Law of demand
... quantity supplied falls to zero. Because the quantity supplied rises as the price rises and falls as the price falls,we say that the quantity supplied is positively related to the price of the good. ...
... quantity supplied falls to zero. Because the quantity supplied rises as the price rises and falls as the price falls,we say that the quantity supplied is positively related to the price of the good. ...
Chapter 5: Using Supply and Demand
... A $4 per unit tax on suppliers shifts the supply curve up by $4 shown as a shift in the supply curve from S0 to S1. Equilibrium price will rise by $4 only if the demand curve is perfectly vertical. In the case of a vertical demand curve, quantity would not change. Otherwise, equilibrium price rises ...
... A $4 per unit tax on suppliers shifts the supply curve up by $4 shown as a shift in the supply curve from S0 to S1. Equilibrium price will rise by $4 only if the demand curve is perfectly vertical. In the case of a vertical demand curve, quantity would not change. Otherwise, equilibrium price rises ...
File - Mr. Catalano
... DEMAND • Quantity demanded : the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase. • Law of Demand • The quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises. ...
... DEMAND • Quantity demanded : the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase. • Law of Demand • The quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises. ...
Lecture 1 - Dr. Rajeev Dhawan
... Other Determinants of Demand Income (I) : – I , D Normal Goods: car, Ferrari – I , D Inferior goods: bus rides, potatoes ...
... Other Determinants of Demand Income (I) : – I , D Normal Goods: car, Ferrari – I , D Inferior goods: bus rides, potatoes ...
AP Economics Semester 1: Microeconomics Homework Check: 150
... Rights, Circular Flow Diagram, Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship, Productions Possibility Curve(Frontier), Microeconomics, Macroeconomics, Positive, Normative, Economic Model, Ceteris Paribus, Absolute Advantage, Comparative Advantage, Specialization, Imports, Exports Graphs to Know: Circular F ...
... Rights, Circular Flow Diagram, Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship, Productions Possibility Curve(Frontier), Microeconomics, Macroeconomics, Positive, Normative, Economic Model, Ceteris Paribus, Absolute Advantage, Comparative Advantage, Specialization, Imports, Exports Graphs to Know: Circular F ...
Midterm #2
... The demand curve facing a firm reflects the firm’s perception that it can sell all it wants at the going market price: if it raises its price above the market price, no one will purchase from that firm since many substitutes are available; alternatively, there is no need for the firm to lower its pr ...
... The demand curve facing a firm reflects the firm’s perception that it can sell all it wants at the going market price: if it raises its price above the market price, no one will purchase from that firm since many substitutes are available; alternatively, there is no need for the firm to lower its pr ...
Understanding Supply and Demand
... • According to the law of demand, as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded rises. Therefore, the demand curve slopes downward. • In addition to price, other determinants of how much consumers want to buy include income, the prices of complements and substitutes, tastes, expectations, and ...
... • According to the law of demand, as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded rises. Therefore, the demand curve slopes downward. • In addition to price, other determinants of how much consumers want to buy include income, the prices of complements and substitutes, tastes, expectations, and ...
Syllabus_micro New Edition2
... definitions and fields of economics; the economic problem of scarcity & choice; consumers' and producers' behavior in input and output markets; and the characteristics of different market structures such as perfect competition and monopoly. It also addresses why one should study economics and provid ...
... definitions and fields of economics; the economic problem of scarcity & choice; consumers' and producers' behavior in input and output markets; and the characteristics of different market structures such as perfect competition and monopoly. It also addresses why one should study economics and provid ...
Chapter #3: Short Answer/Essay Solutions
... table form, illustrating the inverse relation between price and quantity demanded; law of demand. A supply schedule shows willingness/ability to provide goods and services in table form, showing a direct relation between price and qty supplied. 11. The factors (determinants) which change supply (shi ...
... table form, illustrating the inverse relation between price and quantity demanded; law of demand. A supply schedule shows willingness/ability to provide goods and services in table form, showing a direct relation between price and qty supplied. 11. The factors (determinants) which change supply (shi ...
E. Consumers expect the price of soft drinks to rise in the
... 17. If market supply of new homes increases while market demand for new homes decrease, what would be the likely effect, ceteris paribus? a. equilibrium quantity will fall while we cannot predict what will happen to equilibrium price b. equilibrium quantity will rise, while we cannot predict what w ...
... 17. If market supply of new homes increases while market demand for new homes decrease, what would be the likely effect, ceteris paribus? a. equilibrium quantity will fall while we cannot predict what will happen to equilibrium price b. equilibrium quantity will rise, while we cannot predict what w ...
Law of Supply
... quantity supplied; can be elastic or inelastic Elastic Supply—when a small change in price causes a major change in the quantity supplied. ...
... quantity supplied; can be elastic or inelastic Elastic Supply—when a small change in price causes a major change in the quantity supplied. ...
Examples: Calculating Elasticity
... You can calculate the market price elasticity of demand using the information contained in the table. For example, suppose you decide to calculate the price elasticity of demand at $2.00 by examining a price decrease from $2.00 to $1.50 per cone. In this case, the demand for ice cream would increase ...
... You can calculate the market price elasticity of demand using the information contained in the table. For example, suppose you decide to calculate the price elasticity of demand at $2.00 by examining a price decrease from $2.00 to $1.50 per cone. In this case, the demand for ice cream would increase ...
Review Questions 2 – 23.11.2016 Question 1 Suppose a perfectly
... a) An increase in marginal costs at all levels of output. b) An increase in marginal revenue at all levels of output. c) A reduction in telecommunication costs. d) An increase in tastes and preferences for the good or service being made. e) An increase in transport costs following an increase in oil ...
... a) An increase in marginal costs at all levels of output. b) An increase in marginal revenue at all levels of output. c) A reduction in telecommunication costs. d) An increase in tastes and preferences for the good or service being made. e) An increase in transport costs following an increase in oil ...
document
... of cheese that sellers are willing & able to sell each week in Richmond at a given price. • Supply: The various amounts of cheese that sellers are willing & able to sell each week in Richmond at all possible prices. ...
... of cheese that sellers are willing & able to sell each week in Richmond at a given price. • Supply: The various amounts of cheese that sellers are willing & able to sell each week in Richmond at all possible prices. ...
Law of Demand
... quantities of a product that producers are willing and able to offer at a given price. ...
... quantities of a product that producers are willing and able to offer at a given price. ...
Quiz 2 Review 1A
... Prices of other goods (Complements and substitutes) Expectations of the future price of the good Market population Price changes influence Qd Supply determinants Technology improvement Input prices Prices of alternative goods Expectations of the future price of the good # firms in in ...
... Prices of other goods (Complements and substitutes) Expectations of the future price of the good Market population Price changes influence Qd Supply determinants Technology improvement Input prices Prices of alternative goods Expectations of the future price of the good # firms in in ...
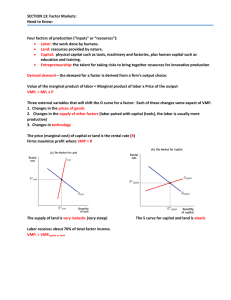
SECTION 13: Factor Markets: Need to Know: Four factors of production (“inputs” or “resources”):
... 2. Changes in the supply of other factors (labor paired with capital (tools), the labor is usually more productive) 3. Changes in technology ...
... 2. Changes in the supply of other factors (labor paired with capital (tools), the labor is usually more productive) 3. Changes in technology ...
Chapter 4 Working with Supply and Demand
... b. Vacuum cleaners: normal good. (Most individual households would have an income elasticity of zero—they would buy just one vacuum cleaner once their income reaches a certain level, and then buy no more as income rises. However, classifying goods as normal or inferior depends on market income elast ...
... b. Vacuum cleaners: normal good. (Most individual households would have an income elasticity of zero—they would buy just one vacuum cleaner once their income reaches a certain level, and then buy no more as income rises. However, classifying goods as normal or inferior depends on market income elast ...
Supply & Demand PPT
... Thus, there is a direct (or positive) relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied. Remember, the supplier is on the receiving end of the product’s price. Therefore, higher prices don’t pose the same obstacle on the supply side as they do on the demand side. ...
... Thus, there is a direct (or positive) relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied. Remember, the supplier is on the receiving end of the product’s price. Therefore, higher prices don’t pose the same obstacle on the supply side as they do on the demand side. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑