Chapter 6 Section Main Menu Combining Supply and Demand How
... • Excess Demand creates a “shortage” – A shortage is a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied – Suppliers react by: • Raising prices…possibly increasing supply • A Decline in Demand itself – Because of a change in market conditions such as: • customer preferences (tas ...
... • Excess Demand creates a “shortage” – A shortage is a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied – Suppliers react by: • Raising prices…possibly increasing supply • A Decline in Demand itself – Because of a change in market conditions such as: • customer preferences (tas ...
File
... Click the button next to the response that best answers the question. 1. Driving to different stores to locate a product is an example of ...
... Click the button next to the response that best answers the question. 1. Driving to different stores to locate a product is an example of ...
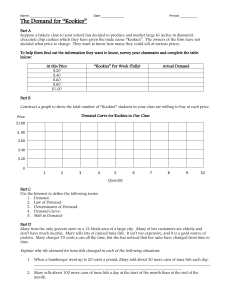
The Demand for “Kookies”
... Suppose a bakery close to your school has decided to produce and market large (6 inches in diameter) chocolate chip cookies which they have given the trade name “Kookies”. The owners of the firm have not decided what price to charge. They want to know how many they could sell at various prices. To h ...
... Suppose a bakery close to your school has decided to produce and market large (6 inches in diameter) chocolate chip cookies which they have given the trade name “Kookies”. The owners of the firm have not decided what price to charge. They want to know how many they could sell at various prices. To h ...
Market Situation & Outlook Interpret market factors that impact prices
... Evaluating Source of Information Know the source of data and analysis Understand the motivation of the source ...
... Evaluating Source of Information Know the source of data and analysis Understand the motivation of the source ...
經濟學原理一
... This assumes that people would still prefer the original bundle. Because they are facing a new set of relative prices, compensating people so that they could purchase the original bundle will allow them to be able to achieve a higher level of utility than they did before the price changes. 5. If a m ...
... This assumes that people would still prefer the original bundle. Because they are facing a new set of relative prices, compensating people so that they could purchase the original bundle will allow them to be able to achieve a higher level of utility than they did before the price changes. 5. If a m ...
Consumer Equilibrium and Market Demand Chapter 4
... An important extension of the market demand curve is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
... An important extension of the market demand curve is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
ECON 3070-001 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... Pp: Price of Popcorn = $3.00 PM: Price of Movie Tickets There are two movie theatres in Gunnison, each with a seating capacity of 1 00 seats. If either theatre trys to sell more tickets than its 100 seats, they get into BIG trouble. The trouble is big enough that they never exceed their 100 seat cap ...
... Pp: Price of Popcorn = $3.00 PM: Price of Movie Tickets There are two movie theatres in Gunnison, each with a seating capacity of 1 00 seats. If either theatre trys to sell more tickets than its 100 seats, they get into BIG trouble. The trouble is big enough that they never exceed their 100 seat cap ...
Ch. 4: Consumer Equilibrium and Market Demand
... is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
... is the concept of consumer surplus, or economic well being consumers derive in the market. The demand curve reveals the willingness of consumers to pay a certain price for a corresponding quantity. ...
Solutions for HW #5
... to the price of both goods reduces the relative price of the more expensive good for the Andersons, but not for the Smiths. Since both couples are sufficiently wealthy that their expenditure on movies and plays is a negligible fraction of their total expenditures, there will be no income effect and ...
... to the price of both goods reduces the relative price of the more expensive good for the Andersons, but not for the Smiths. Since both couples are sufficiently wealthy that their expenditure on movies and plays is a negligible fraction of their total expenditures, there will be no income effect and ...
Chapter 3: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
... • The labor market, in which households supply work for wages to firms that demand labor. • The capital market, in which households supply their savings, for interest or for claims to future profits, to firms that demand funds to buy capital goods. • The land market, in which households supply land ...
... • The labor market, in which households supply work for wages to firms that demand labor. • The capital market, in which households supply their savings, for interest or for claims to future profits, to firms that demand funds to buy capital goods. • The land market, in which households supply land ...
Esame di Microeconomia avanzata (16 aprile 2004)
... In a market characterized by the following inverse demand function: P = 10 - Q if Q 10 0 if Q 10 where Q is the total quantity produced by all the suppliers, suppose that only one firm (firm 1) is active on the market and that its production cost is described by the function C1 (q1 ) 2q1 . a) ...
... In a market characterized by the following inverse demand function: P = 10 - Q if Q 10 0 if Q 10 where Q is the total quantity produced by all the suppliers, suppose that only one firm (firm 1) is active on the market and that its production cost is described by the function C1 (q1 ) 2q1 . a) ...
Chapter 2 Demand and Supply
... The Veblen Effect In rare situations the relationship between price and quantity demanded can be direct – the demand curve has a positive (upward) slope Happens when a product’s price is seen as a status symbol Consumers who can afford the product are attracted to it because its high price ma ...
... The Veblen Effect In rare situations the relationship between price and quantity demanded can be direct – the demand curve has a positive (upward) slope Happens when a product’s price is seen as a status symbol Consumers who can afford the product are attracted to it because its high price ma ...
A Bit of a Stretch
... and “inelastic.” Imagine two objects: (1) an Ace elastic bandage used to wrap injured joints and (2) a relatively firm rubber tie‐down used for securing items for transport. The Ace bandage stretches a great deal when pulled with a particular force; the rubber tie‐down stretches some ...
... and “inelastic.” Imagine two objects: (1) an Ace elastic bandage used to wrap injured joints and (2) a relatively firm rubber tie‐down used for securing items for transport. The Ace bandage stretches a great deal when pulled with a particular force; the rubber tie‐down stretches some ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑