surplus (P.S.) The difference between the lowest price a firm would be willing to accept for a good or service and the price it actually receives. Marginal cost (MC) The additional cost to a firm of producing one more unit of a ...
... Producer surplus (P.S.) The difference between the lowest price a firm would be willing to accept for a good or service and the price it actually receives. Marginal cost (MC) The additional cost to a firm of producing one more unit of a ...
Industry Structure III
... – A few, concentrated sellers who act and react to each other – All firms are selling undifferentiated products ...
... – A few, concentrated sellers who act and react to each other – All firms are selling undifferentiated products ...
Document
... If $1 = 150 yen and 1 yen = 75 British pounds, then 150 x 1 yen = 150 x 75 British pounds and $1 = 11,250 pounds. If $1 = 11,250 pounds, then 1 pound = $1/11,250 = .000888. If the yen/dollar exchange rate is 125, how much will 25,000 yen cost? If the exchange rate appreciates to 150, how much will t ...
... If $1 = 150 yen and 1 yen = 75 British pounds, then 150 x 1 yen = 150 x 75 British pounds and $1 = 11,250 pounds. If $1 = 11,250 pounds, then 1 pound = $1/11,250 = .000888. If the yen/dollar exchange rate is 125, how much will 25,000 yen cost? If the exchange rate appreciates to 150, how much will t ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑