Lecture 1: Demand and Supply
... Law of Supply and Demand was first stated in 1776 – Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations. Economic Theory or Laws – generalizations about the working of an abstract economy - rules that economists use to predict actual market behavior - Price up – quantity demanded down Demand Curve - A demand curve, ...
... Law of Supply and Demand was first stated in 1776 – Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations. Economic Theory or Laws – generalizations about the working of an abstract economy - rules that economists use to predict actual market behavior - Price up – quantity demanded down Demand Curve - A demand curve, ...
Name: Date - Holtville FFA The Farmer in All of Us.
... a. The price is positively related to quantity supplied. b. There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. c. There is a direct relationship between price and quantity demanded. d. When the price falls, buyers willingly buy less. 20. Holding the nonprice determinants of supply ...
... a. The price is positively related to quantity supplied. b. There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. c. There is a direct relationship between price and quantity demanded. d. When the price falls, buyers willingly buy less. 20. Holding the nonprice determinants of supply ...
Problem Set #9 Solutions
... i) The supply curve is simply the marginal cost curve, which is equal to 5. ii) The market equilibrium is found by equating Marginal cost with demand, as this is a competitive market. Doing this yields: 53-4Q=5 48=4Q Q=12 which is the equilibrium quantity. The equilibrium price can be found by subst ...
... i) The supply curve is simply the marginal cost curve, which is equal to 5. ii) The market equilibrium is found by equating Marginal cost with demand, as this is a competitive market. Doing this yields: 53-4Q=5 48=4Q Q=12 which is the equilibrium quantity. The equilibrium price can be found by subst ...
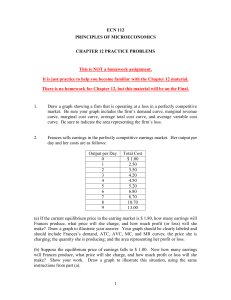
Practice Problems
... This is NOT a homework assignment. It is just practice to help you become familiar with the Chapter 12 material. There is no homework for Chapter 12, but this material will be on the Final. ...
... This is NOT a homework assignment. It is just practice to help you become familiar with the Chapter 12 material. There is no homework for Chapter 12, but this material will be on the Final. ...
MODEL handout
... The Cobb-Douglas production function is: Q = A La Kb Rc If a+b+c > 1, then there are economies of scale or increasing returns to scale. If a+b+c < 1, then decreasing returns to scale exist. If a+b+c = 1, then constant returns to scale exist. In this last case (crs): the marginal product of labor = a ...
... The Cobb-Douglas production function is: Q = A La Kb Rc If a+b+c > 1, then there are economies of scale or increasing returns to scale. If a+b+c < 1, then decreasing returns to scale exist. If a+b+c = 1, then constant returns to scale exist. In this last case (crs): the marginal product of labor = a ...
Chapter 3 and Chapter 5
... that good which delivers the most marginal utility per dollar. Optimal utility is then achieved. Optimal consumption= mix of output that maximizes total utility for the limited amount of income you have to spend. ...
... that good which delivers the most marginal utility per dollar. Optimal utility is then achieved. Optimal consumption= mix of output that maximizes total utility for the limited amount of income you have to spend. ...
4. More on Supply and Demand Curves
... scale of the graph, try a Qs about ½ of that. In this case, 50 would take us way off the scale, so we are going to try Ps = 25. Plugging that into the supply function we get Ps = 100, perfect! Now connect the two with your ruler and find out where the supply curve intersects the demand curve, this i ...
... scale of the graph, try a Qs about ½ of that. In this case, 50 would take us way off the scale, so we are going to try Ps = 25. Plugging that into the supply function we get Ps = 100, perfect! Now connect the two with your ruler and find out where the supply curve intersects the demand curve, this i ...
supply and demand
... w The demand curve represents the quantity buyers are willing to purchase at each price, holding constant factors other than price that might affect demand. w The supply curve represents the quantity sellers are willing to part with at each price, holding constant factors other than price. w Market ...
... w The demand curve represents the quantity buyers are willing to purchase at each price, holding constant factors other than price that might affect demand. w The supply curve represents the quantity sellers are willing to part with at each price, holding constant factors other than price. w Market ...
Chapter 6 Section Main Menu Combining Supply and Demand How
... control prices. These interventions appear as price ceilings and price floors. • A price ceiling is a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good. • An example of a price ceiling is rent control, a situation where a government sets a maximum amount that can be charged for rent in an area. ...
... control prices. These interventions appear as price ceilings and price floors. • A price ceiling is a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good. • An example of a price ceiling is rent control, a situation where a government sets a maximum amount that can be charged for rent in an area. ...
Oct5
... What is the lowest hourly wage at which you would be willing to spend 10 hours per week at a retail sales job during the school year? ...
... What is the lowest hourly wage at which you would be willing to spend 10 hours per week at a retail sales job during the school year? ...
lec10. markets
... curve. MC P= = AR They over price. will cuts the AC curve at sell each extra unit its lowest point for the same price. because of the Price therefore = MR mathematical and AR relationship between marginal and average Output/Sales values. ...
... curve. MC P= = AR They over price. will cuts the AC curve at sell each extra unit its lowest point for the same price. because of the Price therefore = MR mathematical and AR relationship between marginal and average Output/Sales values. ...
The Market Forces of Supply and Demand - mrski-apecon-2008
... economic competition for the good or service.(a specific individual or enterprise has sufficient control over a particular product or service to determine significantly the terms on which other individuals shall have access to it) ...
... economic competition for the good or service.(a specific individual or enterprise has sufficient control over a particular product or service to determine significantly the terms on which other individuals shall have access to it) ...
Name: Per. ____ Date: Ch. 5 Study Guide / Review Multiple Choice
... 13. When the selling price of a good goes up, what is the relationship to the quantity supplied? A. The cost of production goes down. B. The profit made on each item goes down. C. It becomes practical to produce more goods. D. There is no relationship between the two. ...
... 13. When the selling price of a good goes up, what is the relationship to the quantity supplied? A. The cost of production goes down. B. The profit made on each item goes down. C. It becomes practical to produce more goods. D. There is no relationship between the two. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑